|
Uroplectes Otjimbinguensis
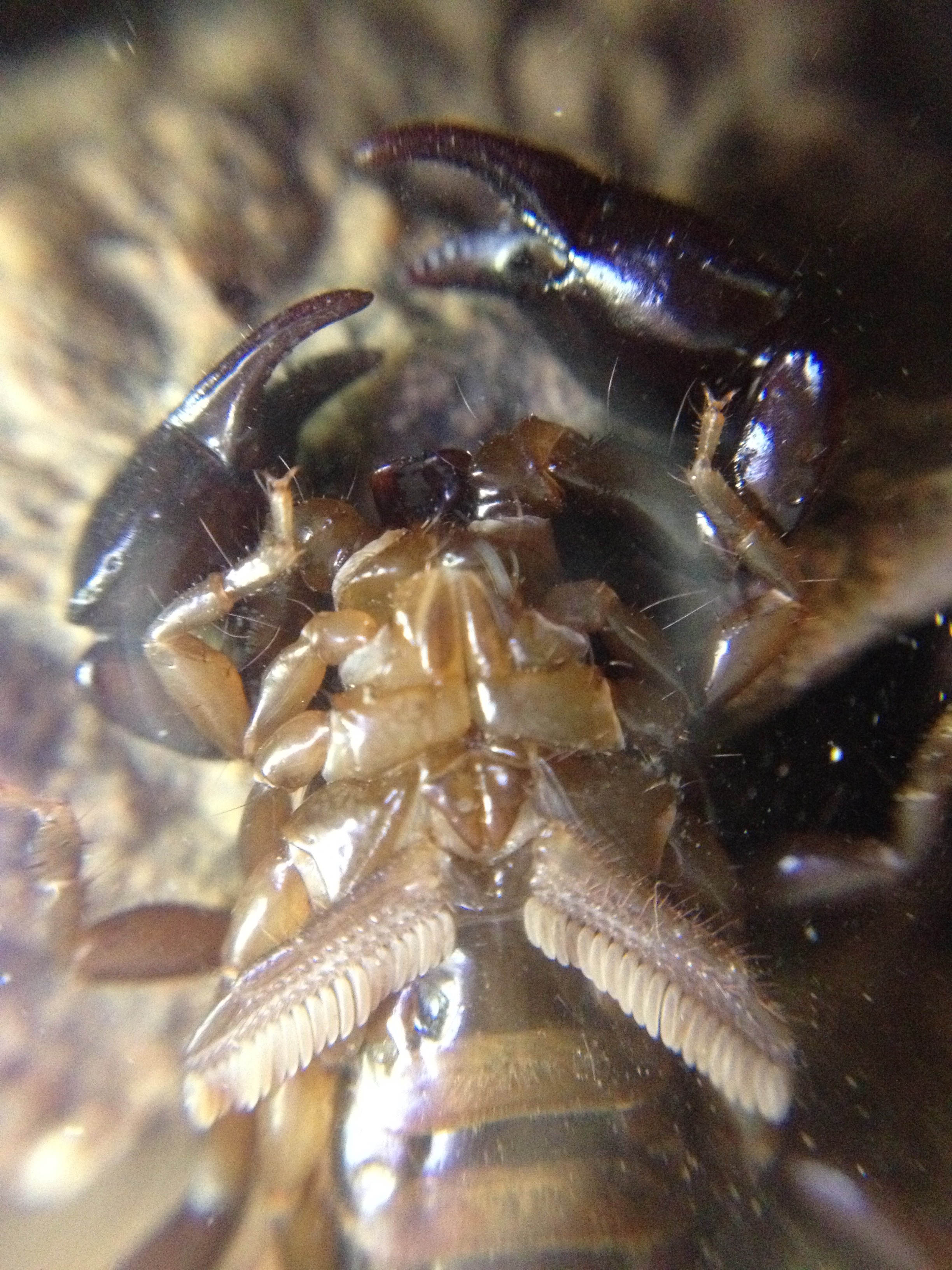
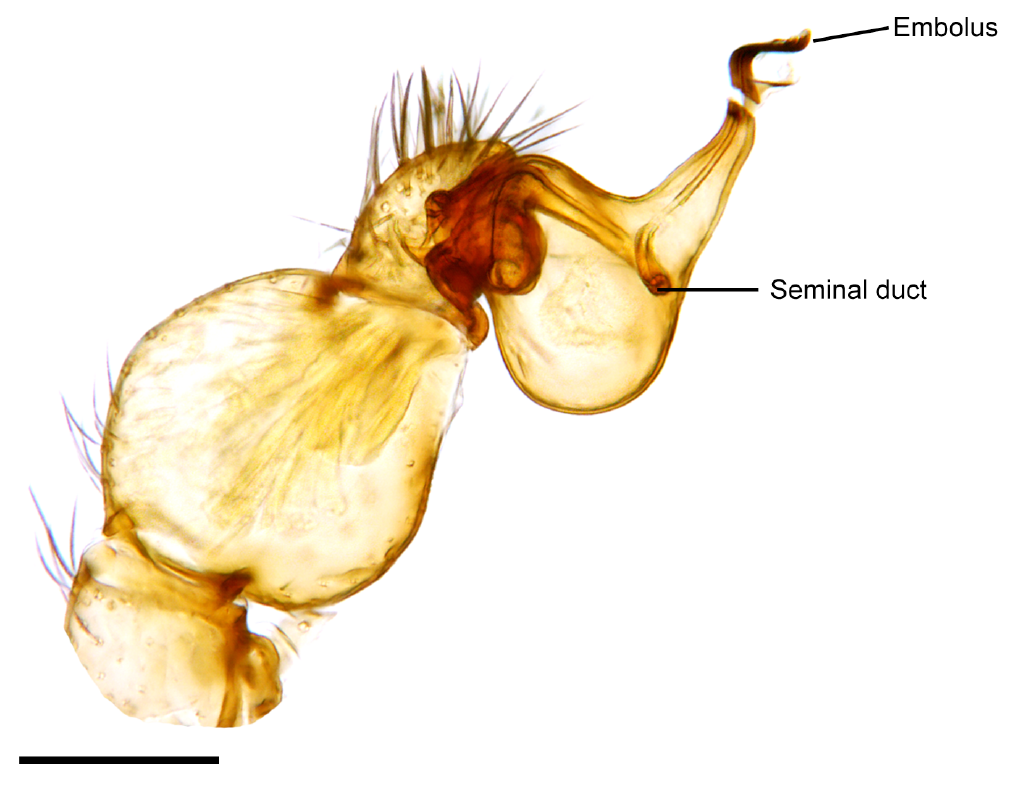
''Uroplectes otjimbinguensis'' is a species of scorpion in the family Buthidae, endemic to Angola and Namibia. Taxonomy This species was originally described by Ferdinand Karsch as ''Lepreus otjimbinguensis'' in 1879 based on specimens collected near Otjimbingwe, Namibia. It was later moved to ''Uroplectes'' by Karl Kraepelin in 1899. Etymology The specific name ''otjimbinguensis'' is a combination of ''Otjimbingu ' and the Latin suffix ''-ensis'', "of or from place, therefore translating as "from Otjimbingue," in reference to the town where the species was first discovered. Description ''Uroplectes otjimbinguensis'' is a small scorpion, achieving a maximum length of 40 mm. It is overall pale-yellow, with a broad dark band running down the center of the dorsal side of the abdomen, ending in a triangular dark patch on the cephalothorax. The third, fourth and fifth tail segments are black at the base, with the coloration extending farther down each segment as they approach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalothorax
The cephalothorax, also called prosoma in some groups, is a tagma of various arthropods, comprising the head and the thorax fused together, as distinct from the abdomen behind. (The terms ''prosoma'' and ''opisthosoma'' are equivalent to ''cephalothorax'' and ''abdomen'' in some groups.) The word ''cephalothorax'' is derived from the Greek words for head (, ') and thorax (, '). This fusion of the head and thorax is seen in chelicerates and crustaceans; in other groups, such as the Hexapoda (including insects), the head remains free of the thorax. In horseshoe crabs and many crustaceans, a hard shell called the carapace covers the cephalothorax. Arachnid anatomy Fovea The fovea is the centre of the cephalothorax and is located behind the head (only in spiders).Dalton, Steve (2008). ''Spiders; The Ultimate Predators''. A & C Black, London. P.p. 19. . It is often important in identification. It can be transverse or procurved Smith, A. M. (1990c). Baboon spiders: Tarantulas of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animals Described In 1879
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Over 1.5 million living animal species have been described—of which around 1 million are insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a bilaterally symmetric body plan. The Bilateria include the protostomes, containing animals such as nematodes, arthropods, flatworms, annelids and molluscs, and the deuterostomes, containing the echinoderms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cunene River
The Cunene (Portuguese spelling) or Kunene (common Namibian spelling) is a river in Southern Africa. It flows from the Angola highlands south to the border with Namibia. It then flows west along the border until it reaches the Atlantic Ocean. It is one of the few perennial rivers in the region. It is about long, with a drainage basin in area. Its mean annual discharge is 174 m3/s (6,145 cfs) at its mouth. The Epupa Falls lie on the river. Olushandja Dam dams a tributary of the river, the Etaka, and helps provide the Ruacana Power Station with water. Dam controversies The Namibian government proposed in the late 1990s to build the Epupa Dam, a controversial hydroelectric dam on the Cunene. In 2012 the Governments of Namibia and Angola announced plans to jointly build the Orokawe dam in the Baynes Mountains. According to the indigenous Himba who would have been most affected by the construction of the dam, the dam threatens the local ecosystem and therefore the economic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allopatric Speciation
Allopatric speciation () – also referred to as geographic speciation, vicariant speciation, or its earlier name the dumbbell model – is a mode of speciation that occurs when biological populations become geographically isolated from each other to an extent that prevents or interferes with gene flow. Various geographic changes can arise such as the movement of continents, and the formation of mountains, islands, bodies of water, or glaciers. Human activity such as agriculture or developments can also change the distribution of species populations. These factors can substantially alter a region's geography, resulting in the separation of a species population into isolated subpopulations. The vicariant populations then undergo genetic changes as they become subjected to different selective pressures, experience genetic drift, and accumulate different mutations in the separated populations' gene pools. The barriers prevent the exchange of genetic information between th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uroplectes Planimanus
''Uroplectes'' is a genus of scorpions in the family Buthidae. They are known commonly as the lesser thick-tailed scorpions. There are about 40 species distributed in the Afrotropical realm.''Uroplectes''. Biodiversity Explorer. Iziko Museums. They are most diverse in .Prendini, L. (2015) A remarkably small species of ''Uroplectes'' Peters, 1861 (Scorpiones: Buthidae), endemic to the Succulent Karoo of South Africa. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coevolutionary Arms Race
In evolutionary biology, an evolutionary arms race is an ongoing struggle between competing sets of co-evolving genes, phenotypic and behavioral traits that develop escalating adaptations and counter-adaptations against each other, resembling an arms race. These are often described as examples of positive feedback.Dawkins, R. 1996. ''The Blind Watchmaker'' New York: W. W. Norton. Note: This book was also published by Penguin in 1991. While the text is identical, page numbers differ The co-evolving gene sets may be in different species, as in an evolutionary arms race between a predator species and its prey (Vermeij, 1987), or a parasite and its host. Alternatively, the arms race may be between members of the same species, as in the manipulation/sales resistance model of communication (Dawkins & Krebs, 1979) or as in runaway evolution or Red Queen effects. One example of an evolutionary arms race is in sexual conflict between the sexes, often described with the term Fisherian runa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venom
Venom or zootoxin is a type of toxin produced by an animal that is actively delivered through a wound by means of a bite, sting, or similar action. The toxin is delivered through a specially evolved ''venom apparatus'', such as fangs or a stinger, in a process called envenomation. Venom is often distinguished from poison, which is a toxin that is passively delivered by being ingested, inhaled, or absorbed through the skin, and toxungen, which is actively transferred to the external surface of another animal via a physical delivery mechanism. Venom has evolved in terrestrial and marine environments and in a wide variety of animals: both predators and prey, and both vertebrates and invertebrates. Venoms kill through the action of at least four major classes of toxin, namely necrotoxins and cytotoxins, which kill cells; neurotoxins, which affect nervous systems; myotoxins, which damage muscles; and haemotoxins, which disrupt blood clotting. Venomous animals cause tens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brandberg Mountain
The Brandberg ( Damara: Dâures; hz, Omukuruvaro) is Namibia's highest mountain. Location and extent Brandberg Mountain is located in former Damaraland, now Erongo, in the northwestern Namib Desert, near the coast, and covers an area of approximately 650 km2.landsat.usgs.gov With its highest point, the Königstein ''( for 'King's Stone')'', standing at above and located on the flat Namib gravel plains, on a clear day 'The Brandberg' can be seen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pecten (biology)
A pecten (plural pectens or pectines) is a comb-like structure, widely found in the biological world. Although pectens in various animals look similar, they have a varied range of uses, from grooming and filtering to sensory adaptations. Etymology The adjective, pectinate, means supplied with a comb-like structure. This form, cognate to pecten with both derived from the Latin for comb, ''pectin'' (genitive ''pectinis''), is reflected in numerous scientific names in forms such as pectinata, pectinatus or pectinatum, or in specific epithets such as '' Murex pecten''. Some toothcombs are referred to as pectinations. Oral use In ducks, they exist on the sides of the bill and serve both as a strainer for food and a comb for preening. Whales have a similar oral comb-like structure called baleen. Retinal use The avian eye also contains a structure called a pecten oculi, which is a comb-like projection of the retina. It is thought to enhance nutrition for the cells of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedipalp
Pedipalps (commonly shortened to palps or palpi) are the second pair of appendages of chelicerates – a group of arthropods including spiders, scorpions, horseshoe crabs, and sea spiders. The pedipalps are lateral to the chelicerae ("jaws") and anterior to the first pair of walking legs. Overview Pedipalps are composed of six segments or articles: the coxa, the trochanter, the femur, the short patella, the tibia, and the tarsus. In spiders, the coxae frequently have extensions called maxillae or gnathobases, which function as mouth parts with or without some contribution from the coxae of the anterior legs. The limbs themselves may be simple tactile organs outwardly resembling the legs, as in spiders, or chelate weapons ( pincers) of great size, as in scorpions. The pedipalps of Solifugae are covered in setae, but have not been studied in detail. Comparative studies of pedipalpal morphology may suggest that leg-like pedipalps are primitive in arachnids. At present, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)