|
Tunica People
The Tunica people are a group of linguistically and culturally related Native Americans in the United States, Native American tribes in the Mississippi River Valley, which include the Tunica (also spelled Tonica, Tonnica, and Thonnica); the Yazoo tribe, Yazoo; the Koroa (Akoroa, Courouais); and possibly the Tioux. They first encountered Europeans in 1541 – members of the Hernando de Soto expedition. The Tunica language is an language isolate, isolate. Over the next centuries, under pressure from hostile neighbors, the Tunica migrated south from the Central Mississippi Valley to the Lower Mississippi Valley. Eventually they moved westward and settled around present-day Marksville, Louisiana. Since the early 19th century, they have intermarried with the Biloxi tribe, an unrelated Siouan-speaking people from the vicinity of Biloxi, Mississippi and shared land. Remnant peoples from other small tribes also merged with them. In 1981 they were federally recognized and now call thems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natchez People
[https://archive.org/details/dcouverteett01marg The Internet Archive website] The Natchez ( , ) are a Native Americans in the United States, Native American people who originally lived in the Natchez Bluffs area in the Lower Mississippi Valley, near the present-day city of Natchez, Mississippi, in the United States. The Hernando de Soto, DeSoto chronicle failed to record their presence when they came down the river in 1543. They speak a language Language isolate, with no known close relatives, although it may be very distantly related to the Muskogean languages of the Muscogee, Creek Confederacy.Geoffrey Kimball, "Natchez" in ''Native Languages of the Southeastern United States'', ed. Janine Scancarelli and Heather Kay Hardy, University of Nebras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siouan
Siouan ( ), also known as Siouan–Catawban ( ), is a language family of North America located primarily in the Great Plains, Ohio and Mississippi valleys and southeastern North America with a few other languages in the east. Name Authors who call the entire family ''Siouan'' distinguish the two branches as Western Siouan and Eastern Siouan or as "Siouan-proper" and "Catawban". Others restrict the name "Siouan" to the western branch and use the name ''Siouan–Catawban'' for the entire family. Generally, however, the name "Siouan" is used without distinction. Family division The Siouan family consists of some 20 languages and various dialects: * Siouan ** Western Siouan *** Mandan **** Nuptare **** Nuetare *** Missouri River Siouan (a.k.a. Crow–Hidatsa) **** Crow (a.k.a. Absaroka, Apsaroka, Apsaalooke, Upsaroka) – 3,500 speakers **** Hidatsa (a.k.a. Minitari, Minnetaree) – 200 speakers *** Mississippi Valley Siouan (a.k.a. Central Siouan) **** Mitchigamea? **** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. The discipline involves Survey (archaeology), surveying, Archaeological excavation, excavation, and eventually Post excavation, analysis of data collected, to learn more about the past. In broad scope, archaeology relies on cross-disciplinary research. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic Warfare
__NOTOC__ Ritual warfare (sometimes called endemic warfare) is a state of continual or frequent warfare, such as is found in (but not limited to) some tribe, tribal societies. Description Ritual fighting (or ritual battle or ritual warfare) permits the display of courage, masculinity, and the expression of emotion while resulting in relatively few wounds and even fewer deaths. Thus such a practice can be viewed as a form of conflict resolution, conflict-resolution and/or as a psycho-social exercise. Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Native Americans often engaged in this activity, but the frequency of warfare in most hunter-gatherer cultures is a matter of dispute. Examples Warfare is known to every tribal society, but some societies developed a particular emphasis of warrior culture. Examples includes the Nuer people, Nuer of South Sudan, the Maasai people, Maasai of East Africa, the Zulu people, Zulu of southeastern Africa, the Iban people, Sea Dayaks of Borneo, the Naga pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palisade
A palisade, sometimes called a stakewall or a paling, is typically a row of closely placed, high vertical standing tree trunks or wooden or iron stakes used as a fence for enclosure or as a defensive wall. Palisades can form a stockade. Etymology ''Palisade'' derives from ''pale'', from the Latin word ', meaning stake, specifically when used side by side to create a wood defensive wall. In turn, ''pālus'' derives from the Old Italic word ''palūts'', which may possibly derive from the Proto-Indo-European word ''pelh'', meaning pale or gray. It may be related to the Proto-Uralic word ''pil'me'' (uncertain meaning) or the word ''pilwe'', meaning cloud. (see wikt:pale#Etymology_2, 'pale', English: Etymology 2 on Wiktionary). Typical construction Typical construction consisted of small or mid-sized tree trunks aligned vertically, with as little free space in between as possible. The trunks were sharpened or pointed at the top, and were driven into the ground and sometimes rein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
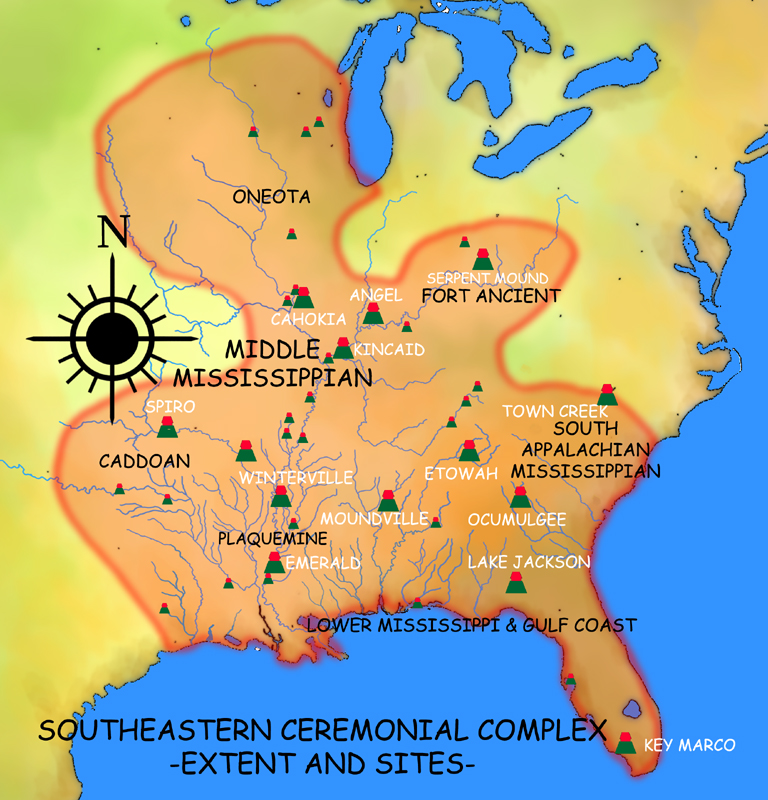
Southeastern Ceremonial Complex
Southeastern Ceremonial Complex (formerly Southern Cult, Southern Death Cult or Buzzard Cult), abbreviated S.E.C.C., is the name given by modern scholars to the regional stylistic similarity of artifacts, iconography, ceremonies, and mythology of the Mississippian culture. It coincided with their adoption of maize agriculture and chiefdom-level complex social organization from 1200 to 1650 CE. Due to some similarities between S.E.C.C. and contemporary Mesoamerican cultures (i.e., artwork with similar aesthetics or motifs; maize-based agriculture; and the development of sophisticated cities with large pyramidal structures), scholars from the late 1800s to mid-1900s suspected there was a connection between the two locations. One hypothesis was that Meso-Americans enslaved by conquistador Tristán de Luna y Arellano (1510–1573) may have spread artistic and religious elements to North America. However, later research indicates the two cultures have no direct links and that thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mississippian Culture Pottery
Mississippian culture pottery is the ceramic tradition of the Mississippian culture (800 to 1600 CE) found as artifacts in archaeological sites in the American Midwest and Southeast. It is often characterized by the adoption and use of riverine (or more rarely marine) shell- tempering agents in the clay paste. Shell tempering is one of the hallmarks of Mississippian cultural practices. Analysis of local differences in materials, techniques, forms, and designs is a primary means for archaeologists to learn about the lifeways, religious practices, trade, and interaction among Mississippian peoples. The value of this pottery on the illegal antiquities market has led to extensive looting of sites. Materials and techniques Mississippian culture pottery was made from locally available clay sources, which often gives archaeologists clues as to where a specific example originated. The clay was tempered with an additive to keep it from shrinking and cracking in the drying and firing pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mussel
Mussel () is the common name used for members of several families of bivalve molluscs, from saltwater and Freshwater bivalve, freshwater habitats. These groups have in common a shell whose outline is elongated and asymmetrical compared with other edible clams, which are often more or less rounded or oval. The word "mussel" is frequently used to mean the bivalves of the marine family Mytilidae, most of which live on exposed shores in the intertidal zone, attached by means of their strong Byssus, byssal threads ("beard") to a firm substrate. A few species (in the genus ''Bathymodiolus'') have colonised hydrothermal vents associated with deep ocean ridges. In most marine mussels the shell is longer than it is wide, being wedge-shaped or asymmetrical. The external colour of the shell is often dark blue, blackish, or brown, while the interior is silvery and somewhat nacreous. The common name "mussel" is also used for many freshwater bivalves, including the freshwater pearl mussels. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
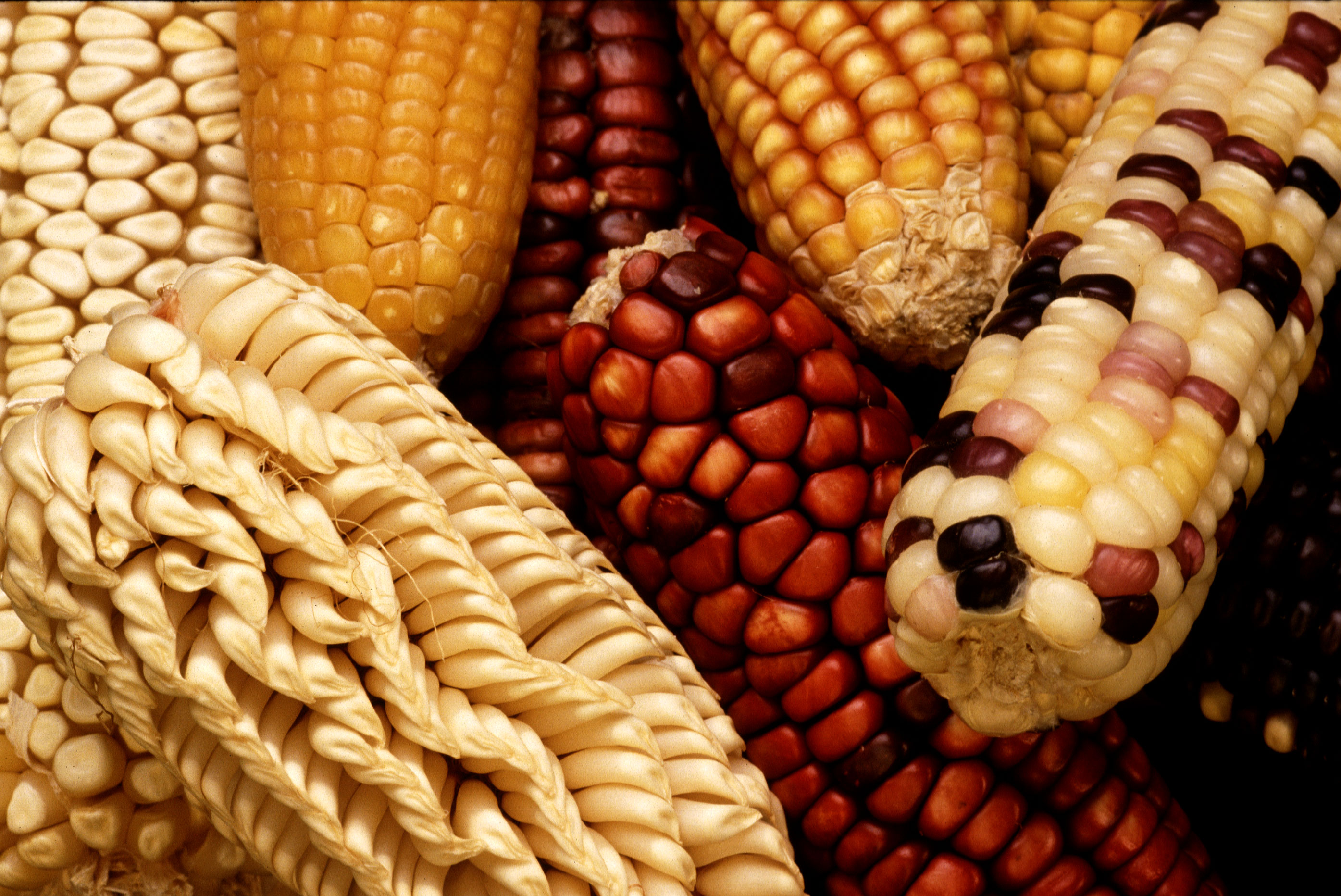
Maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native Americans planted it alongside beans and squashes in the Three Sisters polyculture. The leafy stalk of the plant gives rise to male inflorescences or tassels which produce pollen, and female inflorescences called ears. The ears yield grain, known as kernels or seeds. In modern commercial varieties, these are usually yellow or white; other varieties can be of many colors. Maize relies on humans for its propagation. Since the Columbian exchange, it has become a staple food in many parts of the world, with the total production of maize surpassing that of wheat and rice. Much maize is used for animal feed, whether as grain or as the whole plant, which can either be baled or made into the more palatable silage. Sugar-rich varieties called sw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodland Period
In the classification of :category:Archaeological cultures of North America, archaeological cultures of North America, the Woodland period of North American pre-Columbian cultures spanned a period from roughly 1000 BC to European contact in the eastern part of North America, with some archaeologists distinguishing the Mississippian period, from 1000 AD to European contact as a separate period. The term "Woodland Period" was introduced in the 1930s as a generic term for prehistoric, prehistoric sites falling between the Archaic period in the Americas, Archaic hunter-gatherers and the agriculturalist Mississippian cultures. The Eastern Woodlands cultural region covers what is now eastern Canada south of the Subarctic region, the Eastern United States, along to the Gulf of Mexico. This period is variously considered a developmental stage, a time period, a suite of technological adaptations or "traits", and a "family tree" of cultures related to earlier Archaic cultures. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mississippian Culture
The Mississippian culture was a collection of Native American societies that flourished in what is now the Midwestern, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from approximately 800 to 1600 CE, varying regionally. It was known for building large, earthen platform mounds, and often other shaped mounds as well. It was composed of a series of urban settlements and satellite villages linked together by loose trading networks. The largest city was Cahokia, believed to be a major religious center, located in what is present-day southern Illinois. The Mississippian way of life began to develop in the Mississippi River Valley (for which it is named). Cultures in the tributary Tennessee River Valley may have also begun to develop Mississippian characteristics at this point. Almost all dated Mississippian sites predate 1539–1540 (when Hernando de Soto explored the area), with notable exceptions being Natchez communities. These maintained Mississippian cultural practices into the 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parkin Mounds Aerial HRoe 2016
Parkin may refer to: * Parkin (cake), a type of cake * Parkin (protein), a ligase * Parkin (surname), people with the surname ''Parkin'' * Parkin, a brand name of the drug trihexyphenidyl * Parkin, a brand name of the drug profenamine Places * Parkin, Arkansas, a city in the United States ** Parkin Archeological State Park Parkin Archeological State Park, also known as Parkin Indian Mound, is an archeological site and state park in Parkin, Cross County, Arkansas. Around 1350–1650 CE an aboriginal palisaded village existed at the site, at the confluence ... in Parkin, Arkansas, also known as ''Parkin Site'' See also * Parkan, a brand name of the drug budipine {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |