|
Tungsten(VI) Fluoride
Tungsten(VI) fluoride, also known as tungsten hexafluoride, is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a toxic, corrosive, colorless gas, with a density of about (roughly 11 times heavier than air). It is the densest known gas under standard ambient temperature and pressure (298 K, 1 atm) and the only well characterized gas under these conditions that contains a transition metal. is commonly used by the semiconductor industry to form tungsten films, through the process of chemical vapor deposition. This layer is used in a low-resistivity metallic "interconnect". It is one of seventeen known binary hexafluorides. Properties The molecule is octahedral with the symmetry point group of Oh. The W–F bond distances are . p. 4-93. Between , tungsten hexafluoride condenses into a colorless liquid having the density of at . At it freezes into a white solid having a cubic crystalline structure, the lattice constant of 628 pm and calculated density . At this structure transforms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tungsten Hexachloride
Tungsten hexachloride is an inorganic chemical compound of tungsten and chlorine with the chemical formula . This dark violet-blue compound exists as volatile crystals under standard conditions. It is an important starting reagent in the preparation of tungsten compounds. Other examples of charge-neutral hexachlorides are rhenium(VI) chloride and molybdenum(VI) chloride. The highly volatile tungsten hexafluoride is also known. As a d0 atom, tungsten hexachloride is diamagnetic. Preparation and structure Tungsten hexachloride can be prepared by chlorinating tungsten metal in a sealed tube at 600 °C: : Tungsten hexachloride exists in both blue and red polymorphs, referred to respectively as α and β. The wine-red β can be obtained by rapid cooling, whereas the blue α form is more stable at room temperature. Although these polymorphs are distinctly colored, their molecular structures are very similar. Both polymorphs feature molecules that have octahedral geometry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symmetry Group
In group theory, the symmetry group of a geometric object is the group of all transformations under which the object is invariant, endowed with the group operation of composition. Such a transformation is an invertible mapping of the ambient space which takes the object to itself, and which preserves all the relevant structure of the object. A frequent notation for the symmetry group of an object ''X'' is ''G'' = Sym(''X''). For an object in a metric space, its symmetries form a subgroup of the isometry group of the ambient space. This article mainly considers symmetry groups in Euclidean geometry, but the concept may also be studied for more general types of geometric structure. Introduction We consider the "objects" possessing symmetry to be geometric figures, images, and patterns, such as a wallpaper pattern. For symmetry of physical objects, one may also take their physical composition as part of the pattern. (A pattern may be specified formally as a scalar field, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorine Monofluoride
Chlorine monofluoride is a volatile interhalogen compound with the chemical formula . It is a colourless gas at room temperature and is stable even at high temperatures. When cooled to −100 °C, ClF condenses as a pale yellow liquid. Many of its properties are intermediate between its parent halogens, and . Geometry The molecular structure in the gas phase was determined by microwave spectroscopy; the bond length is ''r''e = 1.628341(4) Å. The bond length in the crystalline ClF is 1.628(1) Å; the lengthening relative to the free molecule is due to an interaction of the type F-Br···ClMe with a distance of 2.640(1) Å. In its molecular packing it shows very short intermolecular Cl···Cl contacts of 3.070(1) Å between neighboring molecules. Reactivity Chlorine monofluoride is a versatile fluorinating agent, converting metals and non-metals to their fluorides and releasing in the process. For example, it converts tungsten to tungsten he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tungsten
Tungsten (also called wolfram) is a chemical element; it has symbol W and atomic number 74. It is a metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively in compounds with other elements. It was identified as a distinct element in 1781 and first isolated as a metal in 1783. Its important ores include scheelite and wolframite, the latter lending the element its alternative name. The free element is remarkable for its robustness, especially the fact that it has the highest melting point of all known elements, melting at . It also has the highest boiling point, at . Its density is 19.254 g/cm3, comparable with that of uranium and gold, and much higher (about 1.7 times) than that of lead. Polycrystalline tungsten is an intrinsically brittle and hard material (under standard conditions, when uncombined), making it difficult to work into metal. However, pure single-crystalline tungsten is more ductile and can be cut with a hard-steel hacksaw. Tungsten occurs in many alloys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorine
Fluorine is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists at Standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions as pale yellow Diatomic molecule, diatomic gas. Fluorine is extremely Reactivity (chemistry), reactive as it reacts with all other Periodic table, elements except for the light Noble gas, noble gases. It is highly toxicity, toxic. Among the elements, fluorine ranks Abundance of the chemical elements, 24th in cosmic abundance and 13th in crustal abundance. Fluorite, the primary mineral source of fluorine, which gave the element its name, was first described in 1529; as it was added to metal ores to lower their melting points for smelting, the Latin verb meaning gave the mineral its name. Proposed as an element in 1810, fluorine proved difficult and dangerous to separate from its compounds, and several early experimenters died or sustained injuries from their attempts. Only in 1886 did French chemist He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exothermic
In thermodynamics, an exothermic process () is a thermodynamic process or reaction that releases energy from the system to its surroundings, usually in the form of heat, but also in a form of light (e.g. a spark, flame, or flash), electricity (e.g. a battery), or sound (e.g. explosion heard when burning hydrogen). The term ''exothermic'' was first coined by 19th-century French chemist Marcellin Berthelot. The opposite of an exothermic process is an endothermic process, one that absorbs energy, usually in the form of heat. The concept is frequently applied in the physical sciences to chemical reactions where chemical bond energy is converted to thermal energy (heat). Two types of chemical reactions Exothermic and endothermic describe two types of chemical reactions or systems found in nature, as follows: Exothermic An exothermic reaction occurs when heat is released to the surroundings. According to the IUPAC, an exothermic reaction is "a reaction for which the overall stand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Chloride
The Chemical compound, compound hydrogen chloride has the chemical formula and as such is a hydrogen halide. At room temperature, it is a colorless gas, which forms white fumes of hydrochloric acid upon contact with atmospheric water vapor. Hydrogen chloride gas and hydrochloric acid are important in technology and industry. Hydrochloric acid, the aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride, is also commonly given the formula HCl. Reactions Hydrogen chloride is a diatomic molecule, consisting of a hydrogen atom H and a chlorine atom Cl connected by a Polar-covalent bond, polar covalent bond. The chlorine atom is much more Electronegativity, electronegative than the hydrogen atom, which makes this bond polar. Consequently, the molecule has a large Molecular dipole moment, dipole moment with a negative partial charge (δ−) at the chlorine atom and a positive partial charge (δ+) at the hydrogen atom. In part because of its high polarity, HCl is very soluble in water (and in other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Ruff
Otto Ruff (30 December 1871 – 17 September 1939) was a German chemist. Life Otto Ruff was born in Schwäbisch Hall, Württemberg. After becoming a pharmacist under the supervision of Carl Magnus von Hell (known from the Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky halogenation) at the University of Stuttgart he joined the group of Hermann Emil Fischer at the University of Berlin. Fischer was noted for his work on carbohydrates (sugars) and so Ruff started his career as an organic chemist. In 1898 he published his work on the transformation of d-Glucose to d-Arabinose, later called the Ruff degradation. Supported by the far-sighted Fischer, who recognized that while organic chemistry was now mature, physical chemistry was growing rapidly, Ruff became head of the new inorganic department in Berlin, working alongside Alfred Stock who was five years his junior. This drastic change in subject benefited Ruff during his work on chlorides sulfur compounds. In 1902 he married Meta Richter, a pharmacist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
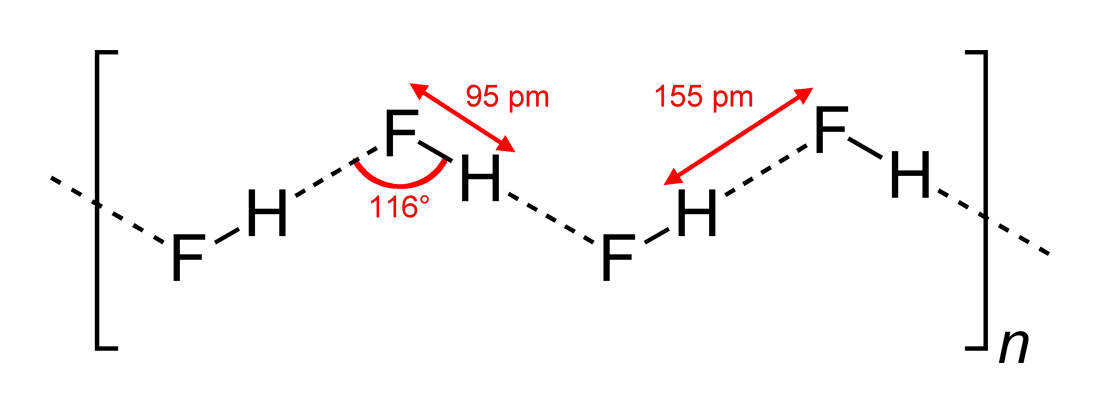
Hydrogen Fluoride
Hydrogen fluoride (fluorane) is an Inorganic chemistry, inorganic compound with chemical formula . It is a very poisonous, colorless gas or liquid that dissolves in water to yield hydrofluoric acid. It is the principal industrial source of fluorine, often in the form of hydrofluoric acid, and is an important feedstock in the preparation of many important compounds including pharmaceuticals and polymers such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). HF is also widely used in the petrochemical industry as a component of superacids. Due to strong and extensive hydrogen bonding, it boils near room temperature, a much higher temperature than other hydrogen halides. Hydrogen fluoride is an extremely dangerous gas, forming corrosive and penetrating hydrofluoric acid upon contact with moisture. The gas can also cause blindness by rapid destruction of the corneas. History In 1771 Carl Wilhelm Scheele prepared the aqueous solution, hydrofluoric acid in large quantities, although hydrofluoric acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tungsten Hexachloride
Tungsten hexachloride is an inorganic chemical compound of tungsten and chlorine with the chemical formula . This dark violet-blue compound exists as volatile crystals under standard conditions. It is an important starting reagent in the preparation of tungsten compounds. Other examples of charge-neutral hexachlorides are rhenium(VI) chloride and molybdenum(VI) chloride. The highly volatile tungsten hexafluoride is also known. As a d0 atom, tungsten hexachloride is diamagnetic. Preparation and structure Tungsten hexachloride can be prepared by chlorinating tungsten metal in a sealed tube at 600 °C: : Tungsten hexachloride exists in both blue and red polymorphs, referred to respectively as α and β. The wine-red β can be obtained by rapid cooling, whereas the blue α form is more stable at room temperature. Although these polymorphs are distinctly colored, their molecular structures are very similar. Both polymorphs feature molecules that have octahedral geometry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bar (unit)
The bar is a metric unit of pressure defined as 100,000 Pa (100 kPa), though not part of the International System of Units (SI). A pressure of 1 bar is slightly less than the current average atmospheric pressure on Earth at sea level (approximately 1.013 bar). By the barometric formula, 1 bar is roughly the atmospheric pressure on Earth at an altitude of 111 metres at 15 °C. The bar and the millibar were introduced by the Norwegian meteorologist Vilhelm Bjerknes, who was a founder of the modern practice of weather forecasting, with the bar defined as one megadyne per square centimetre. The SI brochure, despite previously mentioning the bar, now omits any mention of it.. The bar has been legally recognised in countries of the European Union since 2004. British Standard BS 350:2004 ''Conversion Factors for Units''. The US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) deprecates its use except for "limited use in meteorology" and lists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Logarithm
In mathematics, the common logarithm (aka "standard logarithm") is the logarithm with base 10. It is also known as the decadic logarithm, the decimal logarithm and the Briggsian logarithm. The name "Briggsian logarithm" is in honor of the British mathematician Henry Briggs who conceived of and developed the values for the "common logarithm". Historically', the "common logarithm" was known by its Latin name ''logarithmus decimalis'' or ''logarithmus decadis''. The mathematical notation for using the common logarithm is , , or sometimes with a capital ; on calculators, it is printed as "log", but mathematicians usually mean natural logarithm (logarithm with base ≈ 2.71828) rather than common logarithm when writing "log". Before the early 1970s, handheld electronic calculators were not available, and mechanical calculators capable of multiplication were bulky, expensive and not widely available. Instead, tables of base-10 logarithms were used in science, engineering and navi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |