|
Tusmore, Oxfordshire
Tusmore is a settlement in the civil parish of Hardwick with Tusmore, in the Cherwell (district), Cherwell district, in Oxfordshire, England, about north of Bicester. It is the location of the Tusmore English country house, country house and estate. In 1931 the parish had a population of 82. On 1 April 1932 the parish was abolished and merged with Hardwick, Cherwell, Hardwick to form "Hardwick with Tusmore". Manor Tusmore was settled in Anglo-Saxon England, Saxon times. The Toponymy, toponym comes from Old English, either ''Thures mere'' ("Thur's pool") or ''Þyrsmere'' ("a lake haunted by a giant or demon"). The Domesday Book records that in 1086 the Manorialism, manor of Tusmore belonged to Walter Giffard, 1st Earl of Buckingham, Walter Giffard, 1st Earl of Buckingham. By the early part of the 14th century Tusmore was the poorest village in the Ploughley Hundred (country subdivision)#England, Hundred. Thereafter it was depopulated by the Black Death. By 1358 the village had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Whitfield (architect)
Sir William Whitfield (21 October 1920 – 16 March 2019) was a British architect and town planner. Early life Whitfield was born in Stockton-on-Tees into a coal-owning family and studied architecture at King's College, Newcastle (later the Newcastle University School of Architecture, Planning and Landscape), where he was admitted by a special dispensation at the unusually early age of 15, and where he later studied Town Planning after the Second World War. Career Whitfield designed the Glasgow University Library (1968) and the Hunterian Museum and Art Gallery Extension at the University of Glasgow (1962–81), as well as an extension to the Newcastle University Students' Union building (1964) and University Theatre (now unrecognisable and called the Northern Stage). He designed the business school and the science library at Durham University (both now extended) as well as the departments of geography and psychology, and was a co-author of the 1969 development plan for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
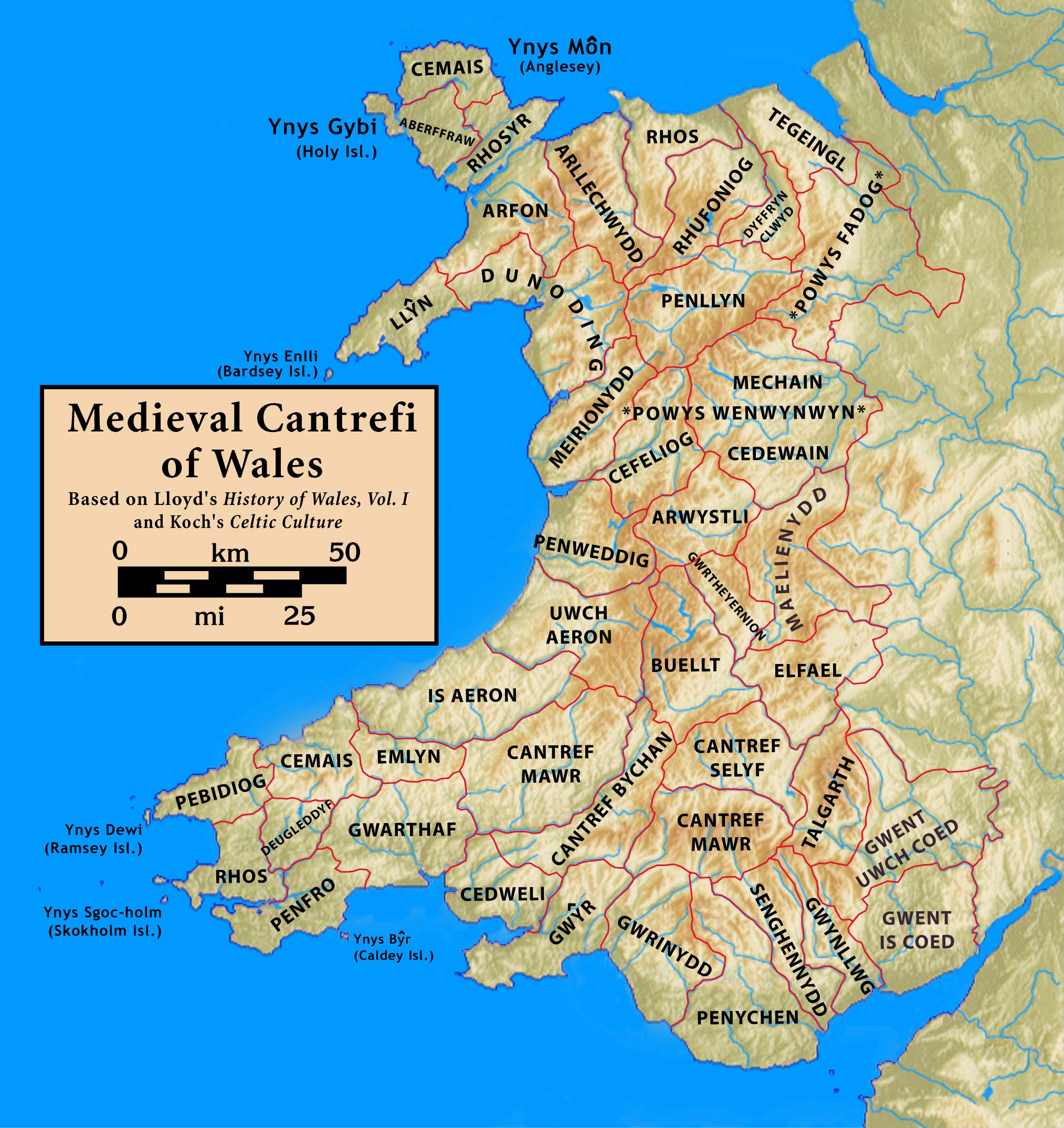
Hundred (country Subdivision)
A hundred is an administrative division that is geographically part of a larger region. It was formerly used in England, Wales, some parts of the United States, Denmark, Sweden, Finland, Norway, and in Cumberland County, New South Wales, Cumberland County in the British Colony of New South Wales. It is still used in other places, including in Australia (in South Australia and the Northern Territory). Other terms for the hundred in English and other languages include ''#wapentake, wapentake'', ''herred'' (Danish and Bokmål, Bokmål Norwegian), ''herad'' (Nynorsk, Nynorsk Norwegian), ''härad'' or ''hundare'' (Swedish), ''Harde'' (German), ''hiird'' (North Frisian language, North Frisian), ''kihlakunta'' (Finnish), and ''cantref'' (Welsh). In Ireland, a similar subdivision of counties is referred to as a Barony (Ireland), barony, and a hundred is a subdivision of a particularly large townland (most townlands are not divided into hundreds). Etymology The origin of the division of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholic Relief Act 1791
The Roman Catholic Relief Act 1791 ( 31 Geo. 3. c. 32) is an act of the Parliament of Great Britain passed in 1791 relieving Roman Catholics of certain political, educational, and economic disabilities. It admitted them to the practice of law, permitted the exercise of their religion, and the existence of their schools. On the other hand, chapels, schools, officiating priests and teachers were to be registered, assemblies with locked doors, as well as steeples and bells to chapels, were forbidden; priests were not to wear vestments or celebrate liturgies in the open air; children of Protestants were not to be admitted to the schools; monastic orders and endowments of schools and colleges were prohibited. The sentiment for reform was helped along by the signing of the Edict of Versailles in France in 1787, whereby non-Catholic French subjects were given full legal status in a kingdom where Catholicism had always been the state religion. Terms The act was significantly grea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Reformation
The English Reformation began in 16th-century England when the Church of England broke away first from the authority of the pope and bishops Oath_of_Supremacy, over the King and then from some doctrines and practices of the Catholic Church. These events were part of the wider European Reformation: various religious and political movements that affected both the practice of Christianity in Western Europe, Western and Central Europe and relations between church and state. The English Reformation began as more of a political affair than a theological dispute. In 1527 Henry VIII requested an annulment of his marriage, but Pope Clement VII refused. In response, the English Reformation Parliament, Reformation Parliament (1529–1536) passed laws abolishing papal authority in England and declared Henry to be Supreme Head of the Church of England, head of the Church of England. Final authority in doctrinal disputes now rested with the monarch. Though a religious traditionalist hims ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.Gerald O'Collins, O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 Catholic particular churches and liturgical rites#Churches, ''sui iuris'' (autonomous) churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and Eparchy, eparchies List of Catholic dioceses (structured view), around the world, each overseen by one or more Bishops in the Catholic Church, bishops. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the Papal supremacy, chief pastor of the church. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recusancy
Recusancy (from ) was the state of those who remained loyal to the Catholic Church and refused to attend Church of England services after the English Reformation. The 1558 Recusancy Acts passed in the reign of Elizabeth I, and temporarily repealed in the Interregnum (1649–1660), remained on the statute books until 1888. They imposed punishments such as fines, property confiscation and imprisonment on recusants. The suspension under Oliver Cromwell was mainly intended to give relief to Nonconformist Protestants rather than to Catholics, to whom some restrictions applied into the 1920s, through the Act of Settlement 1701, despite the 1828–1829 Catholic emancipation. In some cases those adhering to Catholicism faced capital punishment, and some English and Welsh Catholics who were executed in the 16th and 17th centuries have been canonised by the Catholic Church as martyrs of the English Reformation. Today, ''recusant'' applies to the descendants of Catholic families of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benefice
A benefice () or living is a reward received in exchange for services rendered and as a retainer for future services. The Roman Empire used the Latin term as a benefit to an individual from the Empire for services rendered. Its use was adopted by the Western Church in the Carolingian era as a benefit bestowed by the crown or church officials. A benefice specifically from a church is called a precaria (pl. ''precariae''), such as a stipend, and one from a monarch or nobleman is usually called a fief. A benefice is distinct from an allod, in that an allod is property owned outright, not bestowed by a higher authority. Catholic Church Roman imperial origins In ancient Rome a ''benefice'' was a gift of land ( precaria) for life as a reward for services rendered, originally, to the state. The word comes from the Latin noun ''beneficium'', meaning "benefit". Carolingian era In the 8th century, using their position as Mayor of the Palace, Charles Martel, Carloman I and Pepin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parish Church
A parish church (or parochial church) in Christianity is the Church (building), church which acts as the religious centre of a parish. In many parts of the world, especially in rural areas, the parish church may play a significant role in community activities, often allowing its premises to be used for non-religious community events. The Church architecture, church building reflects this status, and there is considerable variety in the size and style of parish churches. Many villages in Europe have churches that date back to the Middle Ages, but all periods of architecture are represented. Catholic Church Each diocese (administrative unit, headed by a bishop) is divided into parishes. Normally, a parish consists of all Catholics living within its geographically defined area. Within a diocese, there can also be overlapping parishes for Catholics belonging to a particular rite, language, nationality, or community. Each parish has its own central church called the parish church, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wafic Saïd
Wafic Rida Saïd () (born 21 December 1939) is a Syrian-Saudi-Canadian businessman, financier, and philanthropist who has resided for many years in Monaco.David Pallister, 'The man of substance in the shadows', ''The Guardian'', London, 22 May 1992, pg. 25 Saïd lived in Syria, the country of his birth, until his early twenties, when he left for Switzerland and worked as a banker, before making his fortune in the Saudi Arabian construction industry in the 1970s. He came to public prominence after helping facilitate the Al-Yamamah arms deal between the United Kingdom and Saudi Arabia in the 1980s. He established the Saïd Foundation in 1982 and the Saïd Business School at the University of Oxford in 1996 with an initial £20 million donation. Saïd owns several properties worldwide, including Tusmore Park in Oxfordshire. He is a Foundation Fellow of Somerville College, Oxford. Biography Saïd was born in Damascus, Syria, in 1939 to a prominent Syrian family. Saïd's gran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vivian Smith, 1st Baron Bicester
Vivian Hugh Smith, 1st Baron Bicester (9 December 1867 – 17 February 1956), was a British merchant banker. Early life Vivian Hugh Smith was born on 9 December 1867. He was the elder son of Hugh Colin Smith (son of John Abel Smith and Governor of the Bank of England from 1897 to 1899) and Constance Maria Josepha (née Adeane). He was educated at Eton College and Trinity College, Cambridge. His brother Aubrey followed the different path of joining the Royal Navy at the age of eleven and later rose to be an admiral. Career Smith served as the Chairman of Yule Catto & Company Ltd (present-day Synthomer), Governor of the Royal Exchange Assurance Corporation from 1914 to 1956, and a Director of Morgan Grenfell & Co. Between 1934 and 1956, he also held the honorary position of Lord Lieutenant of Oxfordshire. On 29 June 1938, Smith was raised to the peerage as Baron Bicester, of Tusmore in the County of Oxford. Personal life In 1897, Smith was married to Lady Sybil Mary Mc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earl Of Effingham
Earl of Effingham, in the County of Surrey, is a title in the Peerage of the United Kingdom, created in 1837 for Kenneth Howard, 11th Baron Howard of Effingham, named after the village of Effingham, Surrey, where heads of the family owned the manor. This branch of the House of Howard stems from the naval commander and statesman Lord William Howard, senior son of Thomas Howard, 2nd Duke of Norfolk from his second marriage to Agnes Tylney. William served as Lord High Admiral of England, as Lord Chamberlain of the Household and as Lord Privy Seal. In 1554 he was created Baron Howard of Effingham in the Peerage of England after leading the defence of London against Wyatt's rebellion. His son and successor was better known to history as Charles Howard, 1st Earl of Nottingham, after being granted that title in 1596. He was Lord High Admiral from 1585 to 1618 and served as commander-in-chief of the English fleet against the Spanish Armada in 1588. In 1603 his eldest son and heir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Howard, 2nd Earl Of Effingham
Henry Howard, 2nd Earl of Effingham, DL (23 August 1806 – 5 February 1889), styled Lord Howard from 1837 to 1845, was a British peer and Member of Parliament. Early life Howard was the eldest son of General Kenneth Howard, 1st Earl of Effingham, from his first marriage to Lady Charlotte Primrose, daughter of Neil Primrose, 3rd Earl of Rosebery. He was educated at Harrow. Career Howard was commissioned an ensign in the 58th (Rutlandshire) Regiment of Foot on 21 July 1825, and a lieutenant on 14 May 1826. On 9 November 1830, he became a captain in the 10th (North Lincoln) Regiment of Foot, resigning his commission on 29 November 1833. He was elected to the House of Commons for Shaftesbury in 1841, a seat he held until 1845, when he succeeded his father in the earldom and entered the House of Lords. On 17 February 1845, he was appointed a deputy lieutenant of Wiltshire, and on 14 March 1853, a deputy lieutenant of the West Riding of Yorkshire. Personal life In 1832, Lord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |