|
University Of Edinburgh School Of Physics And Astronomy
The University of Edinburgh School of Physics and Astronomy is the physics department of the University of Edinburgh. The School was formed in 1993 by a merger of the Department of Physics and the Department of Astronomy, both at the University of Edinburgh. The Department of Physics itself was a merger between the Department of Natural Philosophy and the Department of Mathematical Physics in the late 1960s. The School is part of the University's College of Science and Engineering. Institutes Institutions and research groups based within the school include: * Institute for Astronomy (IfA) – One of the UK's major centres of astronomical research, specialising in survey astronomy, cosmology, active galaxies and the formation of stars and planets. * Institute for Condensed Matter and Complex Systems (ICMCS) * Institute for Particle and Nuclear Physics (IPNP) * Higgs Centre for Theoretical Physics – A new centre established in 2012 to "seek an even deeper understanding of how ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Clerk Maxwell Building - Geograph
James may refer to: People * James (given name) * James (surname) * James (musician), aka Faruq Mahfuz Anam James, (born 1964), Bollywood musician * James, brother of Jesus * King James (other), various kings named James * Prince James (other) * Saint James (other) Places Canada * James Bay, a large body of water * James, Ontario United Kingdom * James College, York, James College, a college of the University of York United States * James, Georgia, an unincorporated community * James, Iowa, an unincorporated community * James City, North Carolina * James City County, Virginia ** James City (Virginia Company) ** James City Shire * James City, Pennsylvania * St. James City, Florida Film and television * James (2005 film), ''James'' (2005 film), a Bollywood film * James (2008 film), ''James'' (2008 film), an Irish short film * James (2022 film), ''James'' (2022 film), an Indian Kannada-language film * "James", a television Adventure Time (season 5)#ep42, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionosphere
The ionosphere () is the ionized part of the upper atmosphere of Earth, from about to above sea level, a region that includes the thermosphere and parts of the mesosphere and exosphere. The ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation. It plays an important role in atmospheric electricity and forms the inner edge of the magnetosphere. It has practical importance because, among other functions, it influences radio propagation to distant places on Earth. Travel through this layer also impacts GPS signals, resulting in effects such as deflection in their path and delay in the arrival of the signal. History of discovery As early as 1839, the German mathematician and physicist Carl Friedrich Gauss postulated that an electrically conducting region of the atmosphere could account for observed variations of Earth's magnetic field. Sixty years later, Guglielmo Marconi received the first trans-Atlantic radio signal on December 12, 1901, in St. John's, Newfoundland (now in Canada) usin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Nobel Laureates Affiliated With The University Of Edinburgh
The following list shows the university affiliations of individual winners of the Nobel Prize since 1901 and the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences since 1969. The affiliations are those at the time of the Nobel Prize announcement. Universities all adopt different metrics to claim Nobel affiliates, some generous while others more stringent, since some only count academicians at the time of announcement while others include all visitors and professors of various ranks as well. Inconsistency thus may occur between those official counts and what this list states. See also * List of Nobel laureates by country This is a list of Nobel Prize laureates by country. Listings for ''Economics'' refer to the related Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences. The Nobel Prizes and the Prize in Economic Sciences have been awarded 577 times to 889 recipients, of w ... References {{Nobel Prizes * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Higgs Field
The Higgs boson, sometimes called the Higgs particle, is an elementary particle in the Standard Model of particle physics produced by the excited state, quantum excitation of the Higgs field, one of the field (physics), fields in particle physics theory. In the Standard Model, the Higgs particle is a massive scalar boson that Coupling (physics), couples to (interacts with) particles whose mass arises from their interactions with the Higgs Field, has zero Spin (physics), spin, even (positive) Parity (physics), parity, no electric charge, and no color charge, colour charge. It is also very unstable, particle decay, decaying into other particles almost immediately upon generation. The Higgs field is a scalar field with two neutral and two electrically charged components that form a complex doublet (physics), doublet of the weak isospin SU(2) symmetry. Its "Spontaneous symmetry breaking#Sombrero potential, sombrero potential" leads it to take a nonzero value everywhere (inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Higgs Mechanism
In the Standard Model of particle physics, the Higgs mechanism is essential to explain the Mass generation, generation mechanism of the property "mass" for gauge bosons. Without the Higgs mechanism, all bosons (one of the two classes of particles, the other being fermions) would be considered Massless particle, massless, but measurements show that the W boson, W+, W−, and Z boson, Z0 bosons actually have relatively large masses of around . The Higgs field resolves this conundrum. The simplest description of the mechanism adds to the Standard Model a quantum field (the Higgs boson, Higgs field), which permeates all of space. Below some extremely high temperature, the field causes spontaneous symmetry breaking during interactions. The breaking of symmetry triggers the Higgs mechanism, causing the bosons with which it interacts to have mass. In the Standard Model, the phrase "Higgs mechanism" refers specifically to the generation of masses for the W and Z bosons, W±, and Z Weak for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Higgs Boson
The Higgs boson, sometimes called the Higgs particle, is an elementary particle in the Standard Model of particle physics produced by the excited state, quantum excitation of the Higgs field, one of the field (physics), fields in particle physics theory. In the Standard Model, the Higgs particle is a massive scalar boson that Coupling (physics), couples to (interacts with) particles whose mass arises from their interactions with the Higgs Field, has zero Spin (physics), spin, even (positive) Parity (physics), parity, no electric charge, and no color charge, colour charge. It is also very unstable, particle decay, decaying into other particles almost immediately upon generation. The Higgs field is a scalar field with two neutral and two electrically charged components that form a complex doublet (physics), doublet of the weak isospin SU(2) symmetry. Its "Spontaneous symmetry breaking#Sombrero potential, sombrero potential" leads it to take a nonzero value everywhere (inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Higgs
Peter Ware Higgs (29 May 1929 – 8 April 2024) was a British theoretical physicist, professor at the University of Edinburgh,Griggs, Jessica (Summer 2008The Missing Piece ''Edit'' the University of Edinburgh Alumni Magazine, p. 17 and Nobel laureate in Physics for his work on the mass of subatomic particles. In 1964, Higgs was the single author of one of the three milestone papers published in ''Physical Review Letters'' (''PRL'') that proposed that spontaneous symmetry breaking in electroweak theory could explain the origin of mass of elementary particles in general and of the W and Z bosons in particular. This Higgs mechanism predicted the existence of a new particle, the Higgs boson, the detection of which became one of the great goals of physics. In 2012, CERN announced the discovery of the Higgs boson at the Large Hadron Collider. The Higgs mechanism is generally accepted as an important ingredient in the Standard Model of particle physics, without which certain p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokamak
A tokamak (; ) is a device which uses a powerful magnetic field generated by external magnets to confine plasma (physics), plasma in the shape of an axially symmetrical torus. The tokamak is one of several types of magnetic confinement fusion, magnetic confinement devices being developed to produce controlled thermonuclear fusion power. The tokamak concept is currently one of the leading candidates for a practical fusion reactor for providing minimally polluting electrical power. The proposal to use controlled thermonuclear fusion for industrial purposes and a specific scheme using thermal insulation of high-temperature plasma by an electric field was first formulated by the Soviet physicist Oleg Lavrentiev in a mid-1950 paper. In 1951, Andrei Sakharov and Igor Tamm modified the scheme by proposing a theoretical basis for a thermonuclear reactor, where the plasma would have the shape of a torus and be held by a magnetic field. The first tokamak was built in the Soviet Union ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonon
A phonon is a collective excitation in a periodic, elastic arrangement of atoms or molecules in condensed matter, specifically in solids and some liquids. In the context of optically trapped objects, the quantized vibration mode can be defined as phonons as long as the modal wavelength of the oscillation is smaller than the size of the object. A type of quasiparticle in physics, a phonon is an excited state in the quantum mechanical quantization of the modes of vibrations for elastic structures of interacting particles. Phonons can be thought of as quantized sound waves, similar to photons as quantized light waves. The study of phonons is an important part of condensed matter physics. They play a major role in many of the physical properties of condensed matter systems, such as thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity, as well as in models of neutron scattering and related effects. The concept of phonons was introduced in 1930 by Soviet physicist Igor Tamm. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
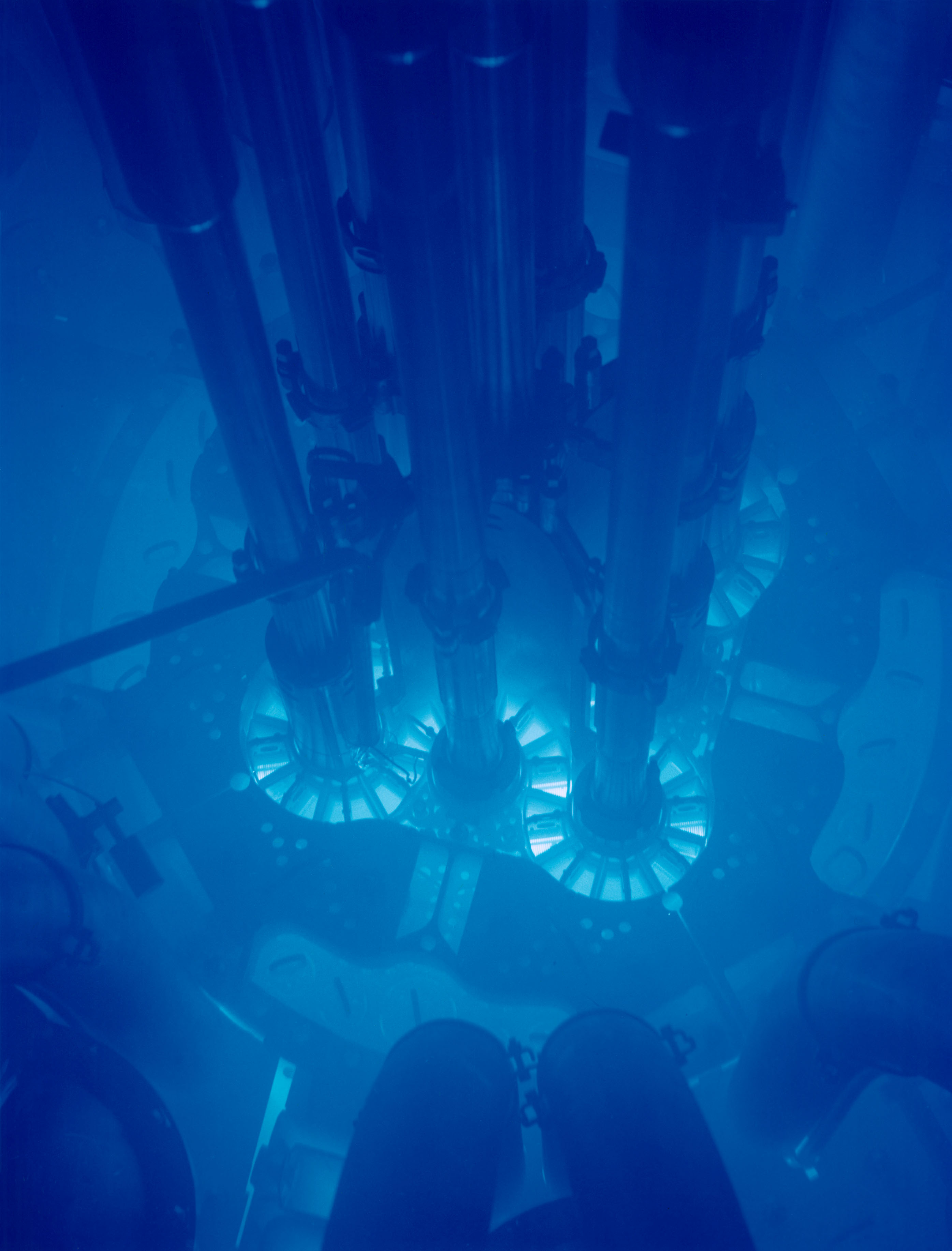
Cherenkov Radiation
Cherenkov radiation () is electromagnetic radiation emitted when a charged particle (such as an electron) passes through a dielectric medium (such as distilled water) at a speed greater than the phase velocity (speed of propagation of a wavefront in a medium) of light in that medium. A classic example of Cherenkov radiation is the characteristic blue glow of an underwater nuclear reactor. Its cause is similar to the cause of a sonic boom, the sharp sound heard when faster-than-sound movement occurs. The phenomenon is named after Soviet physicist Pavel Cherenkov. History The radiation is named after the Soviet scientist Pavel Cherenkov, the 1958 Nobel Prize winner, who was the first to detect it experimentally under the supervision of Sergey Vavilov at the Lebedev Institute in 1934. Therefore, it is also known as Vavilov–Cherenkov radiation. Cherenkov saw a faint bluish light around a radioactive preparation in water during experiments. His doctorate thesis was on lumin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Physics
Particle physics or high-energy physics is the study of Elementary particle, fundamental particles and fundamental interaction, forces that constitute matter and radiation. The field also studies combinations of elementary particles up to the scale of protons and neutrons, while the study of combinations of protons and neutrons is called nuclear physics. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) and bosons (force-carrying particles). There are three Generation (particle physics), generations of fermions, although ordinary matter is made only from the first fermion generation. The first generation consists of Up quark, up and down quarks which form protons and neutrons, and electrons and electron neutrinos. The three fundamental interactions known to be mediated by bosons are electromagnetism, the weak interaction, and the strong interaction. Quark, Quarks cannot exist on their own but form hadrons. Hadrons that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igor Tamm
Igor Yevgenyevich Tamm (; 8 July 1895 – 12 April 1971) was a Soviet Union, Soviet physicist who received the 1958 Nobel Prize in Physics, jointly with Pavel Alekseyevich Cherenkov and Ilya Mikhailovich Frank, for their 1934 discovery and demonstration of Cherenkov radiation. He also predicted the quasi-particle of sound: the phonon; and in 1951, together with Andrei Sakharov, proposed the Tokamak, Tokamak system. Biography Igor Tamm was born in 1895 in Vladivostok into the family of Eugene Tamm, a civil engineer, and his wife Olga Davydova. According to Russian sources, Tamm had German people, German noble descent on his father's side through his grandfather Theodor Tamm, who emigrated from Thuringia. Although his surname "Tamm (surname), Tamm" is rather common in Estonia, other sources state he was Jewish people, Jewish or had Jewish ancestry. He studied at a Gymnasium (school), gymnasium in Elisavetgrad (now Kropyvnytskyi, Ukraine). In 1913–1914 he studied at the Universi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |