|
Unionism In England
In England, Unionism is a political ideology which favours the continuation of some form of political union between England and the other Countries of the United Kingdom, (Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland). As well as the current state of the United Kingdom, It is part of the wider British unionist movement and is closely linked to the notion of Britishness. Unionism in England is characterised by both opposition to England's independence as a separate state and the belief that Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland should continue to be constituent countries of the Union. The Union The political union between the Kingdoms of England (also including Wales as an English possession) and Scotland was created by the Acts of Union, passed in the parliaments of both kingdoms in 1707 and 1706 respectively, which united the governments of what had previously been independent states (though they had shared the same monarch in a personal union since 1603) under the Parliament of Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Map Of England Within The United Kingdom
A map is a symbolic depiction emphasizing relationships between elements of some space, such as objects, regions, or themes. Many maps are static, fixed to paper or some other durable medium, while others are dynamic or interactive. Although most commonly used to depict geography, maps may represent any space, real or fictional, without regard to context or scale, such as in brain mapping, DNA mapping, or computer network topology mapping. The space being mapped may be two dimensional, such as the surface of the earth, three dimensional, such as the interior of the earth, or even more abstract spaces of any dimension, such as arise in modeling phenomena having many independent variables. Although the earliest maps known are of the heavens, geographic maps of territory have a very long tradition and exist from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom Of Great Britain And Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland was a sovereign state in the British Isles that existed between 1801 and 1922, when it included all of Ireland. It was established by the Acts of Union 1800, which merged the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland into a unified state. The establishment of the Irish Free State in 1922 led to the remainder later being renamed the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland in 1927. The United Kingdom, having financed the European coalition that defeated France during the Napoleonic Wars, developed a large Royal Navy that enabled the British Empire to become the foremost world power for the next century. For nearly a century from the final defeat of Napoleon following the Battle of Waterloo to the outbreak of World War I, Britain was almost continuously at peace with Great Powers. The most notable exception was the Crimean War with the Russian Empire, in which actual hostilities were relatively ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
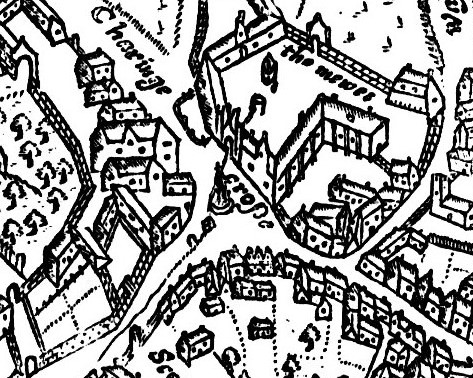
Trafalgar Square
Trafalgar Square ( ) is a public square in the City of Westminster, Central London, laid out in the early 19th century around the area formerly known as Charing Cross. At its centre is a high column bearing a statue of Admiral Nelson commemorating the victory at the Battle of Trafalgar. The battle of 21 October 1805, established the British navy's dominance at sea in the Napoleonic Wars over the fleets of France and Spain. The site around Trafalgar Square had been a significant landmark since the 1200s. For centuries, distances measured from Charing Cross have served as location markers. The site of the present square formerly contained the elaborately designed, enclosed courtyard of the King's Mews. After George IV moved the mews to Buckingham Palace, the area was redeveloped by John Nash, but progress was slow after his death, and the square did not open until 1844. The Nelson's Column at its centre is guarded by four lion statues. A number of commemorative statu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Independence
Scottish independence ( gd, Neo-eisimeileachd na h-Alba; sco, Scots unthirldom) is the idea of Scotland as a sovereign state, independent from the United Kingdom, and refers to the political movement that is campaigning to bring it about. Scotland was an independent kingdom through the Middle Ages, and fought wars to maintain its independence from Kingdom of England, England. The two kingdoms were joined in personal union in 1603 when the Scottish King James VI and I, James VI became James I of England, and the two kingdoms united politically into one kingdom called Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain in Acts of Union 1707, 1707. Political campaigns for Scottish self-government began in the 19th century, initially in the form of demands for home rule within the United Kingdom. Two referendums on devolution in the United Kingdom, devolution were held in 1979 Scottish devolution referendum, 1979 and 1997 Scottish devolution referendum, 1997, with a devolved Scottish Parl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Last Night Of The Proms
The BBC Proms or Proms, formally named the Henry Wood Promenade Concerts Presented by the BBC, is an eight-week summer season of daily orchestral classical music concerts and other events held annually, predominantly in the Royal Albert Hall in central London. The Proms were founded in 1895, and are now organised and broadcast by the BBC. Each season consists of concerts in the Royal Albert Hall, chamber music concerts at Cadogan Hall, additional Proms in the Park events across the UK on the Last Night of the Proms, and associated educational and children's events. The season is a significant event in British culture and in classical music. Czech conductor Jiří Bělohlávek described the Proms as "the world's largest and most democratic musical festival". ''Prom'' is short for ''promenade concert'', a term which originally referred to outdoor concerts in London's pleasure gardens, where the audience was free to stroll around while the orchestra was playing. In the conte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symbols Of The United Kingdom, The Channel Islands And The Isle Of Man
Symbols of the United Kingdom, the Channel Islands and the Isle of Man is a list of the national symbols of the United Kingdom, its constituent countries (England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland), and the Crown Dependencies (the Channel Islands and the Isle of Man). Each separate entry has its own set of unique symbols. United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland Crown Dependencies Channel Islands Bailiwick of Jersey Bailiwick of Guernsey Isle of Man See also * United Kingdom ** England ** Northern Ireland ** Scotland ** Wales * Crown Dependencies ** Channel Islands ** Isle of Man * List of British flags * United Kingdom – Symbols * Channel Islands – Culture * List of national animals – United Kingdom * National emblem – Plants (National flora) * National symbols of England * National symbols of Scotland * National symbols of Northern Ireland * National symbols of Wales * Symbols of the Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Lothian Question
The West Lothian question, also known as the English question, is a political issue in the United Kingdom. It concerns the question of whether MPs from Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales who sit in the House of Commons should be able to vote on matters that affect only England, while MPs from England are unable to vote on matters that have been devolved to the Northern Ireland Assembly, the Scottish Parliament and the Senedd (Welsh Parliament). The term ''West Lothian question'' was coined by Enoch Powell MP in 1977 after Tam Dalyell, the Labour MP for the Scottish constituency of West Lothian, raised the matter repeatedly in House of Commons debates on devolution. In 2011 the UK Government set up the Commission on the consequences of devolution for the House of Commons, chaired by Sir William McKay, former Clerk of the House of Commons, to examine the question. The commission published a report in 2013 which proposed various procedural changes, including the recommendation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunday Telegraph
''The Sunday Telegraph'' is a British broadsheet newspaper, founded in February 1961 and published by the Telegraph Media Group, a division of Press Holdings. It is the sister paper of ''The Daily Telegraph'', also published by the Telegraph Media Group. ''The Sunday Telegraph'' was originally a separate operation with a different editorial staff, but since 2013 the ''Telegraph'' has been a seven-day operation. Digital edition A digital only Christmas edition will be free on Christmas Day in 2022 like in 2005, 2011 and 2016. See also * References External links * 1961 establishments in England Publications established in 1961 Sunday newspapers published in the United Kingdom Telegraph Media Group {{UK-newspaper-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Nationalism
English nationalism is a nationalism that asserts that the English are a nation and promotes the cultural unity of English people. In a general sense, it comprises political and social movements and sentiment inspired by a love for English culture, language and history, and a sense of pride in England and the English people. English nationalists often see themselves as predominantly English rather than British. On the political level, some English nationalists have advocated self-government for England such as the English Democrats. This could take the form either of a devolved English parliament within the United Kingdom or the re-establishment of an independent sovereign state of England outside of the United Kingdom. History The history of English nationalism is a contested area of scholarship. The historian Adrian Hastings has written that: "One can find historians to date 'the dawn of English national consciousness' (or some such phrase) in almost every century from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of The United Kingdom
The national flag of the United Kingdom is the Union Jack, also known as the Union Flag. The design of the Union Jack dates back to the Act of Union 1801 which united the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland (previously in personal union) to create the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. The flag consists of the red cross of Saint George (patron saint of England (which also represents Wales)), edged in white, superimposed on the saltire of St Patrick (patron saint of Ireland), also edged in white, which are superimposed on the saltire of Saint Andrew (patron saint of Scotland). Wales is not represented in the Union Flag by Wales's patron saint, Saint David, because the flag was designed whilst Wales was part of the Kingdom of England. The flag proportions on land and the war flag used by the British Army have the proportions 3:5. The flag's height-to-length proportions at sea are 1:2. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parliament Of Northern Ireland
The Parliament of Northern Ireland was the home rule legislature of Northern Ireland, created under the Government of Ireland Act 1920, which sat from 7 June 1921 to 30 March 1972, when it was suspended because of its inability to restore order during The Troubles, resulting in the introduction of Direct Rule. It was abolished under the Northern Ireland Constitution Act 1973. The Parliament of Northern Ireland was bicameral, consisting of a House of Commons with 52 seats, and an indirectly elected Senate with 26 seats. The Sovereign was represented by the Governor (initially by the Lord Lieutenant), who granted royal assent to Acts of Parliament in Northern Ireland, but executive power rested with the Prime Minister, the leader of the largest party in the House of Commons. House of Commons The House of Commons had 52 members, of which 48 were for territorial seats, and four were for graduates of Queen's University, Belfast (until 1969, when the four university seats ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of Ireland Act 1920
The Government of Ireland Act 1920 (10 & 11 Geo. 5 c. 67) was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. The Act's long title was "An Act to provide for the better government of Ireland"; it is also known as the Fourth Home Rule Bill or (inaccurately) as the Fourth Home Rule Act. The Act was intended to partition Ireland into two self-governing polities: the six north-eastern counties were to form "Northern Ireland", while the larger part of the country was to form " Southern Ireland". Both territories were to remain part of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, and provision was made for their future reunification through a Council of Ireland. The Act was passed by the British Parliament in November 1920, received royal assent in December, and came into force on 3 May 1921. The smaller Northern Ireland was duly created with a devolved government and remained in the UK. The larger Southern Ireland was not recognized by most of its citizens, who instead r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
.jpg)