|
Ukinrek Maars
The Ukinrek maars () are two volcanic craters on the north side of the Aleutian Range in Alaska that were formed by a phreatomagmatic eruption in 1977. The maars are 1.5 km south of Becharof Lake and 12 km northwest of Peulik Volcano, on a low area of the range, bordering the Bering Sea. The western of the two is elliptical in shape and up to 170 m in diameter and 35 m deep. The other lies 600 m to the east and is circular and up to 300 m in diameter and 70 m deep. The east maar has a 49 m-high lava dome within its crater lake. The eruption occurred in March–April 1977 and lasted for ten days. There was no previous eruption. The magmatic material was olivine basalt from a mantle source. Pyroclastic surge from the eruptions traveled to the northwest. The volume of lava erupted was 9×105 m3 and the volume of tephra expelled was 2.6×107 m3. They were named shortly after the eruptions and the literal translation means "Two Holes". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Becharof National Wildlife Refuge
Becharof National Wildlife Refuge is a National Wildlife Refuge in the Aleutian Range of the Alaska Peninsula of southwestern Alaska. It is adjacent to Katmai National Park and Preserve. This national wildlife refuge, which covers an area of , was established in 1980 to conserve major brown bears, salmon, migratory birds, caribou, marine birds, and mammals and to comply with treaty obligations. It lies primarily in the east-central part of Lake and Peninsula Borough, but extends eastward into the mainland portion of Kodiak Island Borough. The refuge is administered from offices in King Salmon. Becharof Wilderness it comprises approximately 500,000 acres (2,000 km2) and is bordered by the Katmai Wilderness on the north. It was designated a wilderness area in 1980 by the Alaska National Interest Lands Conservation Act. History Jimmy Carter created Becharof National Monument by presidential proclamation on December 1, 1978. The refuge was established on December 2, 1980 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantle (geology)
A mantle is a layer inside a planetary body bounded below by a Planetary core, core and above by a Crust (geology), crust. Mantles are made of Rock (geology), rock or Volatile (astrogeology), ices, and are generally the largest and most massive layer of the planetary body. Mantles are characteristic of planetary bodies that have undergone planetary differentiation, differentiation by density. All Terrestrial planet, terrestrial planets (including Earth), half of the giant planets, specifically ice giants, a number of Asteroid, asteroids, and some planetary Natural satellite, moons have mantles. Examples Earth The Earth's mantle is a layer of Silicate minerals, silicate rock between the Crust (geology), crust and the Earth's outer core, outer core. Its mass of 4.01 × 1024 kg is 67% the mass of the Earth. It has a thickness of making up about 84% of Earth's volume. It is predominantly solid, but in Geologic time scale, geological time it behaves as a Viscosity, visc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Crater Lakes
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and because most of Earth's plate boundaries are underwater, most volcanoes are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes resulting from divergent tectonic activity are usually non-explosive whereas those resulting from convergent tectonic activity cause violent eruptions."Mid-ocean ridge tectonics, volcanism and geomorphology." Geology 26, no. 455 (2001): 458. https://macdonald.faculty.geol.ucsb.edu/papers/Macdonald%20Mid-Ocean%20Ridge%20Tectonics.pdf Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maars Of Alaska
A maar is a broad, low-relief volcanic crater caused by a phreatomagmatic eruption (an explosion which occurs when groundwater comes into contact with hot lava or magma). A maar characteristically fills with water to form a relatively shallow crater lake, which may also be called a maar.David S.G. Thomas and Andrew Goudie (eds.), ''The Dictionary of Physical Geography'' (Oxford: Blackwell, 2000), 301. . Maars range in size from across and from deep. Most maars fill with water to form natural lakes. Most maars have low rims composed of a mixture of loose fragments of volcanic rocks and rocks torn from the walls of the diatreme. Etymology The name ''maar'' comes from a Moselle Franconian dialect word used for the circular lakes of the Daun area of Germany. The word evolved from its first use in German in the modern geological sense in 1819 and is now used in English and in the geological sciences as the term for the explosion crater, even if water from rainfall might alway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
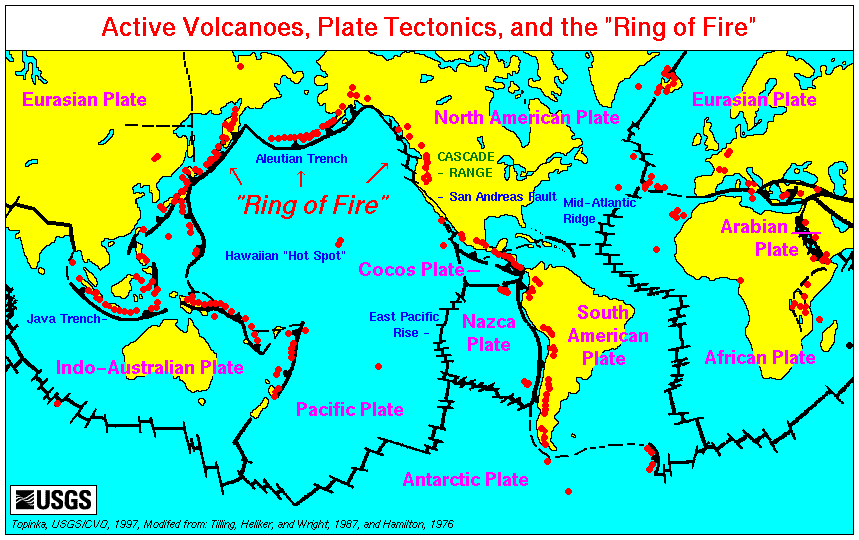
Active Volcanoes
An active volcano is a volcano that is currently erupting, or has the potential to erupt in the future. Conventionally it is applied to any that have erupted during the Holocene (the current geologic epoch that began approximately 11,700 years ago). A volcano that is not currently erupting but could erupt in the future is known as a dormant volcano. Volcanoes that will not erupt again are known as extinct volcanoes. Overview There are 1,350 potentially active volcanoes around the world, 500 of which have erupted in historical time. Many active volcanoes are located along the Pacific Rim, also known as the Pacific Ring of Fire. An estimated 500 million people live near active volcanoes. ''Historical time'' (or recorded history) is another timeframe for ''active''. The span of recorded history differs from region to region. In China and the Mediterranean, it reaches back nearly 3,000 years, but in the Pacific Northwest of the United States and Canada, it reaches back less tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
April 1977 In The United States
April is the fourth month of the year in the Gregorian and Julian calendars. Its length is 30 days. April is commonly associated with the season of spring in the Northern Hemisphere, and autumn in the Southern Hemisphere, where it is the seasonal equivalent to October in the Northern Hemisphere and vice versa. History The Romans gave this month the Latin name ''Aprilis''"April" in ''Chambers's Encyclopædia''. London: George Newnes, 1961, Vol. 1, p. 497. but the derivation of this name is uncertain. The traditional etymology is from the verb ''aperire'', "to open", in allusion to its being the season when trees and flowers begin to "open", which is supported by comparison with the modern Greek use of άνοιξη (''ánixi'') (opening) for spring. Since some of the Roman months were named in honor of divinities, and as April was sacred to the goddess Venus, her Veneralia being held on the first day, it has been suggested that Aprilis was originally her month ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
March 1977 In The United States
March is the third month of the year in both the Julian and Gregorian calendars. Its length is 31 days. In the Northern Hemisphere, the meteorological beginning of spring occurs on the first day of March. The March equinox on the 20 or 21 marks the astronomical beginning of spring in the Northern Hemisphere and the beginning of autumn in the Southern Hemisphere, where September is the seasonal equivalent of the Northern Hemisphere's March. History The name of March comes from '' Martius'', the first month of the earliest Roman calendar. It was named after Mars, the Roman god of war, and an ancestor of the Roman people through his sons Romulus and Remus. His month ''Martius'' was the beginning of the season for warfare, and the festivals held in his honor during the month were mirrored by others in October, when the season for these activities came to a close. ''Martius'' remained the first month of the Roman calendar year perhaps as late as 153 BC, and several religious ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Map Of Alaska Peninsula Volcanoes
A map is a symbolic depiction of interrelationships, commonly spatial, between things within a space. A map may be annotated with text and graphics. Like any graphic, a map may be fixed to paper or other durable media, or may be displayed on a transitory medium such as a computer screen. Some maps change interactively. Although maps are commonly used to depict geographic elements, they may represent any space, real or fictional. The subject being mapped may be two-dimensional such as Earth's surface, three-dimensional such as Earth's interior, or from an abstract space of any dimension. Maps of geographic territory have a very long tradition and have existed from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'of the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to a flat representation of Earth's surface. History Maps have been one of the most important human inventions for millennia, allowing humans t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phreatic Eruption
A phreatic eruption, also called a phreatic explosion, ultravulcanian eruption or steam-blast eruption, occurs when magma heats ground water or surface water. The extreme temperature of the magma (anywhere from ) causes near-instantaneous evaporation of water to steam, resulting in an explosion of steam, water, ash, rock, and volcanic bombs. At Mount St. Helens in Washington state, hundreds of steam explosions preceded the 1980 Plinian eruption of the volcano. A less intense geothermal event may result in a mud volcano. Phreatic eruptions typically include steam and rock fragments; the inclusion of liquid lava is unusual. The temperature of the fragments can range from cold to incandescent. If molten magma is included, volcanologists classify the event as a phreatomagmatic eruption. These eruptions occasionally create broad, low-relief craters called '' maars''. Phreatic explosions can be accompanied by carbon dioxide or hydrogen sulfide gas-emissions. Carbon diox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), as well as the current and most recent of the twelve periods of the Phanerozoic eon. It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million years ago to the present. The Quaternary Period is divided into two epochs: the Pleistocene (2.58 million years ago to 11.7 thousand years ago) and the Holocene (11.7 thousand years ago to today); a proposed third epoch, the Anthropocene, was rejected in 2024 by IUGS, the governing body of the ICS. The Quaternary is typically defined by the Quaternary glaciation, the cyclic growth and decay of continental ice sheets related to the Milankovitch cycles and the associated climate and environmental changes that they caused. Research history In 1759 Giovanni Arduino proposed that the geological strata of northern Italy could be divided into four succ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tephra
Tephra is fragmental material produced by a Volcano, volcanic eruption regardless of composition, fragment size, or emplacement mechanism. Volcanologists also refer to airborne fragments as pyroclasts. Once clasts have fallen to the ground, they remain as tephra unless hot enough to fuse into pyroclastic rock or tuff. When a volcano explodes, it releases a variety of tephra including ash, cinders, and blocks. These layers settle on the land and, over time, sedimentation occurs incorporating these tephra layers into the geologic record. Tephrochronology is a geochronological technique that uses discrete layers of tephra—volcanic ash from a single eruption—to create a chronological framework in which Paleoecology, paleoenvironmental or Archaeology, archaeological records can be placed. Often, when a volcano explodes, biological organisms are killed and their remains are buried within the tephra layer. These fossils are later dated by scientists to determine the age of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |