|
Unovis
UNOVIS (also known as MOLPOSNOVIS and POSNOVIS) was a short-lived but influential group of artists, founded and led by Kazimir Malevich at the Vitebsk Art School in 1919. Initially formed by students and known as MOLPOSNOVIS, the group formed to explore and develop new theories and concepts in art. Under the leadership of Malevich they renamed to UNOVIS, chiefly focusing on his ideas on Suprematism and producing a number of projects and publications whose influence on the avant-garde in Russia and abroad was immediate and far-reaching.Essay: ''Black Square: In the Circle of Malevich and UNOVIS Group'' The group disbanded in 1922. The name UNOVIS is an abbreviation in [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vera Ermolaeva
Vera Ermolaeva ( rus, Ве́ра Миха́йловна Ермола́ева) (November 2, 1893September 26, 1937) was a Russian painter, graphic artist and illustrator who participated in the Russian avant-garde movement. Biography Childhood and early life Vera Mikhailovna Ermolaeva was born November 2, 1893, in the village of Kliuchi in the Petrovsk uyezd of the Saratov Oblast (now – the Maloserdobinsky District of the Penza Oblast). Her father, Mikahil Sergeevich Ermolaev (1847-1911), was a landowner and served as chairman of the zemstvo county government. He also established a cooperative society called “The Labor Society,” and published a liberal journal called “''Zhizn’”'' (Life) (1899 - 1901), in which writings by Lenin, Gorky, and others appeared. Her mother, Anna Vladimirovna, was born the Baroness of Ungern-Unkovskaia (1854 - ?). As a child, Ermolaeva fell from a horse, an accident which crippled her legs and left her unable to walk without the aid of c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Lissitzky
Lazar Markovich Lissitzky (russian: link=no, Ла́зарь Ма́ркович Лиси́цкий, ; – 30 December 1941), better known as El Lissitzky (russian: link=no, Эль Лиси́цкий; yi, על ליסיצקי), was a Russian artist, designer, photographer, typographer, polemicist and architect. He was an important figure of the Russian avant-garde, helping develop suprematism with his mentor, Kazimir Malevich, and designing numerous exhibition displays and propaganda works for the Soviet Union. His work greatly influenced the Bauhaus and constructivist movements, and he experimented with production techniques and stylistic devices that would go on to dominate 20th-century graphic design. Lissitzky's entire career was laced with the belief that the artist could be an agent for change, later summarized with his edict, "" (goal-oriented creation).Glazova Lissitzky, of Lithuanian Jewish оrigin, began his career illustrating Yiddish children's books in an effort to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilya Chashnik
Ilya Grigorevich Chashnik (1902, Lucyn, Russian Empire, currently Ludza, Latvia - 1929, Leningrad) was a suprematist artist, a pupil of Kazimir Malevich and a founding member of the UNOVIS school. Biography Chashnik was born to a Jewish family in 1902, Lucyn, Russian Empire, currently Ludza, Latvia. He started studying in Yehuda Pen's art school at Vitebsk when he was just eleven years old. He became a student of Marc Chagall. By 1918, he moved to Moscow to work in an art workshop directed by Kazimir Malevich. He returned after Malevich accepted a senior teaching position at ''Vitebsk School of Drawing and Painting.'' Chashnik was notably able in a variety of media. Aleksandra Semenovna Shatskikh describes him as "famous for his inexhaustible inventiveness and ability to apply Suprematist principles to virtually all forms of art, including easel painting." He painted, was proficient in metalwork, and designed ceramics produced at the Imperial Porcelain Factory (then known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilia Chashnik
Ilya Grigorevich Chashnik (1902, Lucyn, Russian Empire, currently Ludza, Latvia - 1929, Leningrad) was a suprematist artist, a pupil of Kazimir Malevich and a founding member of the UNOVIS school. Biography Chashnik was born to a Jewish family in 1902, Lucyn, Russian Empire, currently Ludza, Latvia. He started studying in Yehuda Pen's art school at Vitebsk when he was just eleven years old. He became a student of Marc Chagall. By 1918, he moved to Moscow to work in an art workshop directed by Kazimir Malevich. He returned after Malevich accepted a senior teaching position at ''Vitebsk School of Drawing and Painting.'' Chashnik was notably able in a variety of media. Aleksandra Semenovna Shatskikh describes him as "famous for his inexhaustible inventiveness and ability to apply Suprematist principles to virtually all forms of art, including easel painting." He painted, was proficient in metalwork, and designed ceramics produced at the Imperial Porcelain Factory (then known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nina Kogan
Nina Kogan (1887–1942) was a Russian painter known for her Suprematist works. Life and career Nina Osipovna (Iosifovna) Kogan was born in 1887 or 1889 in Vitebsk, Saint Petersburg, or Moscow, and studied at the St. Ekaterina School in St. Petersburg in 1911-1913. In 1919 she helped to organize City Museum in Petrograd. She went on to study at the People's Art School in Vitebsk, Belarus, and soon became a teacher there, together with Marc Chagall, El Lissitzky, and Kazimir Malevich. Kogan became a member of Malevich's UNOVIS art collective. While a member of the group, she created the work ''Suprematist Ballet'' in an attempt to animate Suprematist forms and ideas in dance. She also took part designing new version of futuristic opera '' Victory over the Sun''. Kogan participated in on several exhibitions of early 1920s, such as "Erste Russische Kunstausstellung" in Berlin, 1922; "Exhibition of Works by Women Artists" in Leningrad, 1936; the "Sixth Exhibition of Works by Leningra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolai Suetin
Nikolai Suetin (; 1897–1954) was a Russian Suprematist artist. He worked as a graphic artist, a designer, and a ceramics painter. Suetin studied at the Vitebsk Higher Institute of Art, (1918–1922) under Kazimir Malevich, founder of Suprematism, an early abstract art movement which developed a style based on 'non objective' geometric shapes in alignment. From 1920 the artist participated in exhibitions including those of the UNOVIS group (Vitebsk, 1920 and 1921; Moscow 1929, 1921 and 1922), Petrograd exhibitions, an International Exhibition of Decorative Art (held in Paris, 1925), the Exhibition of Soviet Porcelain (1926 and 1927), and the First Exhibition of Leningrad artists in the Russian Museum among others. He lived in Petrograd from 1923, and worked at the State Lomonosov Ceramics Factory. He also worked at the State Petrograd Lomonossov Porcelain Plant (from 1922 until 1924), and at the Porcelain Plant in Government of Novgorod (from 1924 until 1925). Suetin was a me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
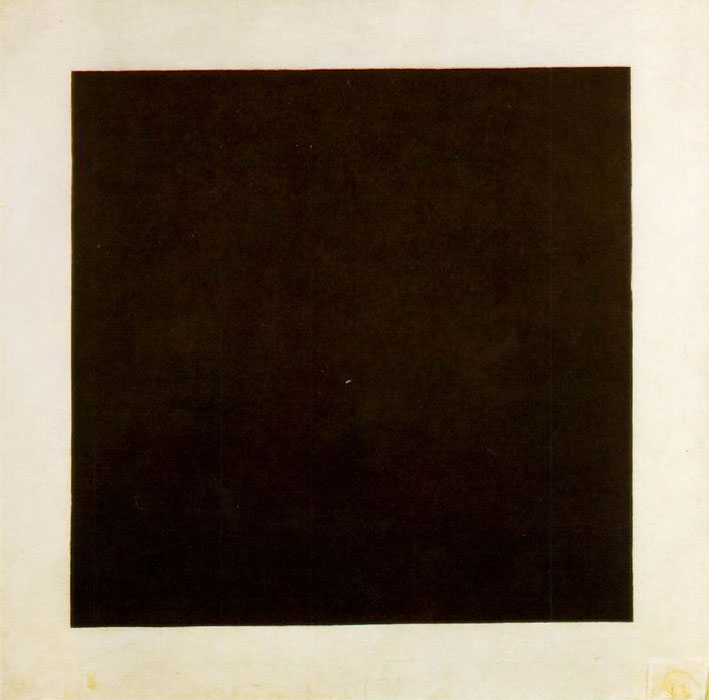
Kazimir Malevich
Kazimir Severinovich Malevich ; german: Kasimir Malewitsch; pl, Kazimierz Malewicz; russian: Казими́р Севери́нович Мале́вич ; uk, Казимир Северинович Малевич, translit=Kazymyr Severynovych Malevych ., group=nb (Запись о рождении в метрической книге римско-католического костёла св. Александра в Киеве, 1879 год // ЦГИАК Украины, ф. 1268, оп. 1, д. 26, л. 13об—14. – 15 May 1935) was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lazar Khidekel
Lazar Markovich Khidekel (Vitebsk 1904 – Leningrad 1986) was an artist, designer, architect and theoretician, who is noted for realizing the abstract, avant-garde Suprematist movement through architecture. Early life In 1918 at the age of 14, Khidekel was selected by Marc Chagall to study at the Vitebsk school of art, where he first met Kazimir Malevich and El Lissitzky. Khidekel became one of the founders of the group UNOVIS UNOVIS (also known as MOLPOSNOVIS and POSNOVIS) was a short-lived but influential group of artists, founded and led by Kazimir Malevich at the Vitebsk Art School in 1919. Initially formed by students and known as MOLPOSNOVIS, the group formed to ... – Affirmers of New Art, led by Malevich and one of a few of Malevich's students, along with Ilya Chashnik and Nikolai Suetin, who deeply embraced Suprematist style and philosophy, and constituted the nucleus of genuine followers who soon become into their master's partners and assistants. Contributions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Art
Soviet art is a form of visual art produced after the October Socialist Revolution of 1917 in Soviet Russia (1917—1922) and the Soviet Union (1922—1991), when the short-lived Russian Republic was overthrown and replaced. This led to an artistic and cultural shift within Russia and the Soviet Union as a whole, including a new focus on Socialist Realism in officially approved art. Soviet art of the post-revolutionary period The consolidation of Soviet art was preceded throughout the 1920s by an era of intense ideological competition between different artistic groupings, with members each striving to ensure their own views would have priority in determining the forms and directions in which Soviet art would develop; seeking to occupy key posts in cultural institutions and to win the favor and support of the authorities. This struggle was made even more bitter by the growing crisis of radical ''leftist'' art. At the turn of the 1930s, many ''avant-garde'' tendencies that ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Avant-garde
The Russian avant-garde was a large, influential wave of avant-garde modern art that flourished in the Russian Empire and the Soviet Union, approximately from 1890 to 1930—although some have placed its beginning as early as 1850 and its end as late as 1960. The term covers many separate, but inextricably related, art movements that flourished at the time; including Suprematism, Constructivism, Russian Futurism, Cubo-Futurism, Zaum and Neo-primitivism. Many of the artists who were born, grew up or were active in what is now Belarus and Ukraine (including Kazimir Malevich, Aleksandra Ekster, Vladimir Tatlin, Wassily Kandinsky, David Burliuk, Alexander Archipenko), are also classified in the Ukrainian avant-garde. The Russian avant-garde reached its creative and popular height in the period between the Russian Revolution of 1917 and 1932, at which point the ideas of the avant-garde clashed with the newly emerged state-sponsored direction of Socialist Realism. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suprematism
Suprematism (russian: Супремати́зм) is an early twentieth-century art movement focused on the fundamentals of geometry (circles, squares, rectangles), painted in a limited range of colors. The term ''suprematism'' refers to an abstract art based upon "the supremacy of pure artistic feeling" rather than on visual depiction of objects. Founded by Russian artist Kazimir Malevich in 1913, Supremus ( Russian: Супремус) conceived of the artist as liberated from everything that pre-determined the ideal structure of life and art. Projecting that vision onto Cubism, which Malevich admired for its ability to deconstruct art, and in the process change its reference points of art, he led a group of Ukrainian and Russian avant-garde artists — including Aleksandra Ekster, Liubov Popova, Olga Rozanova, Ivan Kliun, Ivan Puni, Nadezhda Udaltsova, Nina Genke-Meller, Ksenia Boguslavskaya and others — in what's been described as the first attempt to independently foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


_by_Wassily_Kandinsky.jpg)
