|
Tver Karelian Dialect
The Tver Karelian dialect is a dialect of the Karelian language spoken in the Tver Oblast. It is descended from 17th century South Karelian dialect, South Karelian speakers who migrated to the Tver region. Although Tver Karelian descents from Karelian Proper language, Karelian Proper, it often contains many differences from other Karelian Proper dialects. The Tver Karelian dialect contains very strong influences from the Russian language, especially in the phonetics of the dialect. A standardized written language has been created for the Tver dialect. The earliest translation of the Bible in Karelian was made using the Tver dialect in 1820. Examples The following example of Tver Karelian is from Zoja Turičeva in 1996: References {{Reflist Karelian language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
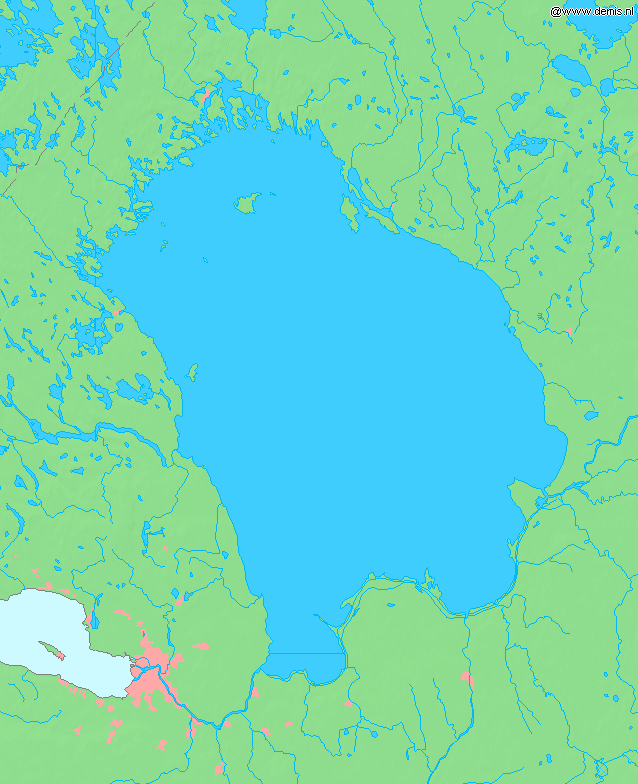
Tver Oblast
Tver Oblast (, ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative center is the city of Tver. From 1935 to 1990, it was known as Kalinin Oblast (). Population: Tver Oblast is a region of lakes, such as Seliger and Brosno. Much of the remaining area is occupied by the Valdai Hills, where the Volga, the Western Dvina, and the Dnieper have their source. Tver Oblast is one of the tourist regions of Russia with a modern tourist infrastructure. There are also many historic towns: Torzhok, Toropets, Zubtsov, Kashin, Vyshny Volochyok, and Kalyazin. The oldest of these is Rzhev, primarily known for the Battles of Rzhev in World War II. Staritsa was the seat of the last appanage principality in Russia. Ostashkov is a major tourist center. Geography Tver Oblast is located in the west of the middle part of the East European Plain. It stretches for 260 km from north to south and 450 km from west to east. The area borders Yaroslavl Oblast in the east, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
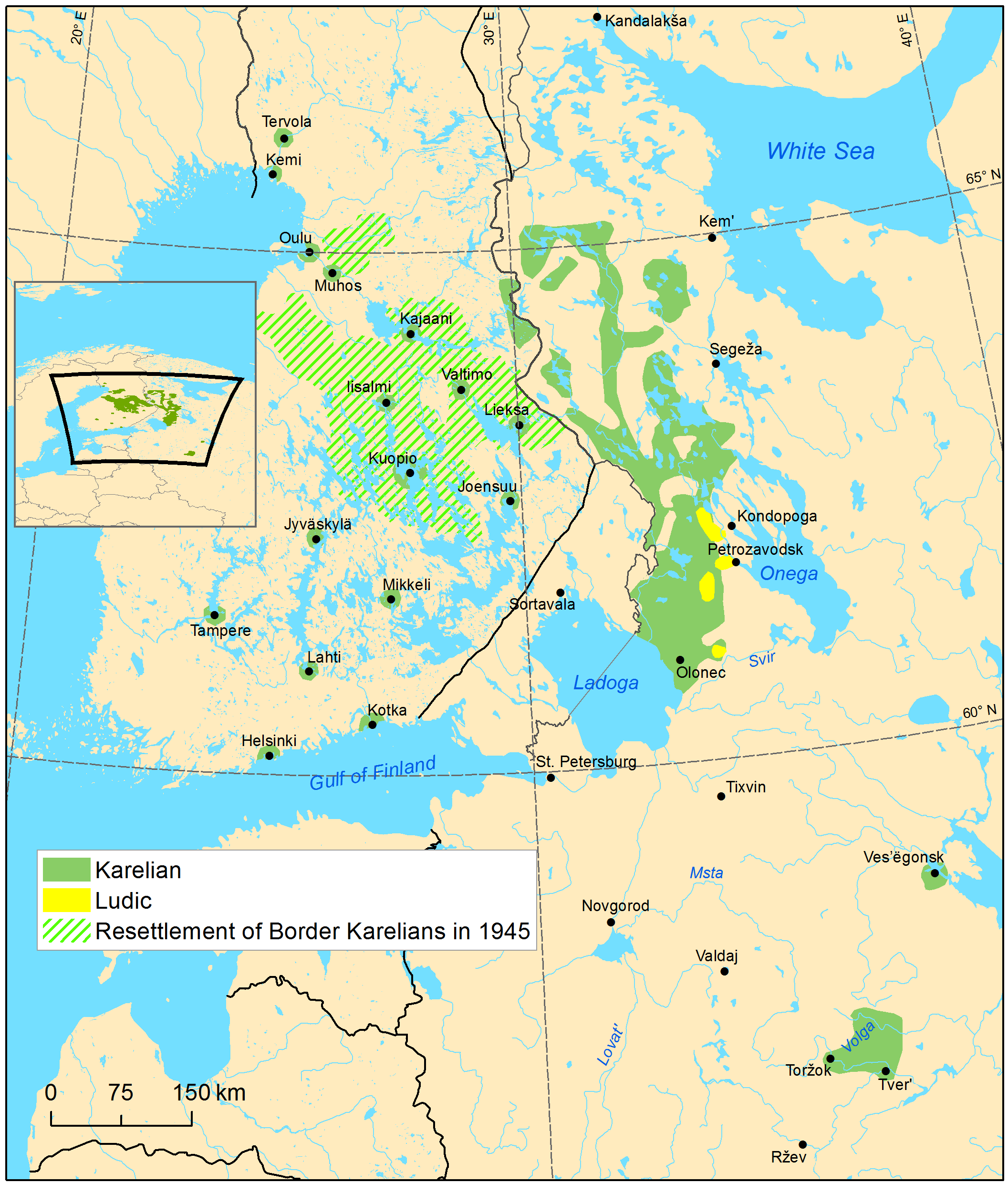
Tver Karelians
Tver Karelians are a people who inhabit regions of Tver, Saint Petersburg, and Moscow. Their dialect is remarkable in that it does not borrow from other Balto-Finnic languages due to centuries of geographical isolation. Although the number of Tver Karelian people was about 14,633 in 2002, very few (about 25 in one census) named the dialect as their primary language. The number of Tver Karelians was 7,394 in 2010 and 2,764 in 2020. Origins The Tver Karelians migrated from Karelia, mostly Kexholm County, to the Tver region during the 16th and 17th centuries to escape war, increased taxes, and forced conversion from the Orthodox religion to Lutheranism imposed by Sweden. The first wave of migrations occurred during the 1570s, when Sweden was attempting to occupy Kexholm. By 1580, when Sweden finally captured Kexholm, the number of farms in the County had decreased by 489, and 800 families had fled the city of Kexholm. In total around 6400 people had fled. They were encoura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karelians
Karelians (; ; ; ) are a Baltic Finnic ethnic group who are indigenous to the historical region of Karelia, which is today split between Finland and Russia. Karelians living in Russian Karelia are considered a distinct ethnic group closely related to Finnish Karelians, who are considered a subset of Finns. This distinction historically arose from Karelia having been fought over and eventually split between Sweden and Novgorod, resulting in Karelians being under different cultural spheres. In Russia, Karelians mostly live in the Republic of Karelia, where they are the designated ethnic group, and in other adjacent north-western parts of the country. They traditionally speak the Karelian language and are Eastern Orthodox Christians. There are also significant Karelian enclaves in the Tver and Novgorod oblasts, as some Karelians migrated to those areas after the Russo-Swedish War of 1656–1658. In Finland, the term Karelian generally refers to the Finnish Karelians, who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uralic
The Uralic languages ( ), sometimes called the Uralian languages ( ), are spoken predominantly in Europe and North Asia. The Uralic languages with the most native speakers are Hungarian, Finnish, and Estonian. Other languages with speakers above 100,000 are Erzya, Moksha, Mari, Udmurt and Komi spoken in the European parts of the Russian Federation. Still smaller minority languages are Sámi languages of the northern Fennoscandia; other members of the Finnic languages, ranging from Livonian in northern Latvia to Karelian in northwesternmost Russia; the Samoyedic languages and the others of members of the Ugric languages, Mansi and Khanty spoken in Western Siberia. The name ''Uralic'' derives from the family's purported "original homeland" (''Urheimat'') hypothesized to have been somewhere in the vicinity of the Ural Mountains, and was first proposed by Julius Klaproth in ''Asia Polyglotta'' (1823). Finno-Ugric is sometimes used as a synonym for Uralic but more accurately ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnic Languages
The Finnic or Baltic Finnic languages constitute a branch of the Uralic language family spoken around the Baltic Sea by the Baltic Finnic peoples. There are around 7 million speakers, who live mainly in Finland and Estonia. Traditionally, eight Finnic languages have been recognized. The major modern representatives of the family are Finnish language, Finnish and Estonian language, Estonian, the official languages of their respective nation states. ''ö'' after front-harmonic vowels. The lack of ''õ'' in these languages as an innovation rather than a retention has been proposed, and recently resurrected. Germanic loanwords found throughout Northern Finnic but absent in Southern are also abundant, and even several Baltic examples of this are known. Northern Finnic in turn divides into two main groups. The most Eastern Finnic group consists of the East Finnish dialects as well as Ingrian, Karelian and Veps; the proto-language of these was likely spoken in the vicinity of Lake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Karelian Language
Proto-Karelian, also known as Old Karelian, was a language once spoken on the western shore of Lake Ladoga in Karelia, from which the dialects of the Karelian language (White, Southern and Livvi), Ludic, the Ingrian language, as well as the South Karelian and Savonian dialects of the Finnish language have developed. It was spoken around the 12th and 13th centuries, and the language was likely quite uniform with little regional variance. The Eastern Finnish dialects developed from Proto-Karelian when the language of the inhabitants who had moved to the area around present-day Mikkeli mixed with western, likely Tavastian, speakers of Finnish. The Livvi-Karelian dialect and Ludic developed from the mixture of the old Vepsian language spoken by the Vepsians of the Olonets Isthmus and Proto-Karelian. Innovations in Proto-Karelian include: the disappearance of *d and *g between vowels, the plural stem *-lOi-, the labialization Labialization is a secondary articulatory feat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karelian Language
Karelian (; ; ; ) is a Finnic language spoken mainly by the Karelians, Karelian people in the Russian Republic of Karelia. Linguistically, Karelian is closely related to the Finnish language, Finnish dialects spoken in eastern Finland, and some Finnish linguists have even classified Karelian as a dialect of Finnish, but nowadays it is widely considered a separate language. Karelian is not to be confused with the South Karelian dialects, Southeastern dialects of Finnish, sometimes referred to as ("Karelian dialects") in Finland. In the Russian 2020–2021 census, around 9,000 people spoke Karelian natively, but around 14,000 said they were able to speak the language. There are around 11,000 speakers of Karelian in Finland, and around 30,000 people in Finland have at least some knowledge of Karelian. The Karelian language is a group of two supradialects. The two supradialects are Karelian Proper language, Karelian Proper (which comprises Northern Karelian dialect, Northern Kareli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karelian Proper Language
Karelian Proper () is a supradialect of the Karelian language, which is a Finnic language. Karelian Proper is one of two/three Karelian dialects, along with Livvi-Karelian and Ludic. Karelian Proper is a direct descendent of the Old Karelian language, compared to Livvi-Karelian and Ludian supradialects which were formed through interactions between the Old Karelian and the Old Veps languages. Karelian Proper is situated in all of White Karelia and ''Central Karelia'' (parts of Olonets Karelia). Dialects Karelian Proper is divided into two main dialects, which are Northern Karelian and South Karelian. The terms North and South Karelian are often avoided to avoid conflict with the Regions of Finland; North Karelia and South Karelia. Karelian Proper and most of its dialects are mostly mutually intelligible with the Finnish language, however Karelian Proper is not entirely mutually intelligible with Livvi-Karelian. * Karelian Proper ** North Karelian (spoken in the parishes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Karelian Dialect
South Karelian (South Karelian: ) is the most spoken of the two dialects of Karelian Proper, and it is spoken in the Republic of Karelia and in the Tver Oblast. South Karelian was also previously spoken in Border Karelia when it was part of Finland. Many speakers of the South Karelian dialect were evacuated from Finnish Karelia into other areas of Finland during the 20th century, where a number of speakers are still retained. South Karelian displays a higher degree of regional variation than any other Karelian dialect. The Karelian enclave dialects such as Tikhvin, Valday and Tver Karelian are also derived from South Karelian. South Karelian is mainly distinguished from North Karelian by containing the sounds b, d, g, z and ž, which are missing from the Northern dialect of Karelian proper. Examples The following example is taken from a 2016 Karelian in Seinäjoki Seinäjoki (; "Wall River"; , formerly ) is a city in Finland and the regional capital of South Ostrobothni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Karelian Dialect
South Karelian (South Karelian: ) is the most spoken of the two dialects of Karelian Proper, and it is spoken in the Republic of Karelia and in the Tver Oblast. South Karelian was also previously spoken in Border Karelia when it was part of Finland. Many speakers of the South Karelian dialect were evacuated from Finnish Karelia into other areas of Finland during the 20th century, where a number of speakers are still retained. South Karelian displays a higher degree of regional variation than any other Karelian dialect. The Karelian enclave dialects such as Tikhvin, Valday and Tver Karelian are also derived from South Karelian. South Karelian is mainly distinguished from North Karelian by containing the sounds b, d, g, z and ž, which are missing from the Northern dialect of Karelian proper. Examples The following example is taken from a 2016 Karelian in Seinäjoki Seinäjoki (; "Wall River"; , formerly ) is a city in Finland and the regional capital of South Ostrobothn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Language
Russian is an East Slavic languages, East Slavic language belonging to the Balto-Slavic languages, Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. It is one of the four extant East Slavic languages, and is the native language of the Russians. It was the ''de facto'' and ''de jure'' De facto#National languages, official language of the former Soviet Union.1977 Soviet Constitution, Constitution and Fundamental Law of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, 1977: Section II, Chapter 6, Article 36 Russian has remained an official language of the Russia, Russian Federation, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Tajikistan, and is still commonly used as a lingua franca in Ukraine, Moldova, the Caucasus, Central Asia, and to a lesser extent in the Baltic states and Russian language in Israel, Israel. Russian has over 253 million total speakers worldwide. It is the List of languages by number of speakers in Europe, most spoken native language in Eur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tver Dialects Of Karelian And VepKar Corpus By Irina Novak 2018
Tver (, ) is a city and the administrative centre of Tver Oblast, Russia. It is situated at the confluence of the Volga and Tvertsa rivers. Tver is located northwest of Moscow. Population: The city is situated where three rivers meet, splitting the town into northern and southern parts by the Volga, and divided again into quarters by the Tvertsa River, which splits the left (northern) bank into east and west halves, and the Tmaka River which does the same along the southern bank. Tver was formerly the capital of a powerful medieval state and a model provincial town in the Russian Empire, with a population of 60,000 by 14 January 1913. The city was known as Kalinin () from 1931 to 1990. Etymology According to one hypothesis, the name of the city is of Finnic origin, ''*Tiheverä''. History Medieval origins Tver's foundation year is officially accepted to be 1135.Charter of Tver, Article 1 Originally a minor settlement of Novgorodian traders, it passed to the grand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |