|
Ultrabright Electron
Ultrabright electrons are an advanced atomic imaging tool that can allow scientists to view atoms and molecules in motion. They were developed at the Max Planck Institute for the Structure and Dynamics of Matter in Hamburg, Germany and at the University of Toronto with the teams led by Professor R.J.D. Miller. Brightness The brightness of an electron beam is defined for any given point as the current per unit area normal to the given direction, per unit solid angle. Mathematically this is defined using limits as the area and solid angle tend to 0. The general formula is, B= \lim_ \lim_ \frac Worster, J. "The brightness of electron beams" British Journal of Applied Physics, 1969, p. 1 An ultrabright electron beam has been defined as having >10 A/cm^2 with spatial coherence of >1 nm. This level of energy in that small of a coherence is a large technical problem, not only in the production of such a beam, but also how to use the beam without destroying the sample in the proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atoms
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished from each other by the number of protons that are in their atoms. For example, any atom that contains 11 protons is sodium, and any atom that contains 29 protons is copper. Atoms with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons are called isotopes of the same element. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. A human hair is about a million carbon atoms wide. Atoms are smaller than the shortest wavelength of visible light, which means humans cannot see atoms with conventional microscopes. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics is not possible due to quantum effects. More than 99.94% of an atom's mass is in the nucleus. Protons have a positive electric charge a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecules
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction from ions is dropped and ''molecule'' is often used when referring to polyatomic ions. A molecule may be homonuclear, that is, it consists of atoms of one chemical element, e.g. two atoms in the oxygen molecule (O2); or it may be heteronuclear, a chemical compound composed of more than one element, e.g. water (two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom; H2O). In the kinetic theory of gases, the term ''molecule'' is often used for any gaseous particle regardless of its composition. This relaxes the requirement that a molecule contains two or more atoms, since the noble gases are individual atoms. Atoms and complexes connected by non-covalent interactions, such as hydrogen bonds or ionic bonds, are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Planck Society
The Max Planck Society for the Advancement of Science (; abbreviated MPG) is a formally independent non-governmental and non-profit association of German research institutes. Founded in 1911 as the Kaiser Wilhelm Society, it was renamed to the Max Planck Society in 1948 in honor of its former president, theoretical physicist Max Planck. The society is funded by the federal and state governments of Germany. Mission According to its primary goal, the Max Planck Society supports basic research, fundamental research in the natural science, natural, life science, life and social science, social sciences, the arts and humanities in its 84 (as of January 2024) institutes and research facilities. , the society has a total staff of 24,655 permanent employees, including 6,688 contractually employed scientists, 3,444 doctoral candidates, and 3,203 guest scientists. 44.9% of all employees are female and 57.2% of the scientists are foreign nationals. The society's budget for 2023 was about � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Toronto
The University of Toronto (UToronto or U of T) is a public university, public research university whose main campus is located on the grounds that surround Queen's Park (Toronto), Queen's Park in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It was founded by royal charter in 1827 as King's College, the first institution of higher learning in Upper Canada. Originally controlled by the Church of England, the university assumed its present name in 1850 upon becoming a secular institution. It has three campuses: University of Toronto Mississauga, Mississauga, #St. George campus, St. George, and University of Toronto Scarborough, Scarborough. Its main campus, St. George, is the oldest of the three and located in Downtown Toronto. U of T operates as a collegiate university, comprising 11 #Colleges, colleges, each with substantial autonomy on financial and institutional affairs and significant differences in character and history. The University of Toronto is the largest university in Canada with a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
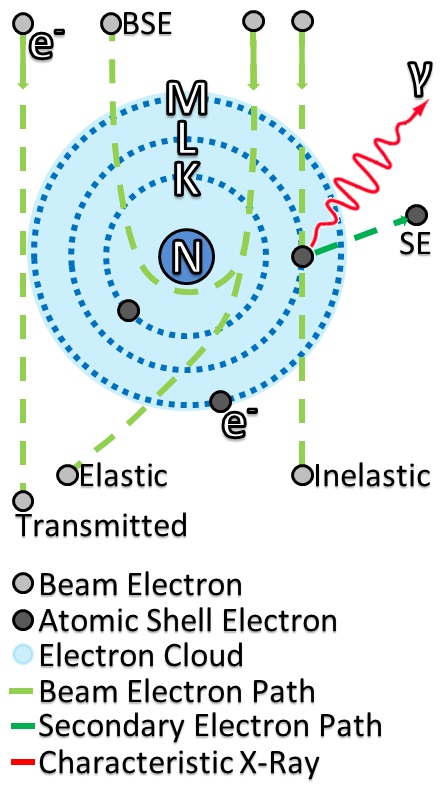
Electron Beam
Since the mid-20th century, electron-beam technology has provided the basis for a variety of novel and specialized applications in semiconductor manufacturing, microelectromechanical systems, nanoelectromechanical systems, and microscopy. Mechanism Free electrons in a vacuum can be manipulated by Electric field, electric and magnetic fields to form a fine beam. Where the beam collides with solid-state matter, electrons are converted into heat or kinetic energy. This concentration of energy in a small volume of matter can be precisely controlled by the fields, which brings many advantages. Applications Electron beam techniques include electron probe microanalysis, transmission electron microscopy, auger spectroscopy, and scanning electron microscopy. The rapid increase of temperature at the location of impact can quickly melt a target material. In extreme working conditions, the rapid temperature increase can lead to evaporation, making an electron beam an excellent tool in heating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Scattering
Electron scattering occurs when electrons are displaced from their original trajectory. This is due to the electrostatic forces within matter interaction or, if an external magnetic field is present, the electron may be deflected by the Lorentz force. This scattering typically happens with solids such as metals, semiconductors and insulators; and is a limiting factor in integrated circuits and transistors. Electron scattering has many applications ranging from the use of swift electron in Electron microscope, electron microscopes to very high energies for hadronic systems that allows the measurement of the distribution of charges for nucleons and nuclear structure. The scattering of electrons has allowed us to understand many details about the atomic structure, from the ordering of atoms to that protons and neutrons are made up of the smaller elementary subatomic particles called quarks. Electrons may be scattered through a solid in several ways: * Not at all: no electron scatte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diarylethene
Diarylethene is the general name of a class of chemical compounds that have aromatic functional groups bonded to each end of a carbon–carbon double bond. The simplest example is stilbene, which has two geometric isomers, E and Z. Under the influence of light, these compounds can generally perform two kinds of reversible isomerizations: * E to Z isomerizations, most common for stilbenes (and azobenzenes). This process goes through an excited state energy minimum where the aromatic rings lie at 90° to each other. This conformation drops to the ground state and generally relaxes to trans and cis forms in a 1:1 ratio, thus the quantum yield for E-Z isomerization is very rarely greater than 0.5. *6π electrocyclizations of the Z form, leading to an additional bond between the two aryl functionalities and a disruption of the aromatic character of these groups.J. March, ''Advanced Organic Chemistry'', 4th ed. (1992). The quantum yield of this reaction is generally less than 0.1, and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |