|
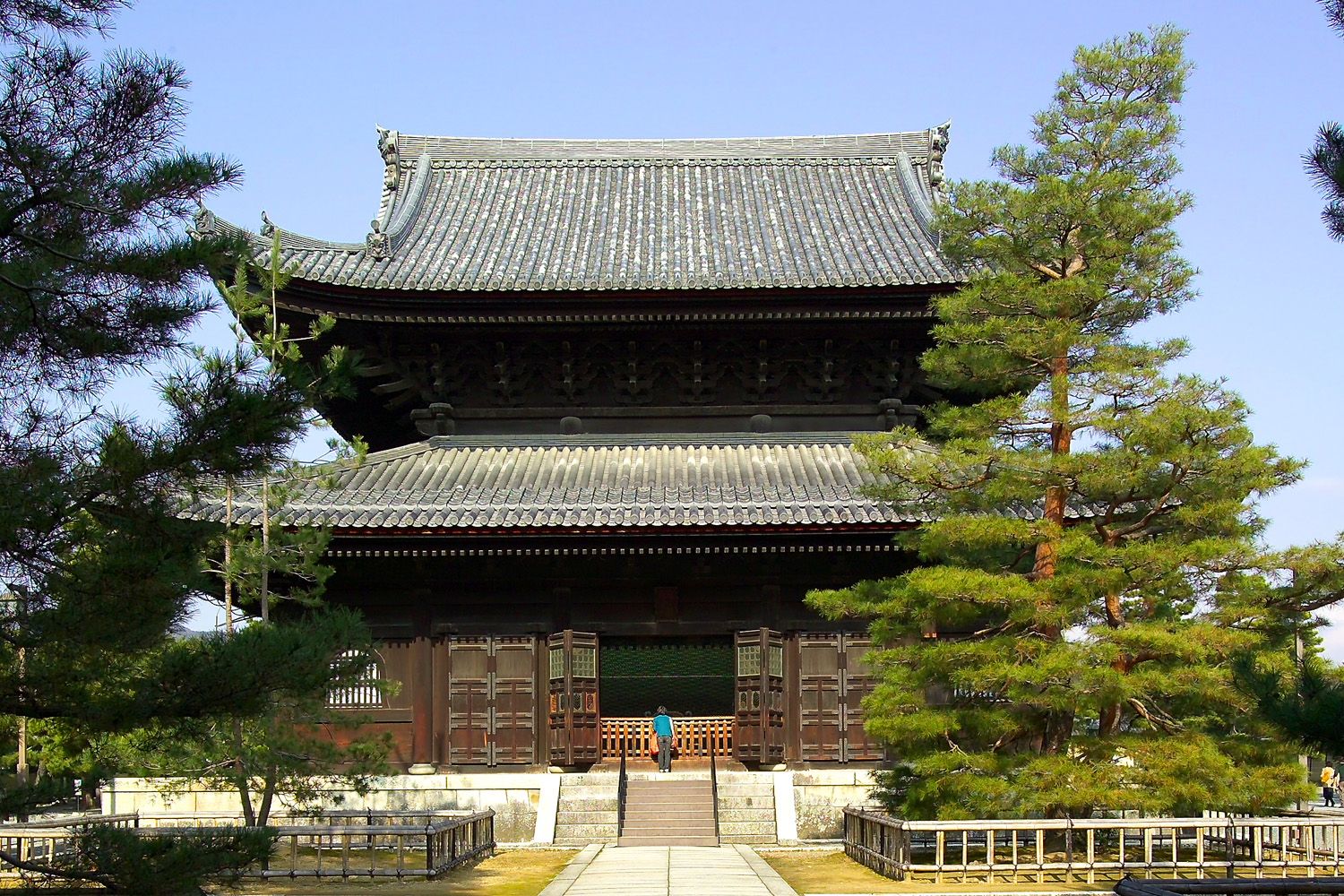
Tōfuku-ji Temples
is a Buddhist temple in Higashiyama-ku, Kyoto, Higashiyama-ku in Kyoto, Japan. Tōfuku-ji takes its name from two temples in Nara, Nara, Nara, Tōdai-ji and Kōfuku-ji.Japan ReferenceTōfuku-ji/ref> It is one of the Five Mountain System, Kyoto ''Gozan'' or "five great Zen temples of Kyoto". Its honorary ''Buddhist temples in Japan#sangō, sangō'' prefix is . History Tōfuku-ji was founded in 1236 by the imperial chancellor Kujō Michiie. He appointed the monk Enni as founding priest, who had studied Rinzai school, Rinzai Zen Buddhism in China under the monk Wuzhun Shifan and who founded Jōten-ji temple in Hakata upon his return to his homeland. Tōfuku-ji temple burned down but was rebuilt in the 15th century according to original plans. It was because of this fire damage that a merchant ship was sent to Yuan China to replace damaged artifacts and to obtain special construction materials. The ship, however that later became known as the Shinan ship sank on her return jour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Main Hall (Japanese Buddhism)
Main hall or Main Temple is the building within a Japanese Buddhist monastery compound ('' garan'') which enshrines the main object of veneration.Kōjien Japanese dictionary Because the various denominations deliberately use different terms, this single English term translates several Japanese words, among them ''butsuden'', ''butsu-dō'', ''kondō'', ''konpon-chūdō'', and ''hondō''. ''Hondō'' is its exact Japanese equivalent, while the others are more specialized words used by particular sects or for edifices having a particular structure. Kondō (Asuka and Nara periods) The term started to be used during the Asuka and Nara periods. A ''kondō'' is the centerpiece of an ancient Buddhist temple's ''garan'' in Japan. The origin of the name is uncertain, but it may derive from the perceived preciousness of its content, or from the fact that the interior was lined with gold. This is the name used by the oldest temples in the country.Iwanami Nihonshi Jiten A ''kondō'', for exa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chancellor
Chancellor () is a title of various official positions in the governments of many countries. The original chancellors were the of Roman courts of justice—ushers, who sat at the (lattice work screens) of a basilica (court hall), which separated the judge and counsel from the audience. A chancellor's office is called a chancellery or chancery. The word is now used in the titles of many various officers in various settings (government, education, religion). Nowadays the term is most often used to describe: *The head of the government *A person in charge of foreign affairs *A person with duties related to justice *A person in charge of financial and economic issues *The head of a university Governmental positions Head of government Austria The Chancellor of Austria ('), is the head of the Government of Austria. Since 2025, the Chancellor of Austria is Christian Stocker. Germany The Chancellor of Germany (') is the head of government in Germany. In German politics, the ' is e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
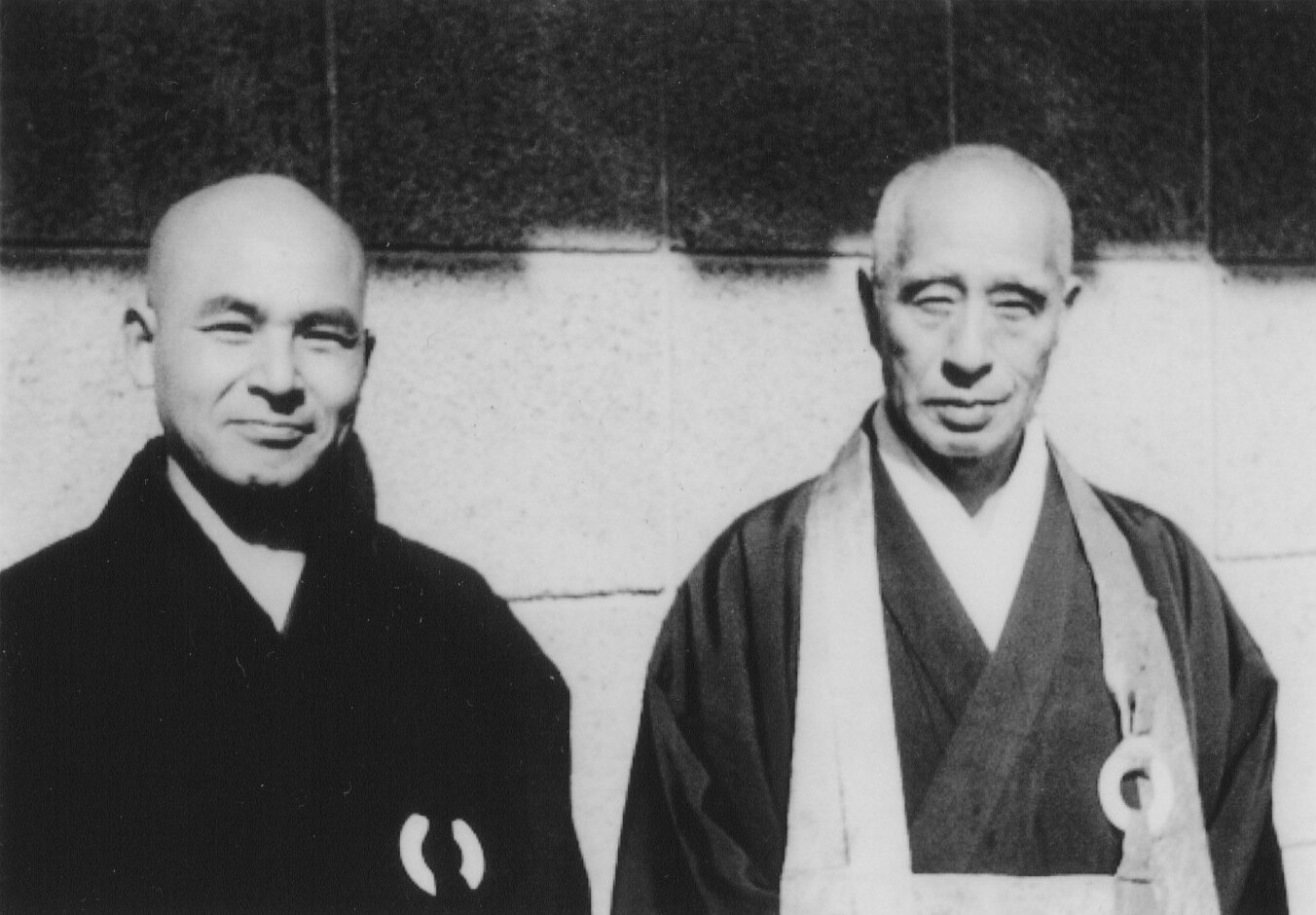
Keido Fukushima
Keidō Fukushima (福島 慶道, Rōmaji: Fukushima Keidō, March 1, 1933 – March 1, 2011) was a Japanese Rinzai Zen master, head abbot of Tōfuku-ji (one of the main branches of the Rinzai sect), centered in Kyoto, Japan. Because of openness to teaching Western students, he had considerable influence on the development of Rinzai Zen practice in the West. Biography Zen studies Fukushima became an acolyte monk at the age of thirteen under his original teacher Kidō Okada, abbot of Hōfuku-ji monastery in Okayama, Japan. Fukushima graduated from Otani University's Department of Buddhist Studies in 1956, following completion of Otani's doctoral course. In 1961 he began monastic training with Zenkei Shibayama at Nanzen-ji Monastery in Kyoto. Fukushima's main teacher, Zenkei Shibayama, was instrumental in helping to transplant Rinzai Zen to the West. He was one of the first Rinzai Zen masters to hold retreats in the United States, and to publish books in English: ''A Flower Does ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankokuji Ekei
was a military monk and descendant of the Takeda clan of Aki province. He served the Mōri clan and later the Toyotomi clan. Biography Although it is certain that he was from the Aki Takeda clan, there are various theories about his birth year and father, and the former is said to have been in 1537 or 1539. There are two theories about the father: one says that Takeda Nobushige († 1541) was his father, and the other says that Takeda Shigekiyo († 1541), the father of Nobushige, was his father. In 1541, when the Aki Takeda were destroyed by Mori Motonari, he was taken away by faithful vassals and put in a safe place in Ankokuji Temple in Aki Province. He became a Rinzai Buddhist monk, and a diplomat of Mōri clan. In 1582, during the Siege of Takamatsu, Mori sent Ekei to Kuroda Kanbei, offering peace negotiations with Hideyoshi. In 1585, he was praised by Toyotomi Hideyoshi for his negotiation when the Mori clan formally served Hideyoshi, and become a close adviser of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ryōan Keigo
was a Japanese Zen Buddhist monk and diplomat in the Muromachi period.Goodrich, L. Carrington ''et al.'' (1976) ''Dictionary of Ming biography, 1368-1644,'' Vol. II, pp. 1149-1150./ref> He was the chief envoy of a 1511–1513 mission sent by the Ashikaga shogunate to the court of the Zhengde Emperor in Beijing. Tofuku-ji abbot In 1486, the Rinzai monk Keigo was the 171st abbot of the Tofuku-ji monastery when the honorific title "Ryōan" was conferred by Emperor Go-Tsuchimikado. He was already considered famous when he was designated by Ashikaga Yoshizumi to lead the 1511 mission to China;Goodrich pp. 1231-1232./ref> and Yoshizumi conferred the further honorific title "Butsunichi Zenji," perhaps with the intention of impressing the Chinese. Mission to China The economic benefit of the Sinocentric tribute system was profitable trade. The tally trade (''kangō bōeki'' or ''kanhe maoyi'' in Chinese) involved exchanges of Japanese products for Chinese goods. The Chinese "t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prisoner-of-war Camp
A prisoner-of-war camp (often abbreviated as POW camp) is a site for the containment of enemy fighters captured as Prisoner of war, prisoners of war by a belligerent power in time of war. There are significant differences among POW camps, internment camps, and military prisons. Purpose-built prisoner-of-war camps appeared at Norman Cross Prison, Norman Cross in England in 1797 during the French Revolutionary Wars and HM Prison Dartmoor, constructed during the Napoleonic Wars, and they have been in use in all the main conflicts of the last 200 years. The main camps are used for marines, sailors, soldiers, and more recently, airmen of an enemy power who have been captured by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. Civilians, such as Merchant navy, merchant mariners and war correspondents, have also been imprisoned in some conflicts. Per the Geneva Convention on Prisoners of War (1929), 1929 Geneva Convention on Prisoners of War, later superseded by the T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War (8 February 1904 – 5 September 1905) was fought between the Russian Empire and the Empire of Japan over rival imperial ambitions in Manchuria and the Korean Empire. The major land battles of the war were fought on the Liaodong Peninsula and near Shenyang, Mukden in Southern Manchuria, with naval battles taking place in the Yellow Sea and the Sea of Japan. Russia had pursued an expansionist policy in Siberia and the Russian Far East, Far East since the reign of Ivan the Terrible in the 16th century. At the end of the First Sino-Japanese War, the Treaty of Shimonoseki of 1895 had ceded the Liaodong Peninsula and Lüshun Port, Port Arthur to Japan before the Triple Intervention, in which Russia, Germany, and France forced Japan to relinquish its claim. Japan feared that Russia would impede its plans to establish a sphere of influence in mainland Asia, especially as Russia built the Trans-Siberian Railway, Trans-Siberian Railroad, began making inroads in K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shinbutsu Bunri
The Japanese term indicates the separation of Shinto from Buddhism, introduced after the Meiji Restoration which separated Shinto ''kami'' from buddhas, and also Buddhist temples from Shinto shrines, which were originally amalgamated. It is a yojijukugo phrase. Background before 1868 Until the end of the Edo period, in 1868, Shinto and Buddhism were intimately connected in what was called ''shinbutsu-shūgō'' (神仏習合), to the point that the same buildings were often used as both Shinto shrines and Buddhist temples, and Shinto gods were interpreted as manifestations of Buddhas. However, the tendency to oppose Buddhism as a foreign import and to uphold Shinto as the native religion can be seen already during the early modern era, partly as a nationalistic reaction.. In a broad sense, the term ''shinbutsu bunri'' indicates the effects of the anti-Buddhist movement that, from the middle of the Edo period onwards, accompanied the spread of Confucianism, the growth of stud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiji (era)
The was an era of Japanese history that extended from October 23, 1868, to July 30, 1912. The Meiji era was the first half of the Empire of Japan, when the Japanese people moved from being an isolated feudal society at risk of colonization by Western powers to the new paradigm of a modern, industrialized nation state and emergent great power, influenced by Western scientific, technological, philosophical, political, legal, and aesthetic ideas. As a result of such wholesale adoption of radically different ideas, the changes to Japan were profound, and affected its social structure, internal politics, economy, military, and foreign relations. The period corresponded to the reign of Emperor Meiji. It was preceded by the Keiō era and was succeeded by the Taishō era, upon the accession of Emperor Taishō. The rapid modernization during the Meiji era was not without its opponents, as the rapid changes to society caused many disaffected traditionalists from the former samu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhejiang Province
) , translit_lang1_type2 = , translit_lang1_info2 = ( Hangzhounese) ( Ningbonese) (Wenzhounese) , image_skyline = 玉甑峰全貌 - panoramio.jpg , image_caption = View of the Yandang Mountains , image_map = Zhejiang in China (+all claims hatched).svg , mapsize = 275px , map_caption = Location of Zhejiang in China , coordinates = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = China , named_for = Old name of Qiantang River , seat_type = Capital and largest city , seat = Hangzhou , established_title = Annexation by the Qin dynasty , established_date = 222 BC , established_title2 = Jiangnandong Circuit , established_date2 = 626 , established_title3 = Liangzhe Circuit , established_date3 = 997 , established_title4 = Zhejiang Province formed , established_date4 = 1368 , established_title5 = Republican Period , established_date5 = 1 January 1912 , established_title6 = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shinan Ship
The Shinan ship (also spelled "Sinan") was a 14th-century Chinese ship that sank near what are today the Shinan islands, South Korea, around the year 1323, and was discovered in 1975. It was likely to have been part of a trade fleet between Port Ningbo, Yuan dynasty China and Port Hakata, Kamakura shogunate of Japan. It has been excavated during several maritime archaeological expeditions from 1976 to 1984. Its excavation has been described as "the first underwater excavation" in South Korea leading to "the advent of underwater archaeology in the history of Korean archaeology". Much of the ship's cargo survived mostly intact, and due to the overwhelming amount of Chinese treasures contained in the ship (over 28 tons of Chinese coins and over 20,000 pieces of Chinese ceramics), in the early 1990s the shipwreck was also described as possibly "the richest ancient shipwreck yet discovered". Discovery and excavation On August 25, 1975, a South Korean fishing boat recovered sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
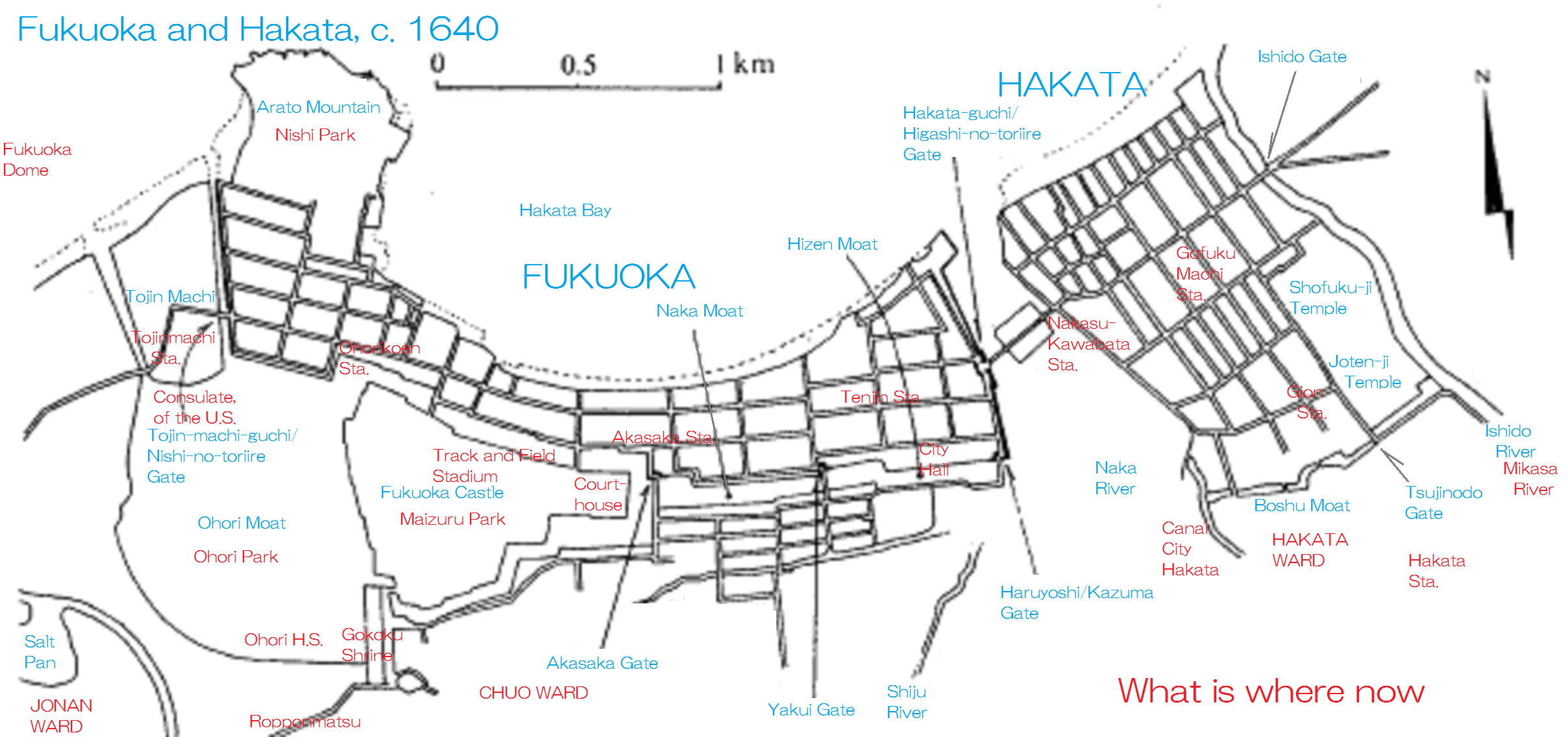
Hakata
is a ward of the city of Fukuoka in Fukuoka Prefecture, Japan. Many of Fukuoka Prefecture and Fukuoka City's principal government, commercial, retail and entertainment establishments are located in the district. Hakata-ku is also the location of Fukuoka's main train station, Hakata Station, Fukuoka Airport and the Hakata Port international passenger ship terminal. Geography Hakata-ku is a ward of Fukuoka City located on its eastern edge. It covers an area of 31.47 km2 with a population of 206,629 (as of January 1, 2009). Much of the ward consists of low-lying plains beside the . The northwestern end of the ward faces Hakata Bay, which includes both ferry and international cruise ship terminals . The northeast end of the ward is slightly elevated, and is named , with nearby Fukuoka Airport. Around Hakata Station is downtown; is the main dining and entertainment district of the ward along the . Hakata-ku also houses the Fukuoka Prefectural office. Economy Many Japanes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |