|
Unisys OS 2200 Communications
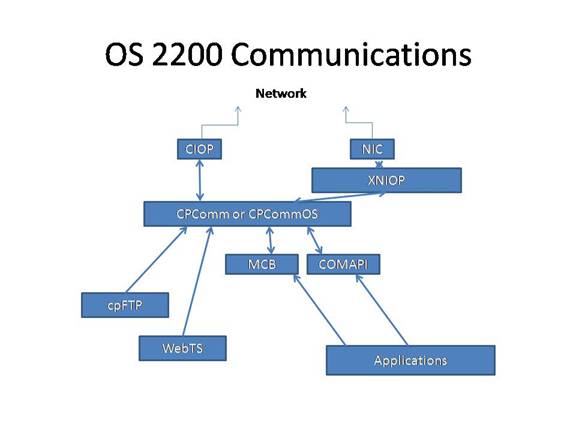
{{Short description, Aspect of Unisys OS 2200 operating system The Unisys OS 2200 operating system, OS 2200 communications management system includes CPComm and MCB along with many programs that provide communications related functions such as file transfer, e-mail, and distributed transaction processing protocols. CPComm CPComm executes as a real time program in a background run. CPComm implements the protocol stacks. CPComm communicates with the CIOP (Communications I/O Processor) to connect to networks. CPcommOS is a variant for 2200 Series systems implemented on Intel architectures. In the most recent systems only various speeds of Ethernet communications are supported. Previous systems supported ATM and FDDI but these were dropped through lack of interest. CPComm and the Exec jointly handle authentication of connection requests and authorization for users and terminals to connect to time-sharing, and the various transaction application groups. SSL is supported for e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unisys OS 2200 Operating System
OS 2200 is the operating system for the Unisys ClearPath Dorado family of mainframe systems. The operating system kernel of OS 2200 is a lineal descendant of Exec 8 for the UNIVAC 1108. Documentation and other information on current and past Unisys systems can be found on the Unisys public support website.Current Unisys documentation is available on thUnisys public support web site For OS 2200 products, select one of the ClearPath Dorado platforms (e.g., Dorado 800 or Dorado 8300) and then the release level (usually the highest numbered one unless you are looking for something specific in an earlier release). That will take you to a search page where you can search by title or document content. See Unisys 2200 Series system architecture for a description of the machine architecture and its relationship to the OS 2200 operating system. Unisys stopped producing ClearPath Dorado hardware in the early 2010s, and the operating system is now run under emulation. History There we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uniscope
Uniscope was a class of computer terminals made by Sperry Rand Corporation, Univac Division, and successors since 1964 that were normally used to communicate with Univac mainframes. As such, it was the successor to various models of Teletype. Due to the text color on the original models, these terminals are informally known as ''green screen terminals''. Unlike Teletype terminals, the Uniscope minimizes the number of I/O interrupts required by accepting large blocks of data, and uses a high speed proprietary communications interface, using coaxial cable and hardware devices known as multiplexors. A Uniscope operator awaits a prompt from the remote mainframe. The prompt indicates that the mainframe is ready to receive input. The operator enters data, offline from the mainframe, and then presses the Transmit button. The terminal locks the keyboard and sends to the mainframe what the operator entered. All the data goes in a single transmission and that causes a single in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertext Transfer Protocol
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is an application layer protocol in the Internet protocol suite model for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web, where hypertext documents include hyperlinks to other resources that the user can easily access, for example by a mouse click or by tapping the screen in a web browser. Development of HTTP was initiated by Tim Berners-Lee at CERN in 1989 and summarized in a simple document describing the behavior of a client and a server using the first HTTP protocol version that was named 0.9. That first version of HTTP protocol soon evolved into a more elaborated version that was the first draft toward a far future version 1.0. Development of early HTTP Requests for Comments (RFCs) started a few years later and it was a coordinated effort by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) and the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), with work later moving to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HTTP Secure
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is an extension of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). It is used for secure communication over a computer network, and is widely used on the Internet. In HTTPS, the communication protocol is encrypted using Transport Layer Security (TLS) or, formerly, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). The protocol is therefore also referred to as HTTP over TLS, or HTTP over SSL. The principal motivations for HTTPS are authentication of the accessed website, and protection of the privacy and integrity of the exchanged data while in transit. It protects against man-in-the-middle attacks, and the bidirectional encryption of communications between a client and server protects the communications against eavesdropping and tampering. The authentication aspect of HTTPS requires a trusted third party to sign server-side digital certificates. This was historically an expensive operation, which meant fully authenticated HTTPS connections were usually found only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |