|
United States Navy Submarine Bases
The United States Navy built permanent and temporary submarine bases around the world to maintain its fleet of submarines and serve the needs of the crews. Submarine bases are military bases that offer good fleet anchorage and are designed to refuel and resupply submarines. The peak number of US submarine bases was during World War II, as the submarine was well suited for fighting in the vast Pacific War, often in enemy waters. Many of the United States submarine bases were closed after the war. History The need for US submarine bases was created with the completion of the first submarine launched in May 1897. The USS ''Holland'' was acquired by the Navy 11 April 1900. On 16 October 1900, the USS ''Holland'' departed for her first port, United States Naval Academy at Annapolis, Maryland for crew training. USS ''Holland'' had a crew of one officer, and five enlisted men. Annapolis being a training center was not designated a submarine base, though the USS ''Holland'' was statio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Francisco Bay
San Francisco Bay (Chochenyo language, Chochenyo: 'ommu) is a large tidal estuary in the United States, U.S. state of California, and gives its name to the San Francisco Bay Area. It is dominated by the cities of San Francisco, California, San Francisco, San Jose, California, San Jose, and Oakland, California, Oakland. The San Francisco Bay drains water from approximately 40 percent of California. Water from the Sacramento River, Sacramento and San Joaquin River, San Joaquin rivers, and from the Sierra Nevada mountains, flow into Suisun Bay, which then travels through the Carquinez Strait to meet with the Napa River at the entrance to San Pablo Bay, which connects at its south end to San Francisco Bay. It then connects to the Pacific Ocean via the Golden Gate strait. However, this entire group of interconnected bays is often called the ''San Francisco Bay''. The bay was designated a Ramsar Convention, Ramsar Wetland of International Importance on February 2, 2013, and the Port ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seattle Construction And Drydock Company
The Seattle Construction and Drydock Company was a shipbuilding company based in Seattle, Washington (state), Washington. Between 1911 and 1918, it produced a substantial number of ships for both commercial and military uses. In the beginning of the 20th century, until its significance was diluted by the emergence of a number of shipyards during the World War I shipbuilding boom, it was the largest of its kind in Seattle and one of the few significant ship yards along the West Coast of the United States, second only to the Union Iron Works in San Francisco. History Formally established in 1911, the shipyard could trace its history back to 1882, when Robert Moran (shipbuilder), the Moran brothers operated a machine shop at Yesler's Wharf () in the lower story of a new sawmill employing 8 to 10 men, built by John Anderson and owned by Anderson and Henry Yesler, who is often regarded as the founder of the city of Seattle. At the end of the year 1882 they were constructing their ow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
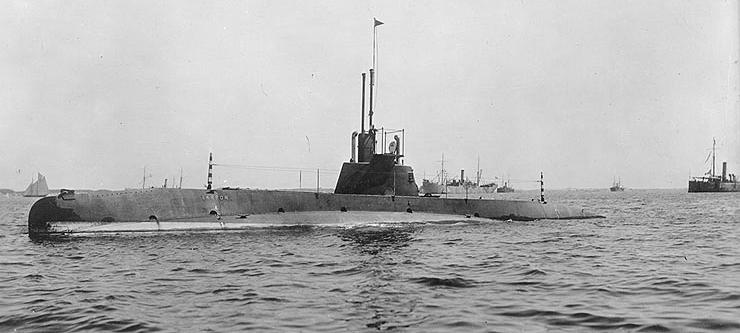
USS F-4
USS ''F-4'' (SS-23) was a United States Navy F-class submarine. Her keel was laid down by the Moran Company of Seattle, Washington, sponsored by Mrs. Manson Franklin Backus, wife of a successful Seattle business man and banker. The submarine was originally named ''Skate'', making her the first ship of the United States Navy named for the skate. She was renamed ''F-4'' on 17 November 1911, launched on 6 January 1912 and commissioned on 3 May 1913. Service history Joining the First Submarine Group, Pacific Torpedo Flotilla, ''F-4'' participated in the development operations of that group along the west coast in 1913 and into 1914. In August 1914, all four F-class boats were transferred to duty in Hawaii, the first submarines to operate from that territory. The facilities in Pearl Harbor were still under construction so the submarines were based at rented pier space in Honolulu. During training maneuvers off the entrance to Honolulu Harbor on 25 March 1915, ''F-4'' suffere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS F-3
USS ''F-3'' (SS-22), was a United States F-class submarine, F-class submarine. She was named ''Pickerel'' when her keel was laid down by The Moran Company of Seattle, Washington, making her the first ship of the United States Navy to be named for the pickerel, a type of Esox, pike. She was renamed ''F-3'' on 17 November 1911, ship naming and launching, launched on 6 January 1912 sponsored by Mrs. M. F. Backus, and ship commissioning, commissioned on 5 August 1912. Service history ''F-3'' completed her trials in the Puget Sound area before reporting for duty at San Francisco, California, on 15 October 1912, when she joined the First Submarine Group, Pacific Torpedo Flotilla. The Flotilla operated along the coast of California, conducting constant exercises and experiments to develop the techniques of submarine warfare, and from August 1914 to November 1915, carried out similar operations in the Hawaiian Islands out of Naval Submarine Base Pearl Harbor. ''F-3'' was placed in ordi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Boat
An electric boat is a powered watercraft driven by electric motors, which are powered by either on-board battery packs, solar panels or generators. While a significant majority of water vessels are powered by diesel engines, with sail power and gasoline engines also popular, boats powered by electricity have been used for over 120 years. Electric boats were very popular from the 1880s until the 1920s, when the internal combustion engine became dominant. Since the energy crises of the 1970s, interest in this quiet and potentially renewable marine energy source has been increasing steadily, especially as more efficient solar cells have become available, for the first time making possible motorboats with a theoretically infinite cruise range like sailboats. The first practical solar boat was probably constructed in 1975 in England. The first electric sailboat to complete a round-the-world tour (including a transit of the Panama Canal) using only green technologies is EcoSailin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States F-class Submarine
The F-class submarines were a group of four submarines designed for the United States Navy by Electric Boat in 1909. ''F-1'' and ''F-2'' were built by Union Iron Works in San Francisco, while ''F-3'' and ''F-4'' were built by The Moran Company in Seattle, Washington. Design They were generally similar to the C-class and D-class submarines built by Electric Boat, but larger at 400 tons submerged vs. 337 tons for the D class. They were single-hulled boats with circular sections laid along the longitudinal axis. Overall length was and the beam was . The E-class and the F-class submarines were the first US submarines to have bow planes. Like the E class, their early-model diesels had problems and were replaced in 1915. The hull contained three compartments separated by partial strength watertight bulkheads: *torpedo room with four 18 inch (450 mm) torpedo tubes, * control room/battery rooms with the ballast control valves, hydroplane controls and periscope. Two battery wel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States E-class Submarine
The E-class submarines were a class of two United States Navy submarines, built by the Fore River Shipbuilding Company of Quincy, Massachusetts, under a subcontract from the Electric Boat Company. They were used as coastal and harbor defense submarines prior to World War I. When hostilities broke out, the E class were mostly used as training boats; however, ''E-1'' operated on war patrols based in the Azores. During this time, the need for an improved permanent bridge structure was discovered; the temporary piping-and-canvas bridges were inadequate in the North Atlantic. Design The two E-class submarines were analogous to the preceding D-class submarine, with very similar size and displacement and the same armament. They were essentially diesel powered D-class boats, and were the first U.S. diesel-powered submarines. The French "Z" (Q 36) was the first in the world, in 1905. Although early diesels were unreliable and the E class engines were replaced in 1915, diesels rapidly s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States D-class Submarine
The United States D-class submarines were a trio of submarines built for the United States Navy in the first decade of the 20th century. All three ships served during World War I providing training for crews and officers on the U.S. East Coast, before the class was decommissioned and sold for scrap in 1922. Description The D-class submarines were enlarged and iterative improvements over the preceding C class, and were the first American submarines armed with four torpedo tubes. They were built by the Fore River Shipbuilding Company of Quincy, Massachusetts, under a subcontract from the Electric Boat Company of Groton, Connecticut. They had a length of overall, a beam of and a mean draft of . They displaced on the surface and submerged. The D-class boats had a crew of 1 officer and 14 enlisted men. They had a diving depth of .Friedman, p. 306 For surface running, they were powered by two Electric Boat/ Craig gasoline engines, each driving one propeller shaft.Gardiner a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States C-class Submarine
The C-class submarines were five United States Navy submarines built by the Fore River Shipbuilding Company in Quincy, Massachusetts, under a subcontract from the General Dynamics Electric Boat, Electric Boat Company. Built between 1906 and 1909, and in commission from 1908 to 1919, all five were subsequently sold for scrap in 1920. They were considerably larger than the preceding United States B-class submarine, B-class at 275 tons submerged vs. 173 tons submerged, and were the first United States submarines with two-shaft propulsion, doubling the machinery of the B class. Design The C-class boats were the first to be designed solely by Electric Boat's new chief designer Lawrence York Spear, Lawrence Spear. They were the first USN submarines to have two propellers, a design trend that would last until 1953. Electric Boat made the design available for export, and two boats (with rights for a third) were sold to the Austro-Hungarian Navy and commissioned as the U-5-class submarine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States B-class Submarine
The B-class submarines were three United States Navy submarines built by the Fore River Shipbuilding Company in Quincy, Massachusetts, under a subcontract from the Electric Boat Company. They were eventually stationed in the Philippines, an American possession, beginning in 1912–15. They were shipped there on colliers (coal-carrying ships). All three were stricken and expended as targets 1919–22. Design These were the last submarines designed directly by John Holland. In a series of business organizational moves, Holland had essentially been forced out of Electric Boat by Isaac Rice and Elihu Frost and he resigned from the company on March 28, 1904. They were also the last submarines in the USN with a single, axial mounted propeller until the experimental submarine USS ''Albacore'' (AGSS-569) of 1953. These vessels introduced some features intended to increase underwater speed, including a small sail and a rotating cap over the torpedo tube muzzles. The streamlined, rot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
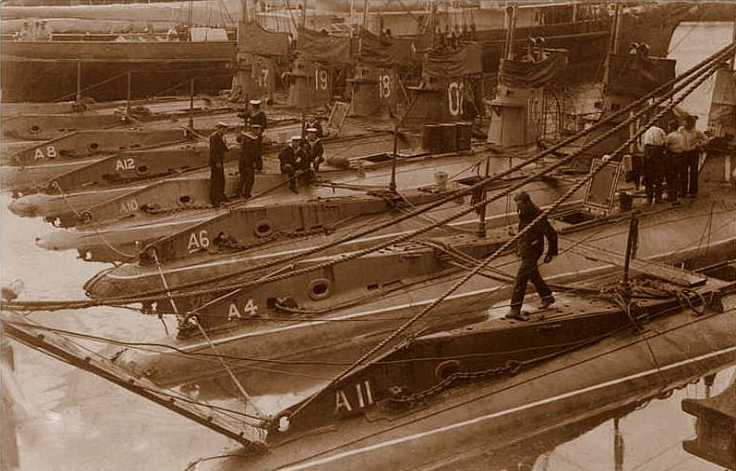
A-class Submarine (1903)
The A-class was the Royal Navy's first Ship class, class of British-designed submarines. Thirteen were built by Vickers at Barrow-in-Furness between 1902 and 1905 as an improvement on the US . Design and construction While there was considerable variation amongst the boats of the class, they were around long and displaced around 200 tons when submerged. The first, ''A1'' (ordered as ''Holland No. 6''), was launched in July 1902, the last, ''A13'', in April 1905. Propulsion All were propelled underwater by battery-powered electric motors and on the surface by shaft-drive Wolseley Motors, Wolseley petrol engines of (''A1''), (''A2-A4'') or (''A5''-''A12''). ''A13'' had an experimental Vickers diesel engine, which proved to be unreliable. Armaments Armament was two British 18 inch torpedo, torpedo tubes with four torpedoes except for ''A1'', which had 1 tube and 3 torpedoes. Service history This submarine class was plagued by numerous accidents and failures; al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |