|
Two Pass Verification
Two-pass verification, also called double data entry, is a data entry quality control method that was originally employed when data records were entered onto sequential 80-column Hollerith cards with a keypunch. In the first pass through a set of records, the data keystrokes were entered onto each card as the data entry operator typed them. On the second pass through the batch, an operator at a separate machine, called a ''verifier'', entered the same data. The verifier compared the second operator's keystrokes with the contents of the original card. If there were no differences, a verification notch was punched on the right edge of the card. The IBM 056 and 059 Card Verifiers were companion machines to the IBM 026 and 029 keypunches, respectively. The later IBM 129 keypunch also could operate as a verifier. In that mode, it read a completed card (record) and loaded the 80 keystrokes into a buffer. A data entry operator reentered the record and the keypunch compared the new keyst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Hollerith Card
A punched card (also punch card or punched-card) is a stiff paper-based medium used to store digital information via the presence or absence of holes in predefined positions. Developed over the 18th to 20th centuries, punched cards were widely used for data processing, the control of automated machines, and computing. Early applications included controlling weaving looms and recording census data. Punched cards were widely used in the 20th century, where unit record machines, organized into data processing systems, used punched cards for data input, data output, and data storage. The IBM 12-row/80-column punched card format came to dominate the industry. Many early digital computers used punched cards as the primary medium for input of both computer programs and data. Punched cards were used for decades before being replaced by magnetic storage and terminals. Their influence persists in cultural references, standardized data layouts, and computing conventions such as 80-cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Keypunch
A keypunch is a device for precisely punching holes into stiff paper cards at specific locations as determined by keys struck by a human operator. Other devices included here for that same function include the gang punch, the pantograph punch, and the stamp. The term was also used for similar machines used by humans to transcribe data onto punched tape media. For Jacquard looms, the resulting punched cards were joined together to form a paper tape, called a "chain", containing a Program (machine), program that, when read by a loom, directed its operation.Bell, T.F. (1895) '' Jacquard Weaving and Designing'', Longmans, Green And Co. For Unit record equipment, Hollerith machines and other Unit record equipment, unit record machines the resulting punched cards contained Data (computing), data to be processed by those machines. For computers equipped with a punched card input/output device the resulting punched cards were either data or programs directing the computer's operation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Therac 25
The Therac-25 is a computer-controlled radiation therapy machine produced by Atomic Energy of Canada Limited (AECL) in 1982 after the Therac-6 and Therac-20 units (the earlier units had been produced in partnership with of France). The Therac-25 was involved in at least six accidents between 1985 and 1987, in which some patients were given massive overdoses of radiation. Because of concurrent programming errors (also known as race conditions), it sometimes gave its patients radiation doses that were hundreds of times greater than normal, resulting in death or serious injury. These accidents highlighted the dangers of software control of safety-critical systems. The Therac-25 has become a standard case study in health informatics, software engineering, and computer ethics. It highlights the dangers of engineer overconfidence after the engineers dismissed user-end reports, leading to severe consequences. History The French company CGR, a subsidiary of Thomson-CSF, manu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
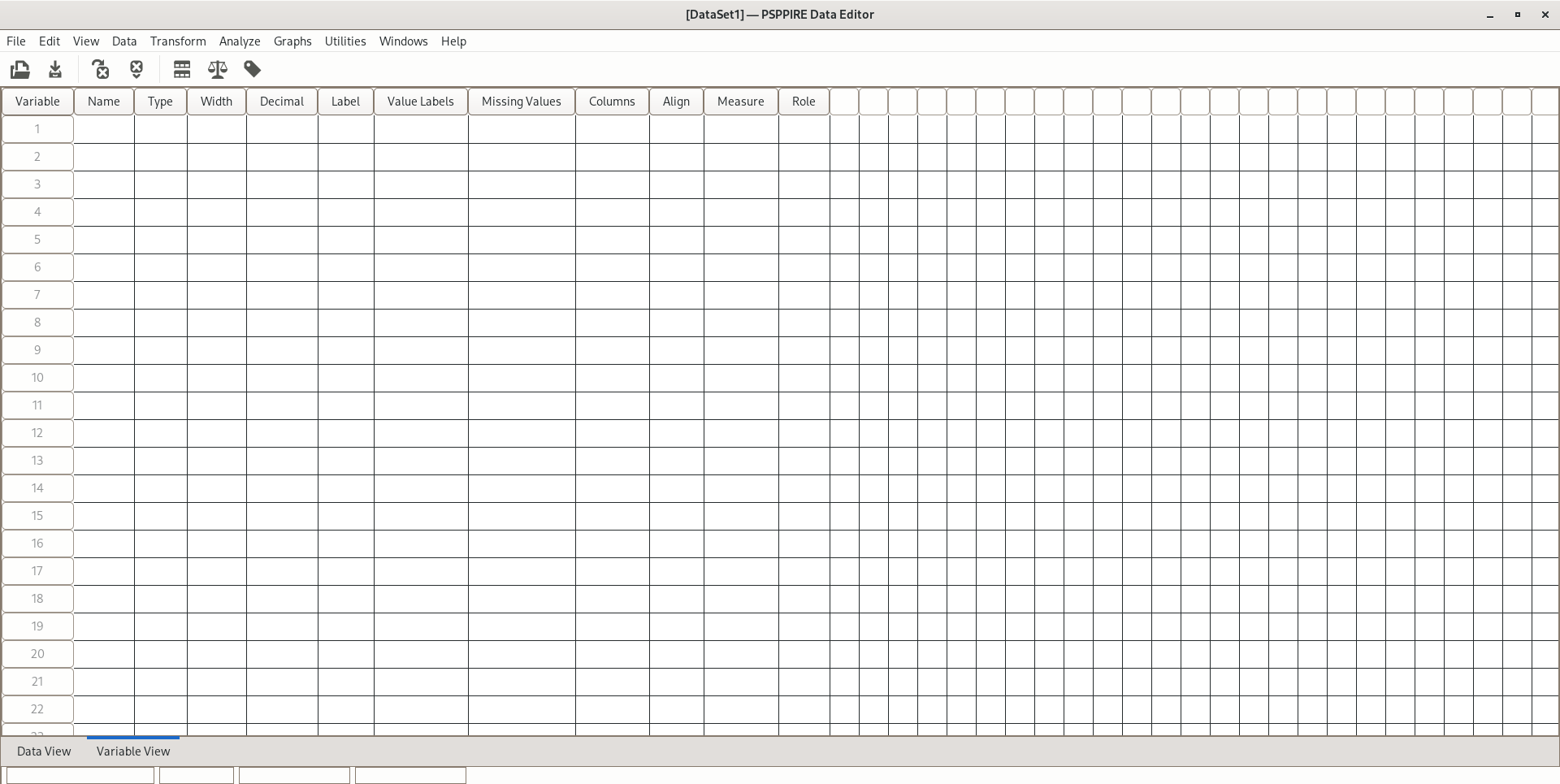 |
PSPP
PSPP is a free software application for analysis of sampled data, intended as a free alternative for IBM SPSS Statistics. It has a graphical user interface and conventional command-line interface. It is written in C and uses GNU Scientific Library for its mathematical routines. The name has "no official acronymic expansion". Features This software provides a comprehensive set of capabilities including frequencies, cross-tabs comparison of means (t-tests and one-way ANOVA), linear regression, logistic regression, reliability (Cronbach's alpha, not failure or Weibull), and re-ordering data, non-parametric tests, factor analysis, cluster analysis, principal components analysis, chi-square analysis and more. At the user's choice, statistical output and graphics are available in ASCII, PDF, PostScript, SVG or HTML formats. A range of statistical graphs can be produced, such as histograms, pie-charts, scree plots, and np-charts. PSPP can import Gnumeric and OpenDocument spr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
SPSS
SPSS Statistics is a statistical software suite developed by IBM for data management, advanced analytics, multivariate analysis, business intelligence, and criminal investigation. Long produced by SPSS Inc., it was acquired by IBM in 2009. Versions of the software released since 2015 have the brand name IBM SPSS Statistics. The software name originally stood for Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS), reflecting the original market, then later changed to Statistical Product and Service Solutions. Overview SPSS is a widely used program for statistics, statistical analysis in social science. It is also used by market researchers, health researchers, survey companies, government, education researchers, industries, marketing organizations, data miners, and others. The original SPSS manual (Nie, Bent & Hull, 1970) has been described as one of "sociology's most influential books" for allowing ordinary researchers to do their own statistical analysis. In addition to statist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Data Quality
Data quality refers to the state of qualitative or quantitative pieces of information. There are many definitions of data quality, but data is generally considered high quality if it is "fit for tsintended uses in operations, decision making and planning". Data is deemed of high quality if it correctly represents the real-world construct to which it refers. Apart from these definitions, as the number of data sources increases, the question of internal data consistency becomes significant, regardless of fitness for use for any particular external purpose. People's views on data quality can often be in disagreement, even when discussing the same set of data used for the same purpose. When this is the case, businesses may adopt recognised international standards for data quality (See #International Standards for Data Quality below). Data governance can also be used to form agreed upon definitions and standards, including international standards, for data quality. In such cases, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |