|
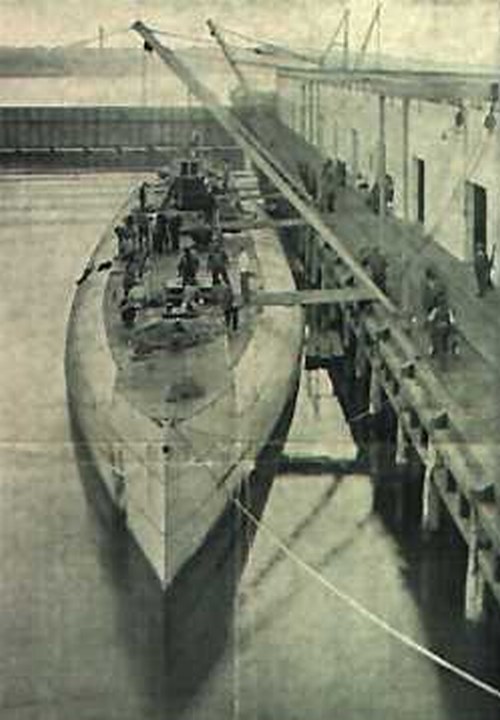
Type U 139 Submarine
U-139, originally designated "Project 46", was a class of large, long-range U-boats built during World War I by the Kaiserliche Marine. Description Three large U-cruisers, designated Type 139, were ordered from Germaniawerft of Kiel, in August 1916. Displacing nearly 2,000 tons, and with a surface speed of , they were armed with 24 torpedoes and two 15 cm deck guns, and had a cruising range of around . They carried a large enough complement to furnish captured vessels with prize crews and their intended purpose was to capture or destroy merchant ships on the surface; their large-calibre deck guns and comparatively high speed allowed them to engage even armed merchant vessels. Unlike the earlier Type U-151 submarines (originally designed as merchant submarines to evade naval blockades), the Type 139 was designed from the outset for combat service. Four bow and two stern torpedo tubes were fitted, but the main armament was the two 15 cm deck guns, which could be laid o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Krupp Germaniawerft
Friedrich Krupp Germaniawerft (often just called Germaniawerft, "Germania shipyard") was a German shipbuilding company, located in the harbour at Kiel, and one of the largest and most important builders of U-boats for the Kaiserliche Marine in World War I and the Kriegsmarine in World War II. The original company was founded in 1867 but went bankrupt and was bought out by Friedrich Krupp. Krupp was very interested in building warships and in the time before the First World War built a number of battleships for the Kaiserliche Marine, including , , , and . A total of 84 U-boats were built in the shipyard during the war. After the war it returned to the normal production of yachts and transports. History The company was founded in 1867 by Lloyd Foster, as the Norddeutsche Schiffbau-Gesellschaft, in the town of Gaarden, near Kiel. The idea of the company was to construct war and merchant ships. In 1876 the company built the personal yacht of Kaiser Wilhelm II, the . The company ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Displacement (ship)
The displacement or displacement tonnage of a ship is its weight. As the term indicates, it is measured indirectly, using Archimedes' principle, by first calculating the volume of water displaced by the ship, then converting that value into weight. Traditionally, various measurement rules have been in use, giving various measures in long tons. Today, tonnes are more commonly used. Ship displacement varies by a vessel's degree of load, from its empty weight as designed (known as "lightweight tonnage") to its maximum load. Numerous specific terms are used to describe varying levels of load and trim, detailed below. Ship displacement should not be confused with measurements of volume or capacity typically used for commercial vessels and measured by tonnage: net tonnage and gross tonnage. Calculation The process of determining a vessel's displacement begins with measuring its draft.George, 2005. p. 5. This is accomplished by means of its "draft marks". A merchant vessel has t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submarine Classes
A submarine (often shortened to sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. (It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability.) The term "submarine" is also sometimes used historically or informally to refer to remotely operated vehicles and robots, or to medium-sized or smaller vessels (such as the midget submarine and the wet sub). Submarines are referred to as ''boats'' rather than ''ships'' regardless of their size. Although experimental submarines had been built earlier, submarine design took off during the 19th century, and submarines were adopted by several navies. They were first used widely during World War I (1914–1918), and are now used in many navies, large and small. Their military uses include: attacking enemy surface ships (merchant and military) or other submarines; aircraft carrier protection; blockade running; nuclear deterrence; stealth operations in denied areas when gathering intelligence and doing reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penzance
Penzance ( ; ) is a town, civil parish and port in the Penwith district of Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is the westernmost major town in Cornwall and is about west-southwest of Plymouth and west-southwest of London. Situated in the shelter of Mount's Bay, the town faces south-east onto the English Channel, is bordered to the west by the fishing port of Newlyn, to the north by the civil parish of Madron and to the east by the civil parish of Ludgvan. The civil parish includes the town of Newlyn and the villages of Mousehole, Paul, Cornwall, Paul, Gulval, and Heamoor. Granted various royal charters from 1512 onwards and Incorporation (municipal government), incorporated on 9 May 1614, it has a population of 21,200 (2011 census). Penzance's former main street Chapel Street has a number of interesting features, including the Egyptian House, Penzance, Egyptian House, The Admiral Benbow public house (home to a real life 19th-century smuggling gang and allegedly the inspira ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship Commissioning
Ship commissioning is the act or ceremony of placing a ship in active service and may be regarded as a particular application of the general concepts and practices of project commissioning. The term is most commonly applied to placing a warship in active duty with its country's military forces. The ceremonies involved are often rooted in centuries-old naval tradition. Ship naming and launching endow a ship hull with her identity, but many milestones remain before it is completed and considered ready to be designated a commissioned ship. The engineering plant, weapon and Electronics, electronic systems, Galley (kitchen), galley, and other equipment required to transform the new hull into an operating and habitable warship are installed and tested. The prospective commanding officer, ship's officers, the petty officers, and seamen who will form the crew report for training and familiarization with their new ship. Before commissioning, the new ship undergoes sea trials to identify a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walther Schwieger
Kapitänleutnant Wilhelm Otto Walther Schwieger (7 April 1885 – 5 September 1917) was a German military officer. He was a U-boat commander in the Imperial German Navy (''Kaiserliche Marine'') during First World War. In 1915, he sank the passenger liner with the loss of 1,199 lives. Military career In 1903, he joined the Imperial German Navy and from 1911 onwards he served with the U-boat Service. In 1912, he took over the command of the . After the outbreak of World War I in 1914 he was promoted to ''Kapitänleutnant'' and given command of the . As a submarine captain, Schwieger has been noted for his cavalier approach to attacking without being sure about the identity or nationality of his target, sometimes in breach of orders to the contrary. His policy has been described as 'shoot first and ask questions later'. On 1 February 1915, he attacked the hospital ship HMHS Asturias, but the attack failed. On 7 May 1915, Schwieger was responsible for the ''U-20'' sinking pass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lothar Von Arnauld De La Perière
'' Vizeadmiral'' Lothar von Arnauld de la Perière (; 18 March 1886 – 24 February 1941), born in Posen, Prussia, and of French-German descent, was a German U-boat commander during World War I. With 194 ships and sunk, he is the most successful submarine captain ever. His victories came in the Mediterranean, almost always using his 8.8 cm deck gun. During his career, he fired 74 torpedoes, hitting 39 times. Arnauld de la Perière remained in the German Navy ('' Reichsmarine'') after the war ended. During World War II, he was recalled to active duty as a rear admiral, and was killed when his plane crashed on takeoff close to Le Bourget Airport near Paris in 1941. First World War Arnauld de la Perière entered the Kaiserliche Marine in 1903. After serving on the battleships , and , he served as torpedo officer on the light cruiser from 1911 to 1913. At the outbreak of the First World War, Arnauld de la Perière served as an adjutant to admiral Hugo von Pohl in Berli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equator
The equator is the circle of latitude that divides Earth into the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Southern Hemisphere, Southern Hemispheres of Earth, hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, about in circumference, halfway between the North Pole, North and South Pole, South poles. The term can also be used for any other celestial body that is roughly spherical. In three-dimensional space, spatial (3D) geometry, as applied in astronomy, the equator of a rotating spheroid (such as a planet) is the parallel (circle of latitude) at which latitude is defined to be 0°. It is an imaginary line on the spheroid, equidistant from its geographical pole, poles, dividing it into northern and southern hemispheres. In other words, it is the intersection of the spheroid with the plane (geometry), plane perpendicular to its axis of rotation and midway between its geographical poles. On and near the equator (on Earth), noontime sunlight appears almost directly o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Papiermark
The Papiermark (; 'paper mark') was a derisive term for the Mark (sign: ℳ︁) after it went off the gold standard, and most specifically with the era of hyperinflation in Germany of 1922 and 1923. Formally, the same German mark was used from 1871 to 1923. Like many countries, Germany departed the gold standard due to the outbreak of World War I, and stopped issuing gold coins backed in marks in August 1914. Precious metals rapidly disappeared from circulation, and inflation occurred as paper money was used to cover war debts in 1914 to 1918. Still, the papiermark is more associated with the early Weimar Republic era, when inflation grew out of control. By the time the mark was retired from circulation and renominated in December 1923, banknotes had amounts in the billions and trillions of marks by face value. History From 1914, the value of the mark fell. The rate of inflation rose following the end of World War I and reached its highest point in October 1923. The curre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Blockade
A navy, naval force, military maritime fleet, war navy, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It includes anything conducted by surface ships, amphibious ships, submarines, and seaborne aviation, as well as ancillary support, communications, training, and other fields. The strategic offensive role of a navy is projection of force into areas beyond a country's shores (for example, to protect sea-lanes, deter or confront piracy, ferry troops, or attack other navies, ports, or shore installations). The strategic defensive purpose of a navy is to frustrate seaborne projection-of-force by enemies. The strategic task of a navy also may incorporate nuclear deterrence by use of submarine-launched ballistic missiles. Naval operations can be broadly divided between riverine and littoral applications (brown-water n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merchant Submarine
A merchant submarine is a type of submarine intended for trade, and being without armaments, it is not considered a warship like most other types of submarines. The intended use would be blockade running, or to dive under Arctic ice. Strictly speaking, only two submarines have so far been purpose-built for non-military merchant shipping use, outside of criminal enterprises, though standard or partly converted military submarines have been used to transport smaller amounts of important cargo, especially during wartime, and large-scale proposals for modern merchant submarines have been produced by manufacturers. Criminal enterprises have also built transport submarines to avoid authorities, such as narcosubs. Germany Only two merchant submarines were built, both in Germany during World War I. They were constructed to slip through the naval blockade of the Entente Powers, mainly enforced by the efforts of the United Kingdom's Royal Navy. The British blockade had led to great di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Type U 151 Submarine
Type U 151 U-boats were a class of large, long-range submarines initially constructed during World War I to be merchant submarines and later used by the Kaiserliche Marine (Imperial German Navy). Background In addition to the cargo-carrying submarines and (disappeared on a cargo voyage in 1916 while it was still a merchant submarine), six further large cargo submarines were ordered, originally designed to ship material to and from locations otherwise denied German surface ships, such as the United States. On 16 December 1916, four under construction in the Reiherstieg Schiffswerfte & Maschinenfabrik, Reiherstieg and Flensburger Schiffbau yards were taken over by the navy and converted to military specification as Type U 151 U-boats, being designated to . The remaining two, along with ''Deutschland'', which became , passed into naval control in February 1917, as and . All were fitted with two bow torpedo tubes and could carry 18 torpedoes, with the exception of the former ''De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |