|
Tsarevich Ivan Ivanovich Of Russia
Ivan Ivanovich (; 28 March 1554 – 19 November 1581) was the second son of Russian tsar Ivan the Terrible by his first wife Anastasia Romanovna. He was the tsarevich (heir apparent) until he suddenly died; historians generally believe that his father killed him in a fit of rage. Early life Ivan was the second son of Ivan IV of Russia ("the Terrible") by his first wife Anastasia Romanovna. His brother was Feodor, who would eventually succeed his father as tsar. The young Ivan accompanied his father during the Massacre of Novgorod at the age of 15. For five weeks, he and his father would watch the '' oprichniki'' with enthusiasm and retire to church for prayer. At the age of 27, Ivan was at least as well read as his father, and in his free time, wrote a biography on Antony of Siya. Ivan is reputed to have once saved his father from an assassination attempt. A Livonian prisoner named Bykovski raised a sword against the tsar, only to be rapidly stabbed by the tsarevich. Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
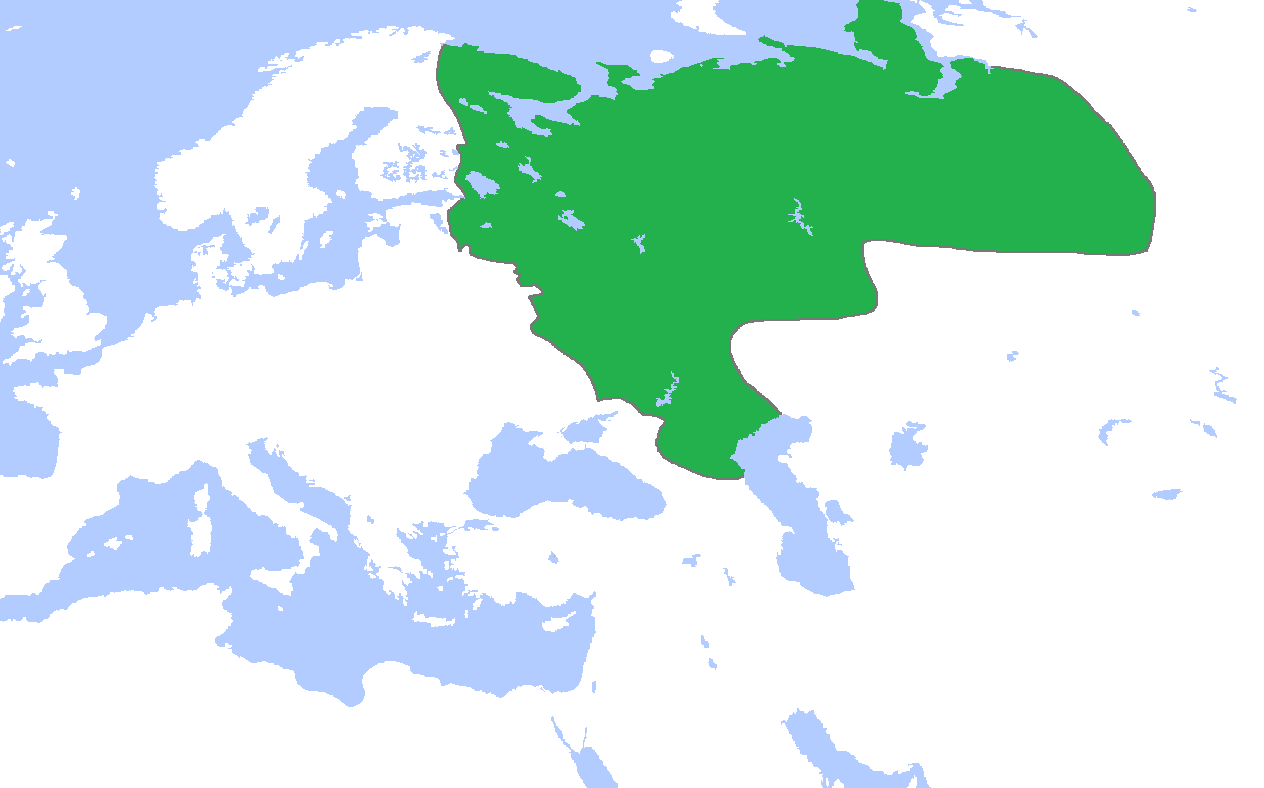
Ivan The Terrible
Ivan IV Vasilyevich (; – ), commonly known as Ivan the Terrible,; ; monastic name: Jonah. was Grand Prince of Moscow, Grand Prince of Moscow and all Russia from 1533 to 1547, and the first Tsar of all Russia, Tsar and Grand Prince of all Russia from 1547 until his death in 1584. Ivan's reign was characterised by Russia's transformation from a medieval state to a fledgling empire, but at an immense cost to its people and long-term economy. Ivan IV was the eldest son of Vasili III of Russia, Vasili III by his second wife Elena Glinskaya, and a grandson of Ivan III of Russia, Ivan III. He succeeded his father after his death, when he was three years old. A group of reformers united around the young Ivan, crowning him as tsar in 1547 at the age of 16. In the early years of his reign, Ivan ruled with the group of reformers known as the Chosen Council and established the ''Zemsky Sobor'', a new assembly convened by the tsar. He also revised the Sudebnik of 1550, legal code and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oprichnik
The oprichnina (, ; ) was a state policy implemented by Tsar Ivan the Terrible in Tsardom of Russia, Russia between 1565 and 1572. The policy included mass Political repression, repression of the boyars (Russian aristocrats), including public executions and confiscation of their land and property. In this context the term can also refer to: *The notorious organization of six thousand Oprichniki, the first political police in the history of Russia. *The portion of Russia, ruled directly by Ivan the Terrible, where his Oprichniki operated. *The corresponding period of Russian history. The term ''oprichnina'', which Ivan coined for this policy, derives from the Russian word ''oprich'' ( 'apart from', 'except'). Causes In 1558, Tsar Ivan IV started the Livonian War. A broad coalition, which included Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569) , Poland, Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Lithuania and Sweden, became drawn into the war against Russia. The war became drawn-out (it continued until 1583) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasili III Of Russia
Vasili III Ivanovich (; 25 March 14793 December 1533) was Grand Prince of Moscow and all Russia from 1505 until his death in 1533. He was the son of Ivan III and Sophia Paleologue and was christened with the name Gavriil (). Following on the ambitions of his predecessor Ivan, Vasili conquered Pskov, Ryazan and Smolensk as well as strengthening Russian influence in Kazan and to the Volga region. Several nobles were either exiled, sentenced or executed for criticizing his policies. Foreign affairs Vasili III maintained the policies initiated by his father Ivan III, focusing much of his reign on consolidating the territorial gains achieved by Ivan. Vasili annexed the last surviving autonomous provinces: Pskov in 1510, appanage of Volokolamsk in 1513, principalities of Ryazan in 1521 and Novgorod-Seversky in 1522. Vasili also took advantage of the difficult position of Sigismund of Poland to capture Smolensk, the great eastern fortress of Lithuania (siege started 1512 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Of Troubles
The Time of Troubles (), also known as Smuta (), was a period of political crisis in Tsardom of Russia, Russia which began in 1598 with the death of Feodor I of Russia, Feodor I, the last of the Rurikids, House of Rurik, and ended in 1613 with the accession of Michael of Russia, Michael I of the House of Romanov. It was a period of deep social crisis and lawlessness following the death of Feodor I, a weak and possibly Intellectual disability, intellectually disabled ruler who died without an heir. His death ended the Rurik dynasty, leading to a violent succession crisis with numerous usurpers and false Dmitrys (imposters) claiming the title of List of Russian monarchs, tsar. Russia experienced the Russian famine of 1601–1603, famine of 1601–1603, which killed almost a third of the population, within three years of Feodor's death. Russia was also occupied by the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth during the Polish–Russian War (1609–1618), Polish–Russian War an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boris Godunov
Boris Feodorovich Godunov (; ; ) was the ''de facto'' regent of Russia from 1585 to 1598 and then tsar from 1598 to 1605 following the death of Feodor I, the last of the Rurik dynasty. After the end of Feodor's reign, Russia descended into the Time of Troubles. Early years Boris was the son of Feodor Ivanovich Godunov "Krivoy" (, died c. 1568–1570) and his wife Stepanida Ivanovna. His older brother Vasily died young and without issue. There is a version according to which the Godunovs were descended from the Tatar ''murza'' Chet, who came to Russia in 1330 during the reign of Ivan Kalita. This version was included in later editions of the 16th-century '' Gosudarev Rodoslovets'', but historians have raised doubts about this version of Godunov's ancestry due to various chronological and genealogical issues. Godunov's career began at the court of Ivan the Terrible. He is mentioned in 1570 for taking part in the Serpeisk campaign as an archer of the guard. The following yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
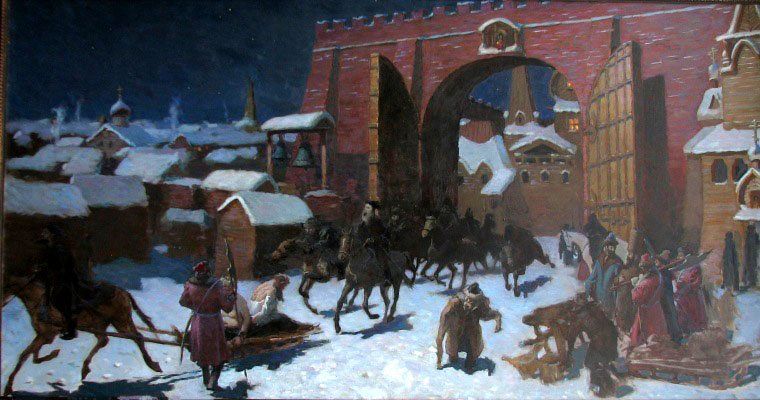
Ivan The Terrible And His Son Ivan
''Ivan the Terrible and His Son Ivan on 16 November 1581'' is a painting by Russian realism (arts), realist artist Ilya Repin made between 1883 and 1885. It depicts the grief-stricken Tsars of Russia, Russian tsar Ivan the Terrible cradling his dying son, the Tsarevich Tsarevich Ivan Ivanovich of Russia, Ivan Ivanovich, shortly after Ivan the Terrible had dealt a fatal blow to his son's head in a fit of anger. The painting portrays the anguish and remorse on the face of the elder Ivan and the shock and heartbreak of the dying Tsarevich, shedding a tear at the unexpected betrayal and shock of having been killed at his father's hands. Repin used Grigoriy Myasoyedov, his friend and fellow artist, as the model for Ivan the Terrible, and writer Vsevolod Garshin for the Tsarevich. In 1885, upon completion of the oil-on-canvas work, Repin sold it to Pavel Tretyakov for display in his Tretyakov Gallery in Moscow. It has been called one of Russia's most famous and controversial paintings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilya Repin
Ilya Yefimovich Repin ( – 29 September 1930) was a Russian painter, born in what is today Ukraine. He became one of the most renowned artists in Russian Empire, Russia in the 19th century. His major works include ''Barge Haulers on the Volga'' (1873), ''Religious Procession in Kursk Province'' (1880–1883), ''Ivan the Terrible and His Son Ivan'' (1885); and ''Reply of the Zaporozhian Cossacks'' (1880–1891). He is also known for the revealing portraits he made of the leading Russian literary and artistic figures of his time, including Mikhail Glinka, Modest Mussorgsky, Pavel Tretyakov, and especially Leo Tolstoy, with whom he had a long friendship. Repin was born in Chuguev, Russian Empire (now in Ukraine). Repin was of the Zaporozhian Cossacks, Zaporozhian Cossack descent on his paternal grandfather's side. His father had served in an Uhlan#Russian Uhlans, Uhlan Regiment in the Russian army, and then sold horses. Repin began painting icons at age sixteen. He failed at his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Pskov
The siege of Pskov, known as the Pskov Defense in Russia (), took place between August 1581 and February 1582, when the army of the Polish king and Grand Duke of Lithuania Stephen Báthory laid an unsuccessful siege and successful blockade of the city of Pskov during the final stage of the Livonian War of 1558–1583. The first detachments of the Polish–Lithuanian army, which in the previous two years captured Polotsk (1579) and Velikiye Luki (1580), appeared at the walls of Pskov on August 18, 1581. This action completely cut off Russian forces from the territory of Livonia. The main invading force (31,000 men, Polish, Lithuanian, Hungarian, Bohemian, Wallachian, and German soldiers) laid siege to the city on August 24-26. Prince Vasili Skopin-Shuisky was nominally in charge of the defense of Pskov, but Prince Ivan Shuisky was the one to actually implement it. The latter had up to 4,000 dvoryane, streltsy, and Cossacks and some 12,000 armed citizens of Pskov and its surro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livonian War
The Livonian War (1558–1583) concerned control of Terra Mariana, Old Livonia (in the territory of present-day Estonia and Latvia). The Tsardom of Russia faced a varying coalition of the Denmark–Norway, Dano-Norwegian Realm, the Kingdom of Sweden (1523–1611), Kingdom of Sweden, and the Polish–Lithuanian union, Union (later Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Commonwealth) of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569), Kingdom of Poland. From 1558 to 1578, Russia dominated the region with early military successes at Tartu, Dorpat (Tartu) and Narva. The Russian dissolution of the Livonian Confederation brought Poland–Lithuania into the conflict, and Sweden and Denmark-Norway intervened between 1559 and 1561. Swedish Estonia was established despite constant invasion from Russia, and Frederick II of Denmark, Frederick II of Denmark-Norway bought the old Bishopric of Ösel–Wiek, which he placed under the control of his brother Magnus of Holstein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iván El Terrible Y Su Hijo, Por Iliá Repin
Ivan () is a Slavic male given name, connected with the variant of the Greek name (English: John) from Hebrew meaning 'God is gracious'. It is associated worldwide with Slavic countries. The earliest person known to bear the name was the Bulgarian Saint Ivan of Rila. It is very popular in Russia, Ukraine, Croatia, Serbia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Slovenia, Bulgaria, Belarus, North Macedonia, and Montenegro and has also become more popular in Romance-speaking countries since the 20th century. Etymology Ivan is the common Slavic Latin spelling, while Cyrillic spelling is two-fold: in Bulgarian, Russian, Macedonian, Serbian and Montenegrin it is , while in Belarusian and Ukrainian it is . The Old Church Slavonic (or Old Cyrillic) spelling is . It is the Slavic relative of the Latin name , corresponding to English ''John''. This Slavic version of the name originates from New Testament Greek (''Iōánnēs'') rather than from the Latin . The Greek name is in turn deriv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bride-show
The bride-show (; ; zh, 后妃選納) was a custom of Byzantine emperors and Russian tsars to choose a wife from among the most beautiful maidens of the country. A similar practice also existed in Imperial China. Byzantine Empire The method to select a bride for the emperor through the method of bride-show is known to have been used at least from the 8th century onward. Irene of Athens was likely chosen for Leo IV the Khazar by this method, though it has not been confirmed. The first recorded bridal show in Byzantine was however the one in 788, in which Maria of Amnia was selected for emperor Constantine. The method was regularly used in the 8th and 9th centuries. Among notable bride-shows was the one in which Theodora was selected by Theophilos and Kassia rejected. None of the empresses of the 10th century onward, however, are confirmed to have been selected this way, and the custom was surely dead by the 13th century. Imperial China Imperial China practiced a simil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eric XIV Of Sweden
Erik XIV or Eric XIV (13 December 153326 February 1577) became King of Sweden following the death of his father, Gustav I, on 29 September 1560. During a 1568 rebellion against him, Erik was incarcerated by his half-brother John III. He was formally deposed by the Riksdag on 26 January 1569. Erik was also ruler of Estonia, after it placed itself under Swedish protection in 1561. While Erik has been regarded as intelligent and artistically skilled, as well as politically ambitious, early in his reign he showed signs of mental instability, a condition that eventually led to insanity. Some scholars claim that his illness began early during his reign, while others believe that it first manifested with the Sture murders. Erik, having been imprisoned and deposed, was most likely murdered. An examination of his remains in 1958 confirmed that he probably died of arsenic poisoning. Early years Erik XIV was born at Tre Kronor Castle, the morning of 13 December 1533. His mot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |