|
Turtle Beak (Chinese Constellation)
The Turtle Beak mansion (觜宿, pinyin: Zī Xiù) is one of the twenty-eight mansions of the Chinese constellations. It is one of the western mansions of the White Tiger The white tiger (ashy tiger) is a leucistic morph of the tiger, typically the Bengal tiger. It is occasionally reported in the Indian wilderness. It has the typical black stripes of a tiger, but its coat is otherwise white or near-white, and .... Asterisms References {{DEFAULTSORT:Turtle Beak (Chinese Constellation) Chinese constellations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinyin
Hanyu Pinyin, or simply pinyin, officially the Chinese Phonetic Alphabet, is the most common romanization system for Standard Chinese. ''Hanyu'' () literally means 'Han Chinese, Han language'—that is, the Chinese language—while ''pinyin'' literally means 'spelled sounds'. Pinyin is the official romanization system used in China, Singapore, Taiwan, and by the United Nations. Its use has become common when transliterating Standard Chinese mostly regardless of region, though it is less ubiquitous in Taiwan. It is used to teach Standard Chinese, normally written with Chinese characters, to students in mainland China and Singapore. Pinyin is also used by various Chinese input method, input methods on computers and to lexicographic ordering, categorize entries in some Chinese dictionaries. In pinyin, each Chinese syllable is spelled in terms of an optional initial (linguistics), initial and a final (linguistics), final, each of which is represented by one or more letters. Initi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twenty-eight Mansions
The Twenty-Eight Mansions (), also called or , are part of the Chinese constellations system. They can be considered as the equivalent to the Zodiac, zodiacal constellations in Western astronomy, though the Twenty-eight Mansions reflect the movement of the Moon through a Lunar month, sidereal month rather than the Sun in a tropical year. The lunar mansion system was in use in other parts of East Asia, such as ancient Japan; the ''Bansenshūkai'', written by Fujibayashi Yasutake, mentions the system several times and includes an image of the twenty-eight mansions. A similar system, called nakshatra, is used in traditional Indian astronomy. Overview Ancient Chinese astronomers divided the sky ecliptic into four regions, collectively known as the Four Symbols, each assigned a mysterious animal. They are Azure Dragon (青龍) on the east, Black Tortoise (玄武) on the north, White Tiger (mythology), White Tiger (白虎) on the west, and Vermilion Bird (朱雀) on the south. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Constellation
Traditional Chinese astronomy has a system of dividing the celestial sphere into asterisms or constellations, known as "officials" ( Chinese ''xīng guān''). The Chinese asterisms are generally smaller than the constellations of Hellenistic tradition. The Song dynasty (13th-century) Suzhou planisphere shows a total of 283 asterisms, comprising a total of 1,565 individual stars. The asterisms are divided into four groups, the Twenty-Eight Mansions (, ''Èrshíbā Xiù'') along the ecliptic, and the Three Enclosures of the northern sky. The southern sky was added as a fifth group in the late Ming dynasty based on European star charts, comprising an additional 23 asterisms. The Three Enclosures (, ''Sān Yuán'') include the Purple Forbidden Enclosure, which is centered on the north celestial pole and includes those stars which could be seen year-round,Needham, J.Astronomy in Ancient and Medieval China. ''Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London''. Ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Tiger (Chinese Constellation)
The White Tiger (), is one of the Four Symbols of the Chinese constellations. It is sometimes called the White Tiger of the West (). It represents the west in terms of direction and the autumn season. It is known as ''Byakko'' in Japanese, Baekho in Korean, and in Vietnamese. Seven Mansions As with the other three Symbols, there are seven astrological " Mansions" (positions of the Moon The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar ...) within the White Tiger. The names and determinative stars are: See also * Byakkotai References {{Chinese constellations Chinese constellations Chinese gods Chinese legendary creatures Mythological tigers Tigers in popular culture Four Symbols Onmyōdō deities Animals in Chinese mythology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object. The first constellations were likely defined in prehistory. People used them to relate stories of their beliefs, experiences, creation myth, creation, and mythology. Different cultures and countries invented their own constellations, some of which lasted into the early 20th century before today's constellations were internationally recognized. The recognition of constellations has changed significantly over time. Many changed in size or shape. Some became popular, only to drop into obscurity. Some were limited to a single culture or nation. Naming constellations also helped astronomers and navigators identify stars more easily. Twelve (or thirteen) ancient constellations belong to the zodiac (straddling the ecliptic, which the Sun, Moon, and planets all traver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orion (constellation)
Orion is a prominent set of stars visible during winter in the northern celestial hemisphere. It is one of the IAU designated constellations, 88 modern constellations; it was among :Constellations listed by Ptolemy, the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy. It is named after Orion (mythology), a hunter in Greek mythology. Orion is most prominent during winter evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, as are five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism (astronomy), asterism. Orion's two brightest stars, Rigel (β) and Betelgeuse (α), are both among the List of brightest stars, brightest stars in the night sky; both are supergiants and slightly variable star, variable. There are a further six stars brighter than magnitude 3.0, including three making the short straight line of the Orion's Belt asterism (astronomy), asterism. Orion also hosts the radiant (meteor shower), radiant of the annual Orionids, the strongest meteor shower as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taurus (constellation)
Taurus (Latin, 'Bull') is one of the constellations of the zodiac and is located in the northern celestial hemisphere. Taurus is a large and prominent constellation in the Northern Hemisphere's winter sky. It is one of the oldest constellations, dating back to the Early Bronze Age at least, when it marked the location of the Sun during the spring equinox. Its importance to the agricultural calendar influenced sacred bull, various bull figures in the mythologies of Ancient Sumerian religion, Sumer, Akkadian religion, Akkad, Assyrian religion, Assyria, Babylonian religion, Babylon, Ancient Egyptian religion, Egypt, Ancient Greek religion, Greece, and Religion in ancient Rome, Rome. Its old astronomical symbol is (♉︎), which resembles a bull's head. A number of features exist that are of interest to astronomers. Taurus hosts two of the nearest open clusters to Earth, the Pleiades and the Hyades (star cluster), Hyades, both of which are visible to the naked eye. At first magnitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemini (constellation)
Gemini is one of the constellations of the zodiac and is located in the northern celestial hemisphere. It was one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century AD astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. Its name is Latin for ''twins'', and it is associated with the twins Castor and Pollux in Greek mythology. Its old astronomical symbol is (♊︎). Location Gemini lies between Taurus (constellation), Taurus to the west and Cancer (constellation), Cancer to the east, with Auriga (constellation), Auriga and Lynx (constellation), Lynx to the north, Monoceros (constellation), Monoceros and Canis Minor to the south, and Orion (constellation), Orion to the south-west. In classical antiquity, Cancer was the location of the Sun on the June solstice, northern solstice (June 21). During the first century AD, axial precession shifted it into Gemini. In 1990, the location of the Sun at the northern solstice moved from Gemini into Taurus, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auriga (constellation)
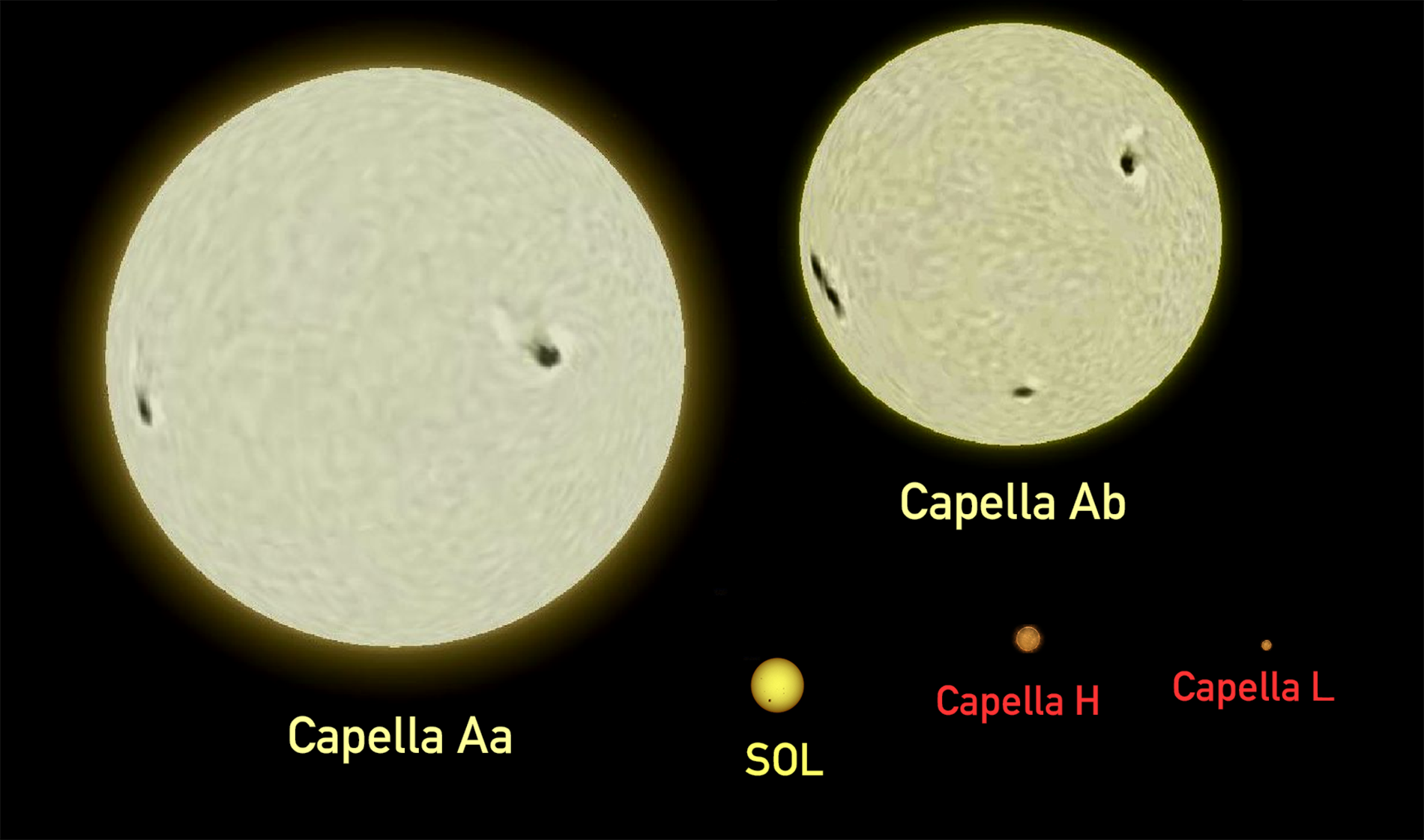
Auriga is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. It is one of the List of constellations, 88 modern constellations; it was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy. Its name is Latin for '(the) charioteer', associating it with various mythological beings, including Erichthonius of Athens, Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the northern Hemisphere, as are five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism (astronomy), asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far south as −34°; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest, Hydra (constellation), Hydra. Its brightest star, Capella (star), Capella, is an unusual Star system, multiple star system among the brightest stars in the night sky. Beta Aurigae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lynx (constellation)
Lynx is a constellation named after lynx, the animal, usually observed in the Northern Celestial Hemisphere. The constellation was introduced in the late 17th century by Johannes Hevelius. It is a faint constellation, with its brightest stars forming a zigzag line. The orange giant Alpha Lyncis is the brightest star in the constellation, and the semiregular variable star Y Lyncis is a target for amateur astronomy, amateur astronomers. Six star systems have been found to contain exoplanet, planets. Those of 6 Lyncis and HD 75898 were discovered by the Doppler spectroscopy, Doppler method; those of XO-2 (star), XO-2, XO-4, XO-5 and WASP-13 were observed as they Methods of detecting extrasolar planets#Transit method, passed in front of the host star. Within the constellation's borders lie NGC 2419, an unusually remote globular cluster; the galaxy NGC 2770, which has hosted three recent Type Ib and Ic supernovae, Type Ib supernovae; the distant quasar APM 08279+5255, whose light is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |