|
UMgungundlovu
uMgungundlovu was the royal capital of the Zulu King Dingane (1828–1840) and one of several military complexes () which he maintained. He established his royal kraal in 1829 in the eMakhosini valley against Lion hill (''Singonyama''), just south of the White Umfolozi River. The name uMgungundlovu stems from the Zulu word or phrase , which means "the secret conclave of the elephant". Some sources also refer to uMgungundlovu as "the place of the elephant". The word (elephant) refers to the king of the Zulu people. Description Dingane established his royal kraal, or capital, at uMgungundlovu in 1829. He took power in 1828 after assassinating Shaka, his half-brother. This was one of the king's military complexes () and was located in the eMakhosini valley, just south of the White Umfolozi River on the slope of the Lion hill. It lay between two streams, the ''Umkhumbane'' to the south and ''Nzololo'' to the north. Encampment () The oval-shaped (military settlement) contain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
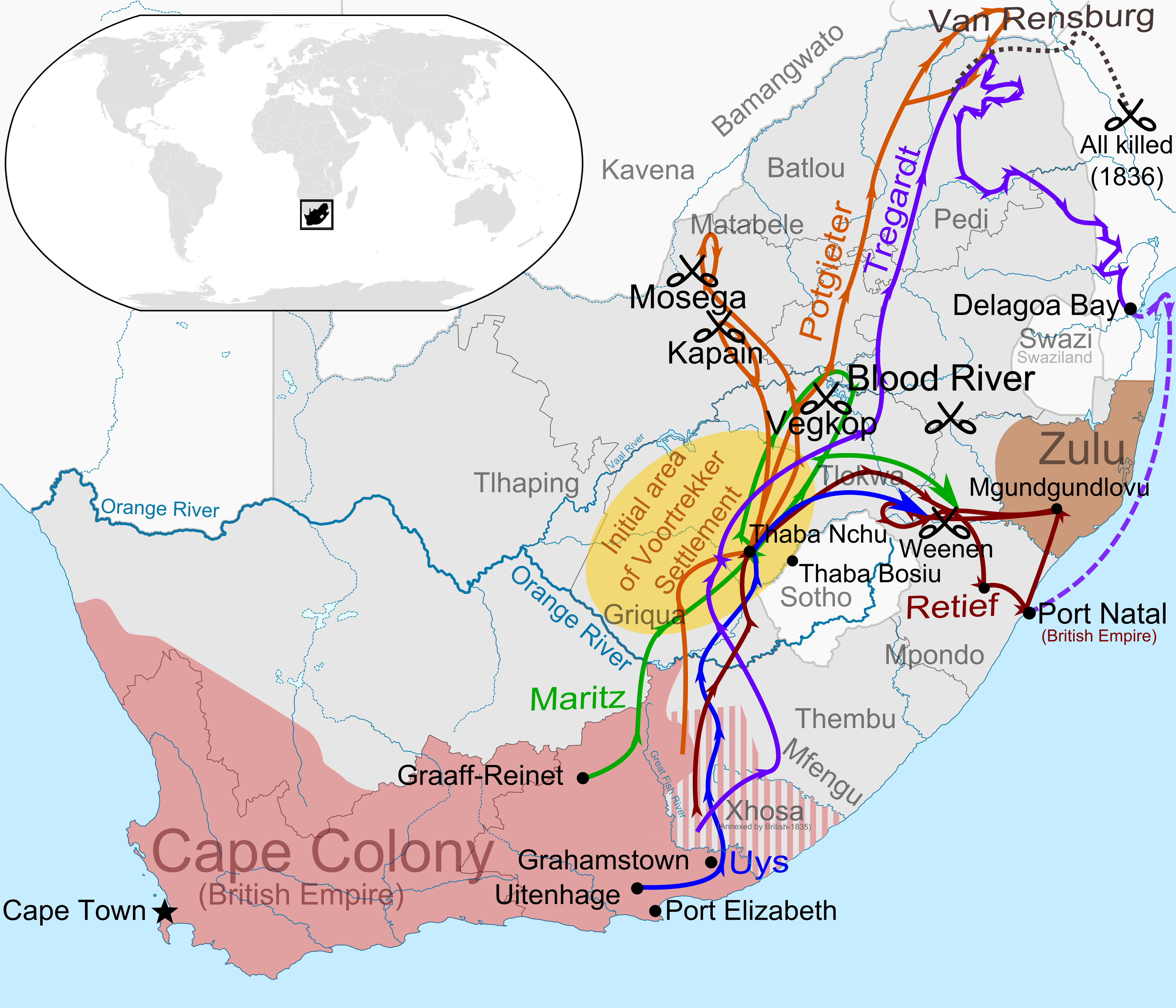
Voortrekker
The Great Trek (, ) was a northward migration of Dutch-speaking settlers who travelled by wagon trains from the Cape Colony into the interior of modern South Africa from 1836 onwards, seeking to live beyond the Cape's British colonial administration. The Great Trek resulted from the culmination of tensions between rural descendants of the Cape's original European settlers, known collectively as Boers, and the British. It was also reflective of an increasingly common trend among individual Boer communities to pursue an isolationist and semi-nomadic lifestyle away from the developing administrative complexities in Cape Town. Boers who took part in the Great Trek identified themselves as ''voortrekkers'', meaning "pioneers" or "pathfinders" in Dutch and Afrikaans. The Great Trek led directly to the founding of several autonomous Boer republics, namely the South African Republic (also known simply as the Transvaal), the Orange Free State and the Natalia Republic. It also led ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piet Retief
Pieter Mauritz Retief (12 November 1780 – 6 February 1838) was a '' Voortrekker'' leader. Settling in 1814 in the frontier region of the Cape Colony, he later assumed command of punitive expeditions during the sixth Xhosa War. He became a spokesperson for the frontier farmers who voiced their discontent, and wrote the Voortrekkers' declaration at their departure from the colony. He was a leading figure during their Great Trek, and at one stage their elected governor. He proposed Natal as the final destination of their migration and selected a location for its future capital, later named Pietermaritzburg in his honour. The massacre of Retief and his delegation by the Zulu King Dingane and the extermination of several Voortrekker laagercamps in the area of the present town of Weenen led to the Battle of Blood River on the Ncome River. The short-lived Boer republic Natalia suffered from ineffective government and was eventually annexed to the British Cape Colony. Early lif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weenen Massacre
The Weenen Massacre, also known as the Bloukrans Massacre, was a series of coordinated attacks by Zulu forces under Dingane, King Dingane on Voortrekker encampments in Natal, present-day South Africa, on 17–18 February 1838. Following the killing of Voortrekker leader Piet Retief and his delegation at Dingane’s royal kraal, uMgungundlovu, on 6 February 1838, approximately 500 Voortrekkers and their servants, including 185 children and 56 women, were killed across sites at Doringkop, Bloukrans, Moordspruit, Rensburgspruit, and Weenen.Binckes, Robin (2013). ''The Great Trek Uncut – Escape from British Rule: The Boer Exodus from the Cape Colony, 1836''. Pinetown, South Africa: 30° South Publishers (Pty) Ltd. / Solihull, UK: Helion & Company Limited. ISBN 978-1-920143-68-8. A pivotal event in the Great Trek, the massacre escalated conflict between the Voortrekkers and the Zulu, leading to the Battle of Blood River in December 1838. Voortrekker accounts allege a calculated betr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dingane KaSenzangakhona
Dingane ka Senzangakhona Zulu (–29 January 1840), commonly referred to as Dingane, Dingarn or Dingaan, was a Zulu people, Zulu prince who became king of the Zulu Kingdom in 1828, after assassinating his half-brother Shaka Zulu. He set up his royal capital, uMgungundlovu, translated to "Place of the Elephant" or "elephant swallower". He also constructed one of numerous military encampments, or kraals, in the eMakhosini Valley just south of the White Umfolozi River, on the slope of Lion Hill (''Singonyama''). Rise to power Dingane came to power in 1828 after assassinating his half-brother Shaka with the help of another brother, Umhlangana, as well as Mbopa, Shaka's bodyguard. Following the death of Nandi (mother of Shaka), Nandi, Shaka's behavior became increasingly erratic and many of his relatives accused Shaka of killing his mother. The true mastermind behind the murder of Shaka was his paternal aunt Mkabayi kaJama, who saw Dingane as the best of the choices for next King of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zulu Kingdom
The Zulu Kingdom ( ; ), sometimes referred to as the Zulu Empire, was a monarchy in Southern Africa. During the 1810s, Shaka established a standing army that consolidated rival clans and built a large following which ruled a wide expanse of Southern Africa that extended along the coast of the Indian Ocean from the Tugela River in the south to the Pongola River in the north. A bitter civil war in the mid-19th century erupted which culminated in the 1856 Battle of Ndondakusuka between the brothers Cetshwayo and Mbuyazi. In 1879, a British force invaded Zululand, beginning the Anglo-Zulu War. After an initial Zulu victory at the Battle of Isandlwana in January, the British regrouped and defeated the Zulus in July during the Battle of Ulundi, ending the war. The area was absorbed into the Colony of Natal and later became part of the Union of South Africa. The current Zulu king is Misuzulu Sinqobile, who serves as the monarch of South Africa's KwaZulu-Natal province. States a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andries Pretorius
Andries Wilhelmus Jacobus Pretorius (27 November 179823 July 1853) was a leader of the Boers who was instrumental in the creation of the South African Republic, as well as the earlier but short-lived Natalia Republic, in present-day South Africa. The large city of Pretoria, executive capital of South Africa, is named after him. Early life and background Pretorius was educated at home and although a school education was not a priority on the eastern frontier of the Cape Colony, he was literate enough to read the Bible and write his thoughts down on paper. Pretorius had five children, the eldest of whom, Marthinus Wessel Pretorius, later became the first President of the South African Republic (Transvaal). Pretorius descended from the line of the earliest Dutch settlers in the Cape Colony. He belonged to the fifth generation of the progenitor, Johannes Pretorius son of Reverend :nl:Wessel Pretorius, Wessel Schulte of the Netherlands. Schulte in his time as a theology student at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matiwane
Matiwane ka Masumpa (died c.1830, uMgungundlovu), son of Masumpa, was the king of an independent Nguni-speaking nation, the amaNgwane, a people named after Matiwane's ancestor Ngwane ka Kgwadi. The amaNgwane lived at the headwaters of the White Umfolozi, in what is now Vryheid in northern KwaZulu-Natal. The cunning of Matiwane would keep the amaNgwane one step ahead of the ravages of the rising Zulu kingdom, but their actions also set the ''Mfecane'' in motion. After his nation was ousted from their homeland by Zwide with Shaka, Matiwane and his armies clashed with neighboring nations as he attempted to nourish his people. Eventually he fled South into lands occupied by abaThembu, amaMpondo and the neighboring Xhosa nations, which ultimately teamed up with the British and got his nation dismantled and scattered as smaller splinters at the Battle of Mbholompo in what is today Mthatha in the Eastern Cape. In his exodus from Mthatha, Matiwane and the biggest of the amaNgwane splint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ndlela KaSompisi
Ndlela kaSompisi (died February 1840) was a key general to Zulu Kings Shaka and Dingane. He rose to prominence as a highly effective warrior under Shaka. Dingane appointed him as his ''inDuna'', or chief advisor. He was also the principal commander of Dingane's armies. However, Ndlela's failure to defeat the Boers under Andries Pretorius and a rebellion against Dingane led to his execution. This made him a failure in the eyes of his people. Career According to E. A. Ritter, Ndlela was a " Ntuli cannibal recruit" to Shaka's army.E. A. Ritter, ''Shaka Zulu: The Rise of the Zulu Empire'': Longmans Green: London. 1955, pp.122 n., 143, 161, 180, 220, 291 His name means "road" or "path". During the Ndwandwe–Zulu War Ndela distinguished himself by his fighting ability, performing "incredible deeds of destruction" on Shaka's enemies. He was severely wounded in battle with the Ndwandwe. Despite his non-Zulu origins, he was rapidly promoted and was appointed chief of the Ntuli. When his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
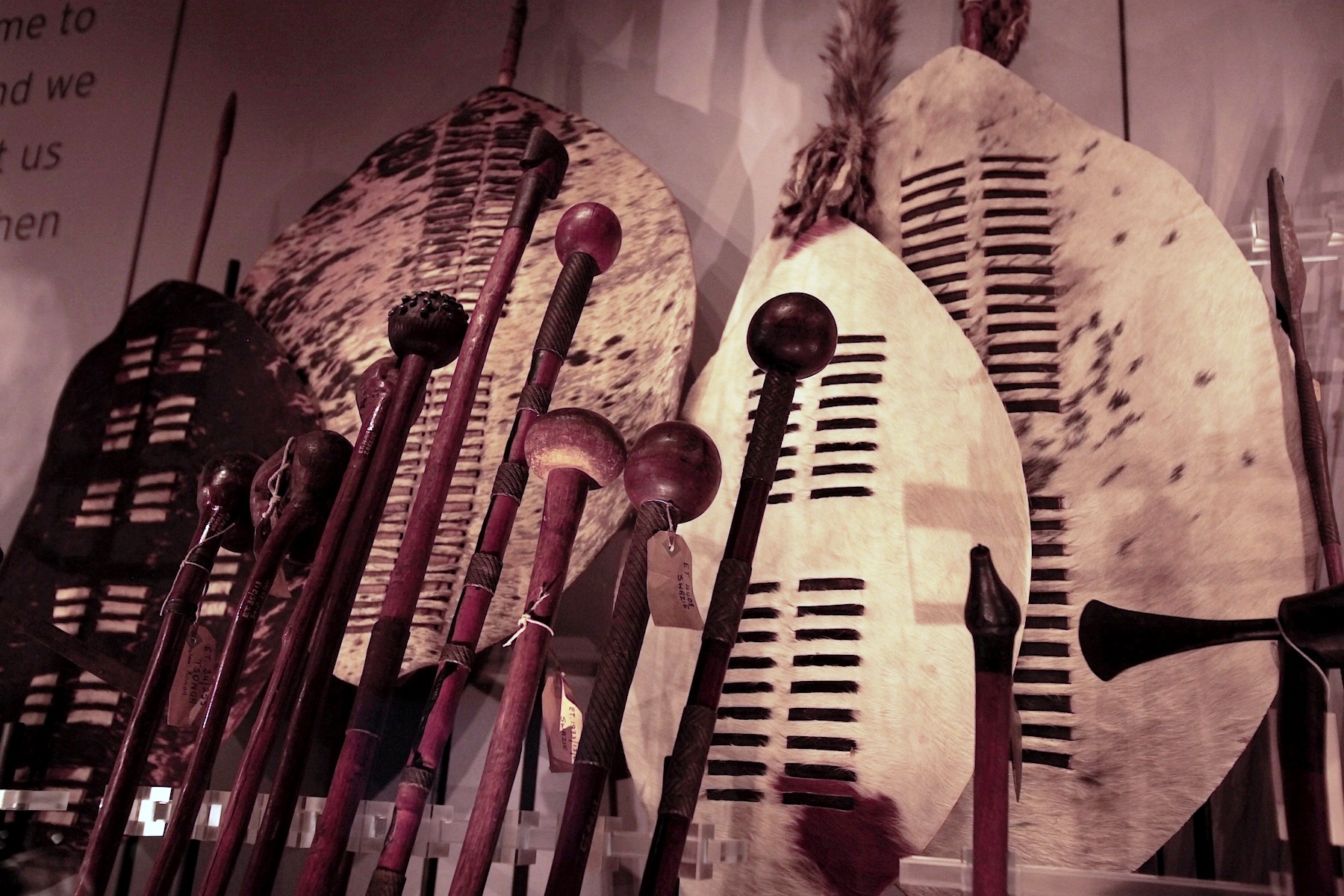
Knobkerrie
A knobkerrie, also spelled knobkerry, knobkierie, and knopkierie (Afrikaans), is a form of wooden club, used mainly in Southern Africa and Eastern Africa. Typically they have a large knob at one end and can be used for clubbing an enemy's head. For the various peoples who use them, they often have marked cultural significance. Being able to carry the knobkerrie has also had a political dimension, especially in South Africa. Name The name derives from the Afrikaans word ''knop'', meaning ''knob'' or ''ball'' and the Khoekhoe or San word ''kirri'', meaning walking stick. The name has been extended to similar weapons used by the native peoples of Australia, the Pacific islands, and other places, and was also used in the British army. Uses in southern Africa and abroad Knobkerries were an indispensable weapon of war both in Africa and abroad. In Africa, the weapon found particular use among Nguni peoples. Among the Zulu people they are known as ''iwisa.'' The iwisa was not typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyena
Hyenas or hyaenas ( ; from Ancient Greek , ) are feliform carnivoran mammals belonging to the family Hyaenidae (). With just four extant species (each in its own genus), it is the fifth-smallest family in the order Carnivora and one of the smallest in the class Mammalia. Despite their low diversity, hyenas are unique and vital components of most African ecosystems. Although phylogenetically closer to felines and viverrids, hyenas are behaviourally and morphologically similar to canids in several elements due to convergent evolution: both hyenas and canines are non-arboreal, cursorial hunters that catch prey with their teeth rather than claws. Both eat food quickly and may store it, and their calloused feet with large, blunt, nonretractable claws are adapted for running and making sharp turns. However, hyenas' grooming, scent marking, defecation habits, mating, and parental behavior are consistent with the behavior of other feliforms. Hyenas feature prominently in the fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |