|
Tropical Storm Frances (other)
The name Frances has been used for eight tropical cyclones in the Atlantic Ocean and for one in the Australian region tropical cyclone, Australian region. Atlantic Ocean * Hurricane Frances (1961): Caused flooding in Puerto Rico, peaked at Category 4 west of Bermuda, subtropical at Nova Scotia * Tropical Storm Frances (1968): Travelled across the central Atlantic Ocean without affecting land * Hurricane Frances (1976): Curved over the central Atlantic, affected the Azores as an extratropical storm * Hurricane Frances (1980): Travelled up the central Atlantic Ocean without affecting land * Hurricane Frances (1986): Briefly drifted over the western Atlantic but never affected land * Hurricane Frances (1992): Threatened Bermuda but did not strike the island, then hit Spain as an extratropical storm * Tropical Storm Frances (1998): A weak storm that caused flooding in East Texas and southern Louisiana * Hurricane Frances (2004): A powerful Category 4 hurricane that struck the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its location and strength, a tropical cyclone is referred to by different names, including hurricane (), typhoon (), tropical storm, cyclonic storm, tropical depression, or simply cyclone. A hurricane is a strong tropical cyclone that occurs in the Atlantic Ocean or northeastern Pacific Ocean, and a typhoon occurs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. In the Indian Ocean, South Pacific, or (rarely) South Atlantic, comparable storms are referred to simply as "tropical cyclones", and such storms in the Indian Ocean can also be called "severe cyclonic storms". "Tropical" refers to the geographical origin of these systems, which form almost exclusively over tropical seas. "Cyclone" refers to their winds moving in a circle, whirling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe and Asia from the "New World" of the Americas in the European perception of Earth, the World. The Atlantic Ocean occupies an elongated, S-shaped basin extending longitudinally between Europe and Africa to the east, and North America, North and South America to the west. As one component of the interconnected World Ocean, it is connected in the north to the Arctic Ocean, to the Pacific Ocean in the southwest, the Indian Ocean in the southeast, and the Southern Ocean in the south (other definitions describe the Atlantic as extending southward to Antarctica). The Atlantic Ocean is divided in two parts, by the Equatorial Counter Current, with the North(ern) Atlantic Ocean and the South(ern) Atlantic Ocean split at about 8th paralle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Region Tropical Cyclone
An Australian region tropical cyclone is a non- frontal, low-pressure system that has developed within an environment of warm sea surface temperatures and little vertical wind shear aloft in either the Southern Indian Ocean or the South Pacific Ocean. Within the Southern Hemisphere there are officially three areas where tropical cyclones develop on a regular basis: the South-West Indian Ocean between Africa and 90°E, the Australian region between 90°E and 160°E, and the South Pacific basin between 160°E and 120°W. The Australian region between 90°E and 160°E is officially monitored by the Australian Bureau of Meteorology, the Indonesian Meteorology, Climatology, and Geophysical Agency, and the Papua New Guinea National Weather Service, while others like the Fiji Meteorological Service and the United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration also monitor the basin. Each tropical cyclone year within this basin starts on 1 July and runs throughout the year, enco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Frances (1961)
The 1961 Atlantic hurricane season was a hyperactive Atlantic hurricane season, with an accumulated cyclone energy (ACE) total of 189. The season, however, was an average one in terms of named storms. The season featured eight hurricanes and a well above average number of five major hurricanes. It was previously thought that the season had a record-tying seven major hurricanes, before the Atlantic hurricane reanalysis project downgraded two storms in 2019. Two Category 5 hurricanes were seen in 1961, making it one of only seven Atlantic hurricane seasons to feature multiple Category 5 hurricanes in one season. The season started on June 15, and ended on November 15. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin. The first system, an operationally unclassified tropical depression, formed offshore east Central Florida on June 10, but dissipated a few days later. Next, Hurricane Anna developed in the eastern C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Storm Frances (1968)
The 1968 Atlantic hurricane season was one of five Atlantic hurricane seasons during the satellite era not to feature a major hurricane, the others being 1972, 1986, 1994, and 2013. The season officially began on June 1 and lasted until November 30, dates which conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin. It was a below average season in terms of tropical storms, with a total of eight nameable storms. The first system, Hurricane Abby, developed in the northwestern Caribbean on June 1. Abby moved northward and struck Cuba, bringing heavy rainfall and flooding to western portions of the island. Making landfall in Florida on June 4, Abby caused flooding and spawned four tornadoes, but left behind little damage. Overall, the hurricane resulted in six deaths and about $450,000 (1968 USD) in damage. In late June, Tropical Storm Candy brought minor flooding and spawned several tornadoes across portions o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
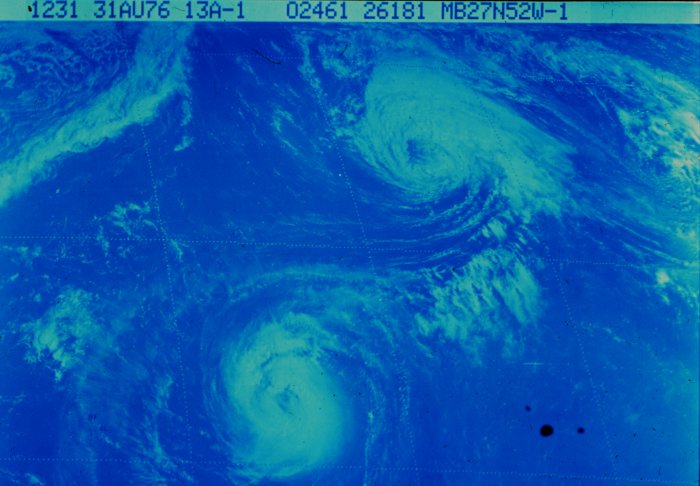
Hurricane Frances (1976)
The 1976 Atlantic hurricane season featured only one fully tropical storm throughout both the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico, a rare occurrence. The season officially began on June 1 and lasted until November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin. However, the first system, a subtropical storm, developed in the Gulf of Mexico on May 21, several days before the official start of the season. The system spawned nine tornadoes in Florida, resulting in about $628,000 (1976 USD) in damage, though impact was minor otherwise. The season was near average, with ten tropical storm forming, of which six became hurricanes. Two of those six became major hurricanes, which are Category 3 or higher on the Saffir–Simpson scale. The strongest hurricane of the season was Hurricane Belle, which reached Category 3 intensity east of North Carolina. Belle later struck Long Island, New York, as a Category 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Frances (1980)
The 1980 Atlantic hurricane season featured nine hurricanes, the most since 1969. The season officially began on June 1, 1980, and lasted until November 30, 1980. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic Ocean. The season was fairly active, with sixteen tropical cyclones forming, eleven of which intensified into a tropical storm. It was the first time since the 1971 season that there were no active tropical cyclones in the Atlantic basin during the month of June. The season occurred during an ENSO-neutral phase, having neither an El Niño nor a La Niña. Three tropical cyclones in the Atlantic Ocean in 1980 were notable. Hurricane Allen was the then-earliest Category 5 hurricane on record, reaching that intensity on August 5. The storm devastated portions of the Caribbean, Mexico, and the United States. Overall, Allen caused about $2.57 billion and at least 269 deaths. Tropical St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Frances (1986)
The 1986 Atlantic hurricane season was a very inactive season that produced 10 depressions, 6 named storms, 4 hurricanes, and no major hurricanes. The season officially began on June 1, 1986, and lasted until November 30, 1986. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin. During the 1986 season, the first subtropical depression formed in the first week of June, while the last tropical cyclone dissipated at the end of the third week of November. The 1986 season had lower than average activity because of an ongoing El Niño event, and was the least active season in the North Atlantic since the 1983 Atlantic hurricane season. This was also the first season since 1972 to have no major hurricanes. The season started on June 5 when Subtropical Depression One formed near the Bahamas, which would later gain tropical characteristics and become the first tropical storm of the season; Tropical Storm Andrew. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Frances (1992)
The 1992 Atlantic hurricane season was a significantly below average season, but it did feature Hurricane Andrew, the costliest Atlantic hurricane known at the time, surpassing Hugo of 1989 and later surpassed by Katrina of 2005. The season officially began on June 1, 1992, and lasted until November 30, 1992. The first storm, an unnamed subtropical storm, developed in the central Atlantic on April 21, over a month before the official start of hurricane season. On August 16, Hurricane Andrew formed and would later strike the Bahamas, as well U.S. States of Florida and Louisiana, becoming the costliest Atlantic hurricane on record until the record was surpassed just over 13 years later. Andrew caused $27.3 billion (1992 USD) in damage, mostly in Florida, as well as 65 fatalities. In addition, Andrew was also the strongest hurricane of the season, reaching winds of while approaching Florida. Later in the season, just under one month after Andrew struck land three times, Hurricanes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Storm Frances (1998)
Tropical Storm Frances caused extensive flooding in Mexico and Texas in September 1998. The sixth tropical cyclone and sixth named storm of the annual hurricane season, Frances developed from a low pressure area in the Gulf of Mexico on September 8. The cyclone moved northward through the western Gulf of Mexico, making landfall across the central Texas coastline before recurving across the Midwest through southeast Canada and New England. A large tropical cyclone for the Atlantic basin,Robert T. Merrill (1984)A Comparison of Large and Small Tropical Cyclones.Monthly Weather Review. Retrieved on 2008-07-14. yet an average sized system by western Pacific standards, the storm produced heavy rains across the Isthmus of Tehuantepec, Texas, western Louisiana and the Great Plains. The interaction between developing Frances and Pacific Tropical Storm Javier produced torrential rainfall in southeastern Mexico, causing flooding that killed over 200 people and caused $63&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Frances
Hurricane Frances was the second most intense tropical cyclone in the Atlantic during 2004 and proved to be very destructive in Florida. It was the sixth named storm, the fourth hurricane, and the third major hurricane of the 2004 Atlantic hurricane season. The system crossed the open Atlantic in late August, moving to the north of the Lesser Antilles while strengthening. Its outer bands struck Puerto Rico and the British Virgin Islands while passing north of the Caribbean Sea. The storm's maximum sustained wind peaked at , achieving Category 4 on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale. As the system's forward motion slowed, the eye passed over San Salvador Island and very close to Cat Island in the Bahamas. Frances was the first hurricane to impact the entire Bahamian archipelago since 1928 and almost completely destroyed their agricultural economy. Frances then passed over the central sections of Florida, three weeks after Hurricane Charley, causing significant damage to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclone Frances (2017)
In meteorology, a cyclone () is a large air mass that rotates around a strong center of low atmospheric pressure, counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above (opposite to an anticyclone). Cyclones are characterized by inward-spiraling winds that rotate about a zone of low pressure. The largest low-pressure systems are polar vortices and extratropical cyclones of the largest scale (the synoptic scale). Warm-core cyclones such as tropical cyclones and subtropical cyclones also lie within the synoptic scale. Mesocyclones, tornadoes, and dust devils lie within smaller mesoscale. Upper level cyclones can exist without the presence of a surface low, and can pinch off from the base of the tropical upper tropospheric trough during the summer months in the Northern Hemisphere. Cyclones have also been seen on extraterrestrial planets, such as Mars, Jupiter, and Neptune. Cyclogenesis is the process of cyclone formation a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |