|
Turing Machine Examples
The following are examples to supplement the article Turing machine. Turing's very first example The following table is Turing's very first example (Turing 1937): :"1. A machine can be constructed to compute the sequence 0 1 0 1 0 1..." (0 1 0...) With regard to what actions the machine actually does, Turing (1936) states the following: : "This xampletable (and all succeeding tables of the same kind) is to be understood to mean that for a configuration described in the first two columns the operations in the third column are carried out successively, and the machine then goes over into the m-configuration in the final column." He makes this very clear when he reduces the above table to a single instruction called "b", but his instruction consists of 3 lines. Instruction "b" has three different symbol possibilities . Each possibility is followed by a sequence of actions until we arrive at the rightmost column, where the final m-configuration is "b": As observed by a number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
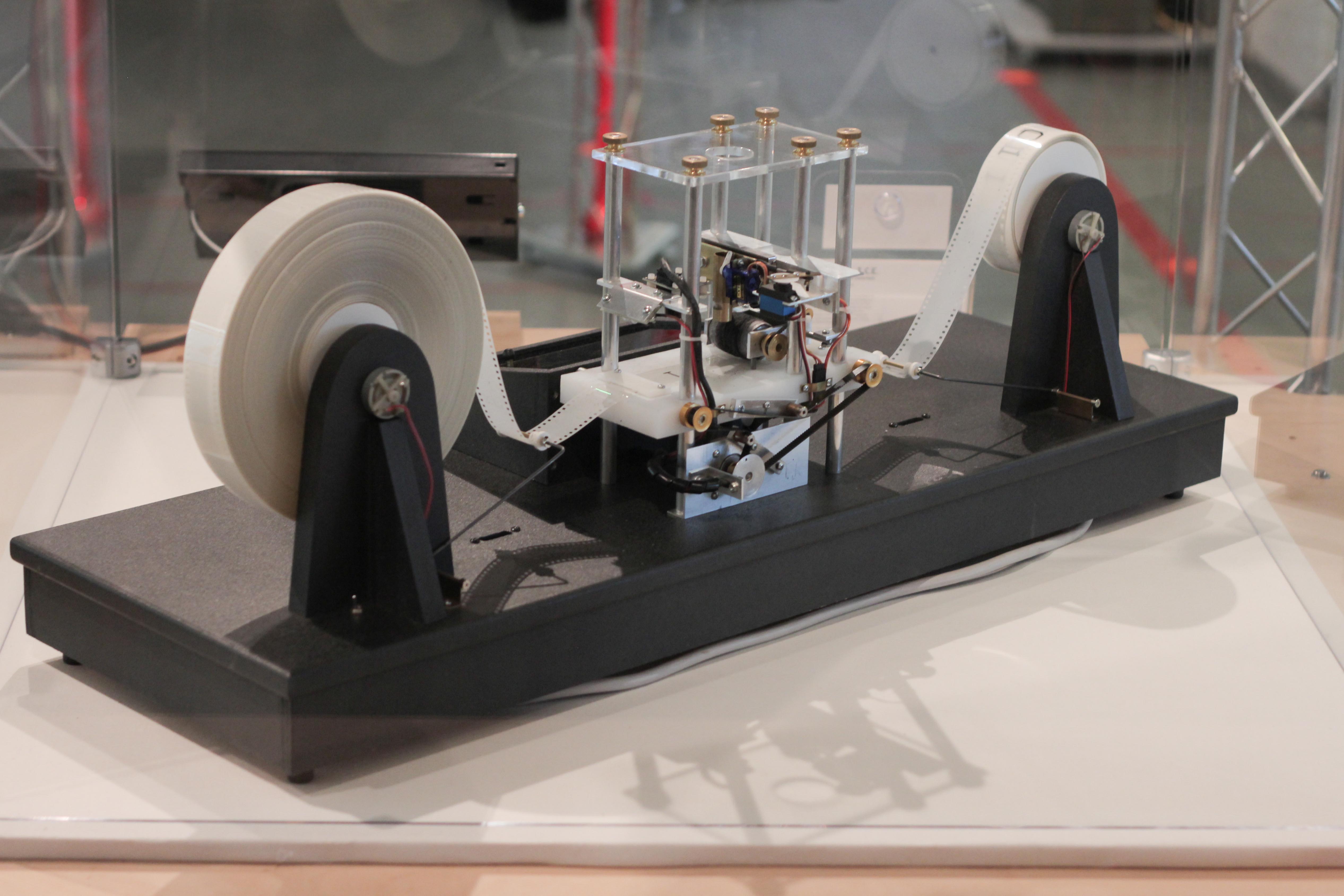
Turing Machine
A Turing machine is a mathematical model of computation describing an abstract machine that manipulates symbols on a strip of tape according to a table of rules. Despite the model's simplicity, it is capable of implementing any computer algorithm. The machine operates on an infinite memory tape divided into discrete mathematics, discrete cells, each of which can hold a single symbol drawn from a finite set of symbols called the Alphabet (formal languages), alphabet of the machine. It has a "head" that, at any point in the machine's operation, is positioned over one of these cells, and a "state" selected from a finite set of states. At each step of its operation, the head reads the symbol in its cell. Then, based on the symbol and the machine's own present state, the machine writes a symbol into the same cell, and moves the head one step to the left or the right, or halts the computation. The choice of which replacement symbol to write, which direction to move the head, and whet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post–Turing Machine
A Post machine or Post–Turing machineRajendra Kumar, ''Theory of Automata'', Tata McGraw-Hill Education, 2010, p. 343. is a "program formulation" of a type of Turing machine, comprising a variant of Emil Post's Turing-equivalent model of computation. Post's model and Turing's model, though very similar to one another, were developed independently. Turing's paper was received for publication in May 1936, followed by Post's in October. A Post–Turing machine uses a binary alphabet, an infinite sequence of binary storage locations, and a primitive programming language with instructions for bi-directional movement among the storage locations and alteration of their contents one at a time. The names "Post–Turing program" and "Post–Turing machine" were used by Martin Davis in 1973–1974 (Davis 1973, p. 69ff). Later in 1980, Davis used the name "Turing–Post program" (Davis, in Steen p. 241). 1936: Post model In his 1936 paper "Finite Combinatory Processes&mdas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finite-state Machine
A finite-state machine (FSM) or finite-state automaton (FSA, plural: ''automata''), finite automaton, or simply a state machine, is a mathematical model of computation. It is an abstract machine that can be in exactly one of a finite number of ''State (computer science), states'' at any given time. The FSM can change from one state to another in response to some Input (computer science), inputs; the change from one state to another is called a ''transition''. An FSM is defined by a list of its states, its initial state, and the inputs that trigger each transition. Finite-state machines are of two types—Deterministic finite automaton, deterministic finite-state machines and Nondeterministic finite automaton, non-deterministic finite-state machines. For any non-deterministic finite-state machine, an equivalent deterministic one can be constructed. The behavior of state machines can be observed in many devices in modern society that perform a predetermined sequence of actions d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microprogramming
In processor design, microcode serves as an intermediary layer situated between the central processing unit (CPU) hardware and the programmer-visible instruction set architecture of a computer. It consists of a set of hardware-level instructions that implement the higher-level machine code instructions or control internal finite-state machine sequencing in many digital processing components. While microcode is utilized in Intel and AMD general-purpose CPUs in contemporary desktops and laptops, it functions only as a fallback path for scenarios that the faster hardwired control unit is unable to manage. Housed in special high-speed memory, microcode translates machine instructions, state machine data, or other input into sequences of detailed circuit-level operations. It separates the machine instructions from the underlying electronics, thereby enabling greater flexibility in designing and altering instructions. Moreover, it facilitates the construction of complex multi-step inst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turing Machine Turing's First Machine
Alan Mathison Turing (; 23 June 1912 – 7 June 1954) was an English mathematician, computer scientist, logician, cryptanalyst, philosopher and theoretical biologist. He was highly influential in the development of theoretical computer science, providing a formalisation of the concepts of algorithm and computation with the Turing machine, which can be considered a model of a general-purpose computer. Turing is widely considered to be the father of theoretical computer science. Born in London, Turing was raised in southern England. He graduated from King's College, Cambridge, and in 1938, earned a doctorate degree from Princeton University. During World War II, Turing worked for the Government Code and Cypher School at Bletchley Park, Britain's codebreaking centre that produced Ultra intelligence. He led Hut 8, the section responsible for German naval cryptanalysis. Turing devised techniques for speeding the breaking of German ciphers, including improvements to the pre-w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Induction
Mathematical induction is a method for mathematical proof, proving that a statement P(n) is true for every natural number n, that is, that the infinitely many cases P(0), P(1), P(2), P(3), \dots all hold. This is done by first proving a simple case, then also showing that if we assume the claim is true for a given case, then the next case is also true. Informal metaphors help to explain this technique, such as falling dominoes or climbing a ladder: A proof by induction consists of two cases. The first, the base case, proves the statement for n = 0 without assuming any knowledge of other cases. The second case, the induction step, proves that ''if'' the statement holds for any given case n = k, ''then'' it must also hold for the next case n = k + 1. These two steps establish that the statement holds for every natural number n. The base case does not necessarily begin with n = 0, but often with n = 1, and possibly with any fixed natural number n = N, establishing the trut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turing Machine Copy Example
Alan Mathison Turing (; 23 June 1912 – 7 June 1954) was an English mathematician, computer scientist, logician, cryptanalyst, philosopher and theoretical biologist. He was highly influential in the development of theoretical computer science, providing a formalisation of the concepts of algorithm and computation with the Turing machine, which can be considered a model of a general-purpose computer. Turing is widely considered to be the father of theoretical computer science. Born in London, Turing was raised in southern England. He graduated from King's College, Cambridge, and in 1938, earned a doctorate degree from Princeton University. During World War II, Turing worked for the Government Code and Cypher School at Bletchley Park, Britain's codebreaking centre that produced Ultra intelligence. He led Hut 8, the section responsible for German naval cryptanalysis. Turing devised techniques for speeding the breaking of German ciphers, including improvements to the pre-w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Busy Beaver
In theoretical computer science, the busy beaver game aims to find a terminating Computer program, program of a given size that (depending on definition) either produces the most output possible, or runs for the longest number of steps. Since an endless loop, endlessly looping program producing infinite output or running for infinite time is easily conceived, such programs are excluded from the game. Rather than traditional programming languages, the programs used in the game are n-state Turing machine, Turing machines, one of the first mathematical models of computation. Turing machines consist of an infinite tape, and a finite set of states which serve as the program's "source code". Producing the most output is defined as writing the largest number of 1s on the tape, also referred to as achieving the highest score, and running for the longest time is defined as taking the longest number of steps to halt. The ''n-''state busy beaver game consists of finding the longest-running ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Diagram 3 State Busy Beaver
State most commonly refers to: * State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory **Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country **Nation state, a state where the majority identify with a single nation (with shared culture or ethnic group) ** Constituent state, a political subdivision of a state ** Federated state, constituent states part of a federation *** U.S. state * State of nature, a concept within philosophy that describes the way humans acted before forming societies or civilizations State may also refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Literature * ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State * ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States * '' Our State'', a monthly magazine published in North Carolina and formerly called ''The State'' * The State (Larry Niven), a fictional future government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turing Machine Example 3 State Busy Beaver
Alan Mathison Turing (; 23 June 1912 – 7 June 1954) was an English mathematician, computer scientist, logician, cryptanalyst, philosopher and theoretical biologist. He was highly influential in the development of theoretical computer science, providing a formalisation of the concepts of algorithm and computation with the Turing machine, which can be considered a model of a general-purpose computer. Turing is widely considered to be the father of theoretical computer science. Born in London, Turing was raised in southern England. He graduated from University of Cambridge, King's College, Cambridge, and in 1938, earned a doctorate degree from Princeton University. During World War II, Turing worked for the Government Code and Cypher School at Bletchley Park, Britain's codebreaking centre that produced Ultra (cryptography), Ultra intelligence. He led Hut 8, the section responsible for German naval cryptanalysis. Turing devised techniques for speeding the breaking of Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |