|
Tube-lipped Nectar Bat
The tube-lipped nectar bat (''Anoura fistulata'') is a bat from Ecuador. It was described in 2005. It has a remarkably long tongue, which it uses to drink nectar. It additionally consumes pollen and insects. Taxonomy and etymology The tube-lipped nectar bat was first described in 2005. The species name ''fistulata'' is derived from the Latin word ''fistula'', meaning "tube". It refers to the bat's lower lip, which extends 3.3–4.8 mm beyond the upper lip and is rolled into a funnel shape. The exact function of the tube-lip is unknown. Description The bat has the longest tongue (8.5 cm) relative to its body size of any mammal. Its tongue is 150% the size of its overall body length. By convergent evolution, pangolins, the giant anteater (''Myrmecophaga tridactyla''), and the tube-lipped nectar bat all have a tongue that is detached from their hyoid bones and extend past the pharynx deep into the thorax. This extension lies between the sternum and the trachea. Biology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecuador
Ecuador, officially the Republic of Ecuador, is a country in northwestern South America, bordered by Colombia on the north, Peru on the east and south, and the Pacific Ocean on the west. It also includes the Galápagos Province which contains the Galapagos Islands in the Pacific, about west of the mainland. The country's Capital city, capital is Quito and its largest city is Guayaquil. The land that comprises modern-day Ecuador was once home to several groups of Indigenous peoples in Ecuador, indigenous peoples that were gradually incorporated into the Inca Empire during the 15th century. The territory was Spanish colonization of the Americas, colonized by the Spanish Empire during the 16th century, achieving independence in 1820 as part of Gran Colombia, from which it emerged as a sovereign state in 1830. The legacy of both empires is reflected in Ecuador's ethnically diverse population, with most of its million people being mestizos, followed by large minorities of Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
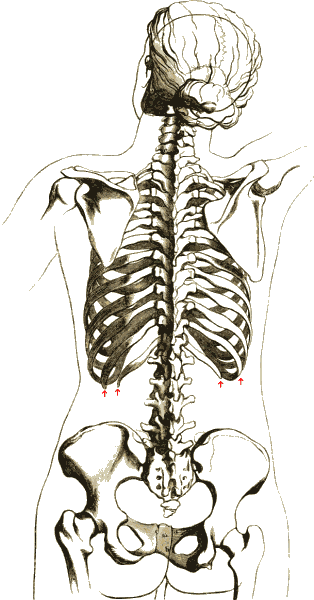
Rib Cage
The rib cage or thoracic cage is an endoskeletal enclosure in the thorax of most vertebrates that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum, which protect the vital organs of the thoracic cavity, such as the heart, lungs and great vessels and support the shoulder girdle to form the core part of the axial skeleton. A typical human thoracic cage consists of 12 pairs of ribs and the adjoining costal cartilages, the sternum (along with the manubrium and xiphoid process), and the 12 thoracic vertebrae articulating with the ribs. The thoracic cage also provides attachments for extrinsic skeletal muscles of the neck, upper limbs, upper abdomen and back, and together with the overlying skin and associated fascia and muscles, makes up the thoracic wall. In tetrapods, the rib cage intrinsically holds the muscles of respiration ( diaphragm, intercostal muscles, etc.) that are crucial for active inhalation and forced exhalation, and therefore has a major ventilatory fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammals Described In 2005
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles and birds, from which their ancestors diverged in the Carboniferous Period over 300 million years ago. Around 6,640 extant species of mammals have been described and divided into 27 orders. The study of mammals is called mammalogy. The largest orders of mammals, by number of species, are the rodents, bats, and eulipotyphlans (including hedgehogs, moles and shrews). The next three are the primates (including humans, monkeys and lemurs), the even-toed ungulates (including pigs, camels, and whales), and the Carnivora (including cats, dogs, and seals). Mammals are the only living members of Synapsida; this clade, together with Sauropsida (reptiles and birds), constitutes the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tailed Tailless Bat
The tailed tailless bat (''Anoura caudifer'') is a species of leaf-nosed bat from South America. Taxonomy The scientific name of this species is variously given as either ''A. caudifer'' or ''A. caudifera'', with scientists having argued for both names on the basis of Latin grammar and of the ICZN rules on the naming of species. When Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire first described the bat in 1818, he used the species name "''caudifer''", and this is the name currently preferred by such influential sources as the International Union for Conservation of Nature and ''Mammal Species of the World''. The common name of the bat is typically given as the "tailed tailless bat". This is because the species belongs to the genus ''Anoura'', commonly called the "tailless bats", yet it possesses a tail. However, the name is arguably somewhat misleading, since only three of the other seven species of "tailless bats" genuinely lack a tail. Of the remaining four, however, three have tails that ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geoffroy's Tailless Bat
Geoffroy's tailless bat (''Anoura geoffroyi'') is a species of phyllostomid bat from the American tropics. Description Geoffroy's tailless bat is a medium-sized bat, measuring around in total length and weighing . It has dark to dull brown fur over much of its body, with greyish-brown underparts and silvery-grey fur on the neck and shoulders. The wings are black or very dark brown, while the membrane between the legs is relatively small and covered in hair. As its name suggests, the bat does not possess a tail. It has a long muzzle, a projecting lower jaw, and short, rounded ears. Its tongue is long and narrow, with a pointed tip covered with fine papillae that help to draw up nectar when it feeds. Males and females do not vary much in size in Brazil, but in Trinidad, another area where ''Anoura geoffroyi'' lives, the females are reported to have slightly longer forearms than the males. Distribution and habitat Geoffroy's tailless bat is found from northern Mexico, through muc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corolla (flower)
Petals are modified leaves that form an inner whorl surrounding the reproductive parts of flowers. They are often brightly coloured or unusually shaped to attract pollinators. All of the petals of a flower are collectively known as the ''corolla''. Petals are usually surrounded by an outer whorl of modified leaves called sepals, that collectively form the ''calyx'' and lie just beneath the corolla. The calyx and the corolla together make up the perianth, the non-reproductive portion of a flower. When the petals and sepals of a flower are difficult to distinguish, they are collectively called tepals. Examples of plants in which the term ''tepal'' is appropriate include genera such as '' Aloe'' and '' Tulipa''. Conversely, genera such as '' Rosa'' and '' Phaseolus'' have well-distinguished sepals and petals. When the undifferentiated tepals resemble petals, they are referred to as "petaloid", as in petaloid monocots, orders of monocots with brightly coloured tepals. Since they in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centropogon
''Centropogon'' is a plant genus in the family (biology), family Campanulaceae. In systems where the Lobeliaceae are recognized as distinct, ''Centropogon'' is placed there. Selected species * ''Centropogon aequatorialis'' * ''Centropogon albostellatus'' * ''Centropogon arcuatus'' * ''Centropogon azuayensis'' * ''Centropogon baezanus'' * ''Centropogon balslevii'' * ''Centropogon brachysiphoniatus'' * ''Centropogon cazaletii'' * ''Centropogon chiltasonensis'' * ''Centropogon chontalensis'' * ''Centropogon coccineus'' * ''Centropogon comosus'' * ''Centropogon cornutus'' * ''Centropogon costaricae'' * ''Centropogon dissectus'' * ''Centropogon erythraeus'' * ''Centropogon eurystomus'' * ''Centropogon fimbriatulus'' * ''Centropogon hartwegii'' * ''Centropogon heteropilis'' * ''Centropogon hirtiflorus'' * ''Centropogon jeppesenii'' * ''Centropogon licayensis'' * ''Centropogon llanganatensis'' * ''Centropogon medusa'' * ''Centropogon nigricans'' * ''Centr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NBC News
NBC News is the news division of the American broadcast television network NBC. The division operates under NBCUniversal Media Group, a division of NBCUniversal, which is itself a subsidiary of Comcast. The news division's various operations report to the president of NBC News, Rebecca Blumenstein. The NBCUniversal News Group also comprises MSNBC, the network's 24-hour liberal cable news channel, as well as business and consumer news channels CNBC and CNBC World, the Spanish language and United Kingdom-based Sky News. NBC News aired the first regularly scheduled news program in American broadcast television history on February 21, 1940. The group's broadcasts are produced and aired from 30 Rockefeller Plaza, NBCUl's headquarters in New York City. The division presides over the flagship evening newscast ''NBC Nightly News'', the world's first of its genre morning television program, ''Today (American TV program), Today'', and the longest-running television series in American hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebrate Trachea
The trachea (: tracheae or tracheas), also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all animals' lungs. The trachea extends from the larynx and branches into the two primary bronchi. At the top of the trachea, the cricoid cartilage attaches it to the larynx. The trachea is formed by a number of horseshoe-shaped rings, joined together vertically by overlying ligaments, and by the trachealis muscle at their ends. The epiglottis closes the opening to the larynx during swallowing. The trachea begins to form in the second month of embryo development, becoming longer and more fixed in its position over time. Its epithelium is lined with column-shaped cells that have hair-like extensions called cilia, with scattered goblet cells that produce protective mucins. The trachea can be affected by inflammation or infection, usually as a result of a viral illness affectin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tongue
The tongue is a Muscle, muscular organ (anatomy), organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for chewing and swallowing as part of the digestive system, digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste buds housed in numerous lingual papillae. It is sensitive and kept moist by saliva and is richly supplied with nerves and blood vessels. The tongue also serves as a natural means of cleaning the teeth. A major function of the tongue is to enable speech in humans and animal communication, vocalization in other animals. The human tongue is divided into two parts, an oral cavity, oral part at the front and a pharynx, pharyngeal part at the back. The left and right sides are also separated along most of its length by a vertical section of connective tissue, fibrous tissue (the lingual septum) that results in a groove, the median sulcus, on the tongue's surface. There are two groups of glossal muscles. The f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternum
The sternum (: sternums or sterna) or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. Shaped roughly like a necktie, it is one of the largest and longest flat bones of the body. Its three regions are the manubrium, the body, and the xiphoid process. The word ''sternum'' originates from Ancient Greek στέρνον (''stérnon'') 'chest'. Structure The sternum is a narrow, flat bone, forming the middle portion of the front of the chest. The top of the sternum supports the clavicles (collarbones) and its edges join with the costal cartilages of the first two pairs of ribs. The inner surface of the sternum is also the attachment of the sternopericardial ligaments. Its top is also connected to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The sternum consists of three main parts, listed from the top: * Man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |