|
Type II Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes (T2D), formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue and unexplained weight loss. Other symptoms include increased hunger, having a sensation of pins and needles, and sores (wounds) that heal slowly. Symptoms often develop slowly. Long-term complications from high blood sugar include heart disease, stroke, diabetic retinopathy, which can result in blindness, kidney failure, and poor blood flow in the lower limbs, which may lead to amputations. A sudden onset of hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state may occur; however, ketoacidosis is uncommon. Type 2 diabetes primarily occurs as a result of obesity and lack of exercise. Some people are genetically more at risk than others. Type 2 diabetes makes up about 90% of cases of diabetes, with the other 10% due primar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocrinology
Endocrinology (from ''endocrine system, endocrine'' + ''wikt:-logy#Suffix, -ology'') is a branch of biology and medicine dealing with the endocrine system, its diseases, and its specific secretions known as hormones. It is also concerned with the integration of developmental events proliferation, growth, and differentiation, and the psychological or behavioral activities of metabolism, human development (biology), growth and development, tissue (biology), tissue function, sleep, digestion, Respiration (physiology), respiration, excretion, mood (psychology), mood, Stress (physiology), stress, lactation, Motor coordination, movement, reproduction, and sensory perception caused by hormones. Specializations include behavioral endocrinology and comparative endocrinology. The endocrine system consists of several glands, all in different parts of the body, that secrete hormones directly into the blood rather than into a Duct (anatomy), duct system. Therefore, endocrine glands are regarde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Healthy Diet
A healthy diet is a diet that maintains or improves overall health. A healthy diet provides the body with essential nutrition: fluid, macronutrients such as protein, micronutrients such as vitamins, and adequate fibre and food energy. A healthy diet may contain fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and may include little to no ultra-processed foods or sweetened beverages. The requirements for a healthy diet can be met from a variety of plant-based and animal-based foods, although additional sources of vitamin B12 are needed for those following a vegan diet. Various nutrition guides are published by medical and governmental institutions to educate individuals on what they should be eating to be healthy. Advertising may drive preferences towards unhealthy foods. To reverse this trend, consumers should be informed, motivated and empowered to choose healthy diets. Nutrition facts labels are also mandatory in some countries to allow consumers to choose between foods base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pins And Needles
Paresthesia is a sensation of the skin that may feel like numbness (''hypoesthesia''), tingling, pricking, chilling, or burning. It can be temporary or chronic and has many possible underlying causes. Paresthesia is usually painless and can occur anywhere on the body, but most commonly in the arms and legs. The most familiar kind of paresthesia is the sensation known as ''pins and needles'' after having a limb "fall asleep" (''obdormition''). A less common kind is formication, the sensation of insects crawling on the skin. Causes Transient Paresthesias of the hands, feet, legs, and arms are common transient symptoms. The briefest electric shock type of paresthesia can be caused by tweaking the ulnar nerve near the elbow; this phenomenon is colloquially known as bumping one's "funny bone". Similar brief shocks can be experienced when any other nerve is tweaked (e.g. a pinched neck nerve may cause a brief shock-like paresthesia toward the scalp). In the older age group, spinal c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatigue
Fatigue is a state of tiredness (which is not sleepiness), exhaustion or loss of energy. It is a signs and symptoms, symptom of any of various diseases; it is not a disease in itself. Fatigue (in the medical sense) is sometimes associated with medical conditions including autoimmune disease, organ failure, chronic pain conditions, mood disorders, heart disease, infectious diseases, and post-infectious-disease states. However, fatigue is complex and in up to a third of primary care cases no medical or psychiatric diagnosis is found. Fatigue (in the general usage sense of normal tiredness) often follows prolonged physical or mental activity. Physical fatigue results from muscle fatigue brought about by intense physical activity. Mental fatigue results from prolonged periods of Cognition, cognitive activity which impairs cognitive ability, can manifest as sleepiness, lethargy, or directed attention fatigue, and can also impair physical performance. Definition Fatigue in a medica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (''INS)'' gene. It is the main Anabolism, anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and protein by promoting the absorption of glucose from the blood into cells of the liver, fat cell, fat, and skeletal muscles. In these tissues the absorbed glucose is converted into either glycogen, via glycogenesis, or Fatty acid metabolism#Glycolytic end products are used in the conversion of carbohydrates into fatty acids, fats (triglycerides), via lipogenesis; in the liver, glucose is converted into both. Glucose production and secretion by the liver are strongly inhibited by high concentrations of insulin in the blood. Circulating insulin also affects the synthesis of proteins in a wide variety of tissues. It is thus an anabolic hormone, promoting the conversion of small molecules in the blood into large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance (IR) is a pathological response in which cells in insulin-sensitive tissues in the body fail to respond normally to the hormone insulin or downregulate insulin receptors in response to hyperinsulinemia. Insulin is a hormone that facilitates the transport of glucose from blood into cells, thereby reducing blood glucose (blood sugar). Insulin is released by the pancreas in response to carbohydrates consumed in the diet. In states of insulin resistance, the same amount of insulin does not have the same effect on glucose transport and blood sugar levels. There are many causes of insulin resistance and the underlying process is still not completely understood. Risk factors for insulin resistance include obesity, sedentary lifestyle, family history of diabetes, various health conditions, and certain medications. Insulin resistance is considered a component of the metabolic syndrome. Insulin resistance can be improved or reversed with lifestyle approaches, such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia is a condition where unusually high amount of glucose is present in blood. It is defined as blood glucose level exceeding 6.9 mmol/L (125 mg/dL) after fasting for 8 hours or 10 mmol/L (180 mg/dL) 2 hours after eating. Blood glucose level indication Patients with diabetes are oriented to avoid exceeding the recommended postprandial threshold of 160 mg/dL (8.89 mmol/L) for optimal glycemic control. Values of blood glucose higher than 160 mg/dL are classified as 'very high' hyperglycemia, a condition in which an excessive amount of glucose (glucotoxicity) circulates in the blood plasma. These values are higher than the renal threshold of 10 mmol/L (180 mg/dL) up to which glucose reabsorption is preserved at physiological rates and insulin therapy is not necessary. Blood glucose values higher than the cutoff level of 11.1 mmol/L (200 mg/dL) are used to diagnose T2DM and strongly associated with metabolic disturbances, although symp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained hyperglycemia, high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of the body becoming unresponsive to insulin's effects. Classic symptoms include polydipsia (excessive thirst), polyuria (excessive urination), polyphagia (excessive hunger), Weight loss#Unintentional, weight loss, and blurred vision. If left untreated, the disease can lead to various health complications, including disorders of the Cardiovascular disease, cardiovascular system, Diabetic retinopathy, eye, Diabetic nephropathy, kidney, and Diabetic neuropathy, nerves. Diabetes accounts for approximately 4.2 million deaths every year, with an estimated 1.5 million caused by either untreated or poorly treated diabetes. The major types of diabetes are Type 1 diabetes, type 1 and Type 2 diabetes, type 2. The most common treatment for ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
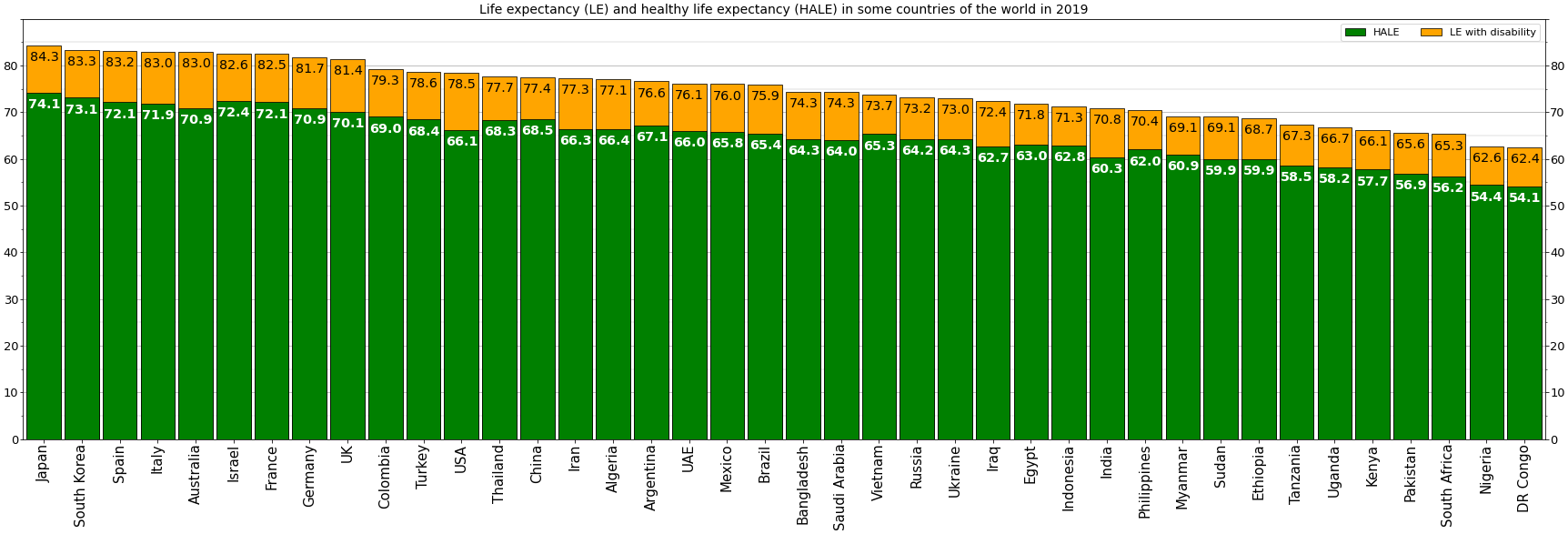
Life Expectancy
Human life expectancy is a statistical measure of the estimate of the average remaining years of life at a given age. The most commonly used measure is ''life expectancy at birth'' (LEB, or in demographic notation ''e''0, where ''e''x denotes the average life remaining at age ''x''). This can be defined in two ways. ''Cohort'' LEB is the mean length of life of a birth Cohort (statistics), cohort (in this case, all individuals born in a given year) and can be computed only for cohorts born so long ago that all their members have died. ''Period'' LEB is the mean length of life of a hypothetical cohort assumed to be exposed, from birth through death, to the mortality rates observed at a given year. National LEB figures reported by national agencies and international organizations for human populations are estimates of ''period'' LEB. Human remains from the early Bronze Age indicate an LEB of 24. In 2019, world LEB was 73.3. A combination of high infant mortality and d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric surgery (also known as metabolic surgery or weight loss surgery) is a surgical procedure used to manage obesity and obesity-related conditions. Long term weight loss with bariatric surgery may be achieved through alteration of gut hormones, physical reduction of stomach size (stomach reduction surgery), reduction of nutrient absorption, or a combination of these. Standard treatment, Standard of care procedures include Gastric bypass surgery#Variations, Roux en-Y bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, and Duodenal switch, biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch, from which weight loss is largely achieved by altering gut hormone levels responsible for hunger and satiety, leading to a new hormonal weight Set point theory, set point. In morbidly obese people, bariatric surgery is the most effective treatment for weight loss and reducing complications. A 2021 meta-analysis found that bariatric surgery was associated with reduction in Mortality rate, all-cause mortality among o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulin (medication)
As a medication, insulin is any pharmaceutical preparation of the protein hormone insulin that is used to treat high blood glucose. Such conditions include type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, gestational diabetes, and complications of diabetes such as diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic states. Insulin is also used along with glucose to treat hyperkalemia (high blood potassium levels). Typically it is given by injection under the skin, but some forms may also be used by injection into a vein or injection into a muscle, muscle. There are various types of insulin, suitable for various time spans. The types are often all called ''insulin'' in the broad word sense, sense, although in a more precise sense, insulin is identical to the naturally occurring molecule whereas insulin analogues have slightly different molecules that allow for modified time of action. It is on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metformin
Metformin, sold under the brand name Glucophage, among others, is the main first-line medication for the treatment of type2 diabetes, particularly in people who are overweight. It is also used in the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome, and is sometimes used as an off-label adjunct to lessen the risk of metabolic syndrome in people who take antipsychotic medication. It has been shown to inhibit inflammation, and is not associated with weight gain. Metformin is taken by mouth. Metformin is generally well tolerated. Common adverse effects include diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal pain. It has a small risk of causing low blood sugar. High blood lactic acid level (acidosis) is a concern if the medication is used in overly large doses or prescribed in people with severe kidney problems. Metformin is a biguanide anti- hyperglycemic agent. It works by decreasing glucose production in the liver, increasing the insulin sensitivity of body tissues, and increasing GDF15 s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |