|
Urban Municipality Of Kostolac
Kostolac ( sr-Cyrl, Костолац) is a town in Serbia and one of two city municipalities which constitute the City of Požarevac. It is situated on the Danube river. The remains of Viminacium, the capital of the Roman province of Moesia Superior, are located near Stari Kostolac, some 2 km to the east of Kostolac. Kostolac is also a center of the area called Stig and home of thermal power plants and coal mines. History A 1.5 million year old mammoth skeleton was uncovered in the Viminacium site in June 2009. A Neolithic Kostolac culture is named after the town. The tribes of Autariatae and Scordisci are thought to have merged into one in this area after 313BC, since excavations show that the two groups made burials at the same exact grave field in Pecine, near Kostolac. Nine graves of Autariatae dating to 4th century BC and scattered Autariatae and Celtic graves around these earlier graves show that the two groups mixed rather than made war and this resulted in the lower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipalities And Cities Of Serbia
The municipalities and cities ( sr-Cyrl-Latn, општине и градови, opštine i gradovi, separator=" / ") are the first-level Administrative divisions of Serbia, administrative division and the basic level of local government of Serbia. The country is divided into 145 Municipality, municipalities (42 in Šumadija and Western Serbia, 38 in Southern and Eastern Serbia, 37 in Vojvodina and 28 in Autonomous Province of Kosovo and Metohija, Kosovo and Metohija) and 29 city, cities (9 in Southern and Eastern Serbia, 10 in Šumadija and Western Serbia, 8 in Vojvodina, 1 in Kosovo and Metohija and the City of Belgrade). Municipalities and cities form 29 List of districts of Serbia, administrative districts in groups, except the City of Belgrade which is not part of any district. Municipalities Like in many other countries, municipalities ( sr-Cyrl-Latn, општине, opštine, separator=" / ") are the basic entities of local government in Serbia. The head of the municipali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autariatae
The Autariatae or Autariatai (alternatively, Autariates; , ''Autariatai''; ) were an Illyrian people that lived between the valleys of the Lim and the Tara, beyond the Accursed Mountains, and the valley of West Morava. Their territory was located inland from the Ardiaei and the Lake Skodra, extending east to the Dardani and north or northeast to the Triballi. Along with the Ardiaei and the Dardani, the Autariatae are mentioned by Strabo in his ''Geographica'' as one of the three strongest Illyrian peoples in the pre- Roman Balkans. Following defeat during the Celtic invasions of the Balkans in the 4th century, a part of the Autariatae who remained in Bosnia adopted Celtic culture later in their history. Another part moved southwards and after an agreement with the Kingdom of Macedonia, 20,000 settled in the Parorbelian mountain range, in the borderlands between modern southeastern North Macedonia, northern Greece and southwestern Bulgaria. Name An Illyrian people name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
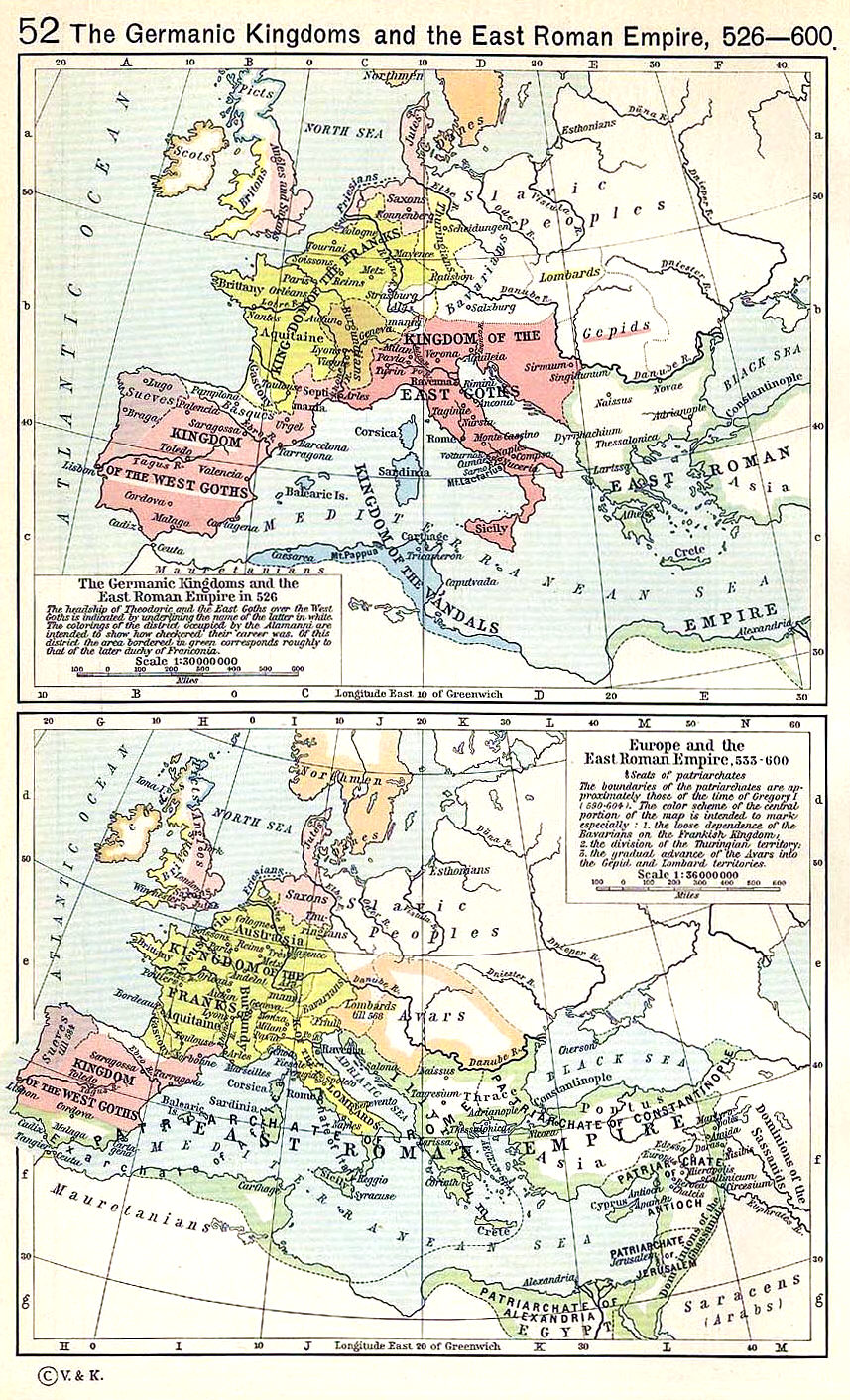
Maurice's Balkan Campaigns
Maurice's Balkan campaigns were a series of military expeditions conducted by Byzantine emperor, Roman Emperor Maurice (emperor), Maurice (reigned 582–602) in an attempt to defend the Balkans, Balkan provinces of the Byzantine Empire, Roman Empire from the Pannonian Avars, Avars and the South Slavs. Maurice was the only East Roman emperor, other than Anastasius I (emperor), Anastasius I, who did his best to implement determined Balkan policies during Late Antiquity by paying adequate attention to the safety of the northern frontier against barbarian incursions. During the second half of his reign, the Balkan campaigns were the main focus of Maurice's foreign policies, as a favourable peace treaty with Sasanian Empire, Persian Empire in 591 enabled him to shift his experienced troops from the Persian front to the region. The refocusing of Roman efforts soon paid off: the frequent Roman failures before 591 were succeeded by a string of successes afterwards. Although it is widely be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Justinian I
Justinian I (, ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was Roman emperor from 527 to 565. His reign was marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovatio imperii'', or "restoration of the Empire". This ambition was expressed by the partial recovery of the territories of the defunct Western Roman Empire. His general, Belisarius, swiftly conquered the Vandal Kingdom in North Africa. Subsequently, Belisarius, Narses, and other generals Gothic War (535–554), conquered the Ostrogothic Kingdom, restoring Dalmatia, Sicily, Italian peninsula, Italy, and Rome to the empire after more than half a century of rule by the Ostrogoths. The Liberius (praetorian prefect), praetorian prefect Liberius reclaimed the south of the Iberian Peninsula, establishing the province of Spania. These campaigns re-established Roman control over the western Mediterranean, increasing the Empire's annual revenue by over a million ''solidi''. During his reign, Justinian also subdued ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legio IV Flavia Felix
Legio IV Flavia Felix ("Lucky Flavian Fourth Legion"), was a Roman legion, legion of the Imperial Roman army founded in AD 70 by the emperor Vespasian (r. 69–79) from the Cadre (military), cadre of the disbanded Legio IV Macedonica, Legio IV ''Macedonica''. The legion was active in Moesia, Moesia Superior in the first half of the 5th century. The legion symbol was a Leo (astrology), lion. History During the Batavian rebellion, the IV ''Macedonica'' fought for Vespasian, but the emperor distrusted his men, probably because they had supported Vitellius year of the four emperors, two years before. Therefore IV ''Macedonica'' was disbanded, and a new Fourth legion, called ''Flavian Felix'' was levied by the emperor, who gave the legio his Roman naming conventions, nomen, ''Flavius, Flavia''. Since the symbol of the legion is a lion, it was probably levied in July/August 70. IV ''Flavia Felix'' was camped in ''Burnum'', Dalmatia (Roman province), Dalmatia (modern Kistanje), where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legio VII Claudia
Legio VII Claudia (Latin for "The 7th Claudian Legion") was a legion of the Ancient Roman army. History Legio VII was the first legion Julius Caesar raised for his campaigns in Cisalpine Gaul. In Caesar's account of the battle against the Nervians, it seems that it was employed during the expedition through western Gaul led by Caesar's deputy Crassus. In 56 BC, the Seventh was present during the Venetic campaign. During the crisis caused by Vercingetorix, it fought in the neighbourhood of Lutetia; it must have been active at Alesia and it was certainly involved in the mopping-up operations among the Bellovaci. Legio VII was one of the two legions used in Caesar's invasions of Britain in 55-54 BC, and played a crucial role in the Battle of Pharsalus in 48 BC. At one point Caesar's Legio VII was disbanded, and its veterans settled at Capua. However, Octavian had need of soldiers and recalled its members to service to fight in the Battle of Mutina.Parker, ''Roman Legi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moesia Superior
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; ) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River. As a Roman domain Moesia was administered at first by the governor of Noricum as 'Civitates of Moesia and Triballia'. It included most of the territory of modern eastern Serbia, Kosovo, north-eastern Albania, northern parts of North Macedonia (Moesia Superior), Northern Bulgaria, Romanian Dobruja and small parts of Southern Ukraine (Moesia Inferior). Geography In ancient geographical sources, Moesia was bounded to the south by the Haemus (Balkan Mountains) and Scardus (Šar) mountains, to the west by the Drinus (Drina) river, on the north by the Donaris (Danube) and on the east by the Euxine (Black Sea). History The region of Moesia was inhabited chiefly by Thracian, Illyrian, and Thraco-Illyrian peoples. The name of the region comes from Moesi, the Latin name of a Thracian tribe who lived there before the Roman conquest. Parts of Moesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viminatium
Viminatium was the name of two Roman settlements: *Viminacium Viminacium (also ''Viminatium)'' was a major city, military camp, and the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman province of Moesia (modern-day Serbia). Following the division of Moesia in 87, following Domitian's Domitian's Dacian War, Dacian War, i ... in Serbia * Terradillos in Spain {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Getae
The Getae or Getai ( or , also Getans) were a large nation who inhabited the regions to either side of the Lower Danube in what is today northern Bulgaria and southern Romania, throughout much of Classical Antiquity. The main source of information about the Getae are Greek and Roman chroniclers, who write that the Getae were closely related to the neighbouring Thracians to the south and Dacians to the north. Cassius Dio writes that the Getae are the same people as the Dacians, Getae being the Greek name for the Dacians. Modern scholars continue to debate the details of these relationships. The Getae first appear in historical records as fierce opponents of the Scythian campaign of Darius I, Persian invasion in 513 BC, as described by the early Greek historian Herodotus. They faded out of historical records during the Roman Empire, when many appear to have become Romans, and others north of the Danube were gradually overwhelmed by other peoples moving from the north and east tow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallic Invasion Of The Balkans
Gallic groups, originating from the various La Tène chiefdoms, began a southeastern movement into the Balkans from the 4th century BC. Although Gallic settlements were concentrated in the western half of the Carpathian basin, there were notable incursions and settlements within the Balkans. From their new bases in northern Illyria and Pannonia, the Gallic invasions climaxed in the early 3rd century BC, with the invasion of Greece. The 279 BC invasion of Greece proper was preceded by a series of other military campaigns waged in the southern Balkans and against the Kingdom of Macedonia, favoured by the state of confusion ensuing from the disputed succession after Alexander the Great's death. A part of the invading Celts crossed over to Anatolia and eventually settled in the area that came to be named after them, Galatia. Settlement of southeastern Europe From the 4th century BC, Celtic groups pushed into the Carpathian region and the Danube basin, coinciding with thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Morava
The Great Morava (, ) is the final section of the Morava ( sr-Cyrl, Морава), a major river system in Serbia. Etymology According to Predrag Komatina from the Institute for Byzantine Studies in Belgrade, the Great Morava is named after the Merehani, an early Slavic tribe who were still unconquered by the Bulgars during the time of the Bavarian Geographer. However, after 845, the Bulgars added these Slavs to their ''societas'' (they are last mentioned in 853). Length The Great Morava begins at the confluence of the South Morava and the West Morava, located near the village of Stalać, a major railway junction in Central Serbia. From there to its confluence with the Danube northeast of the city of Smederevo, the Velika Morava is 185 km long. With its longer branch, the West Morava, it is 493 km long. The South Morava, which represents the natural headwaters of the Morava, used to be longer than the West Morava, but due to the regulations of river bed and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |