|
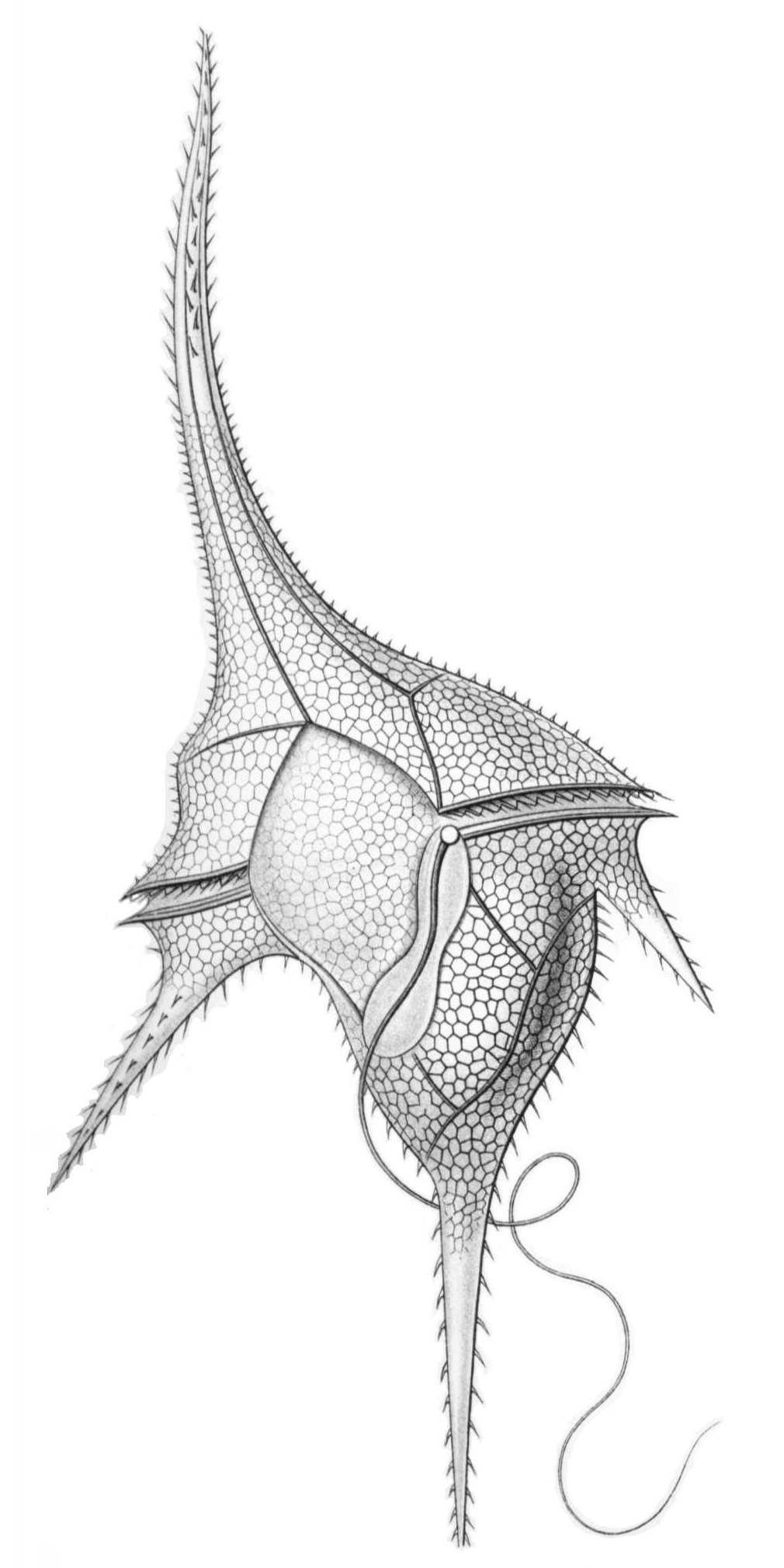
Tripos Elegans
''Tripos elegans'' is a species of dinoflagellates in the family Ceratiaceae Ceratiaceae is a family of dinoflagellates in the order Gonyaulacales Gonyaulacales is an order of dinoflagellate The dinoflagellates (Greek δῖνος ''dinos'' "whirling" and Latin ''flagellum'' "whip, scourge") are a monophyletic group o .... References External links ''Tripos elegans'' at the World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS)''Tripos elegans'' at AlgaeBase Gonyaulacales Protists described in 2013 Dinoflagellate species {{Dinoflagellate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schröder (taxonomic Authority)
Schröder ( Schroeder) is a German surname often associated with the Schröder family. Notable people with the surname include: * Arthur Schröder (1892–1986), German actor * Atze Schröder, stage name of German comedian Hubertus Albers * Bernd Schröder (born 1942), German football manager * Björn Schröder (born 1968), German and Swiss curler and coach * Björn Schröder (born 1980), German cyclist * Bob Schroder (born 1944), American baseball player * Carly Schroeder (born 1990), American actress * Christa Schroeder (1908–1984), Adolf Hitler's personal secretary * Christian Mathias Schröder (1778–1860), German politician * Corina Schröder (born 1986), German footballer * Dennis Schröder (born 1993), German basketball player * Diana Schröder (born 1975), German artistic gymnast * Dominik Schröder (1910–1974), German ethnologist * Doris Schröder-Köpf (born 1963), German journalist * Edward Schröder (1858–1942), German Germanist and mediaevalist * Ernst Schr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceratium
The genus ''Ceratium'' is restricted to a small number (about 7) of freshwater dinoflagellate species. Previously the genus contained also a large number of marine dinoflagellate species. However, these marine species have now been assigned to a new genus called ''Tripos''. ''Ceratium'' dinoflagellates are characterized by their armored plates, two flagella, and horns. They are found worldwide and are of concern due to their blooms. Taxonomy The genus was originally published in 1793 by Shrank, F. von Paula. The taxonomy of C''eratium'' varies among several sources. One source states the taxonomy as: Kingdom Chromista, Phylum Miozoa, Class Dinophyceae, Order Gonyaulacales, and Family Ceratiaceae. Another source lists the taxonomy as Kingdom Protozoa, Phylum Dinoflagellata, Class Dinophyceae, Order Gonyaulacales, and Family Ceratiaceae. The taxonomic information listed on the right includes Kingdom Chromalveolate. Thus, sources disagree on the higher levels of classification, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceratiaceae
Ceratiaceae is a family of dinoflagellates in the order Gonyaulacales Gonyaulacales is an order of dinoflagellate The dinoflagellates (Greek δῖνος ''dinos'' "whirling" and Latin ''flagellum'' "whip, scourge") are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are .... References External links * Gonyaulacales Algae families Dinoflagellate families {{Dinoflagellate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gonyaulacales
Gonyaulacales is an order of dinoflagellate The dinoflagellates (Greek δῖνος ''dinos'' "whirling" and Latin ''flagellum'' "whip, scourge") are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered algae. Dinoflagellates are ...s found in marine environments. References Dinoflagellate orders {{dinoflagellate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protists Described In 2013
A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), the exclusion of other eukaryotes means that protists do not form a natural group, or clade. Therefore, some protists may be more closely related to animals, plants, or fungi than they are to other protists. However, like the groups ''algae'', ''invertebrates'', and ''protozoans'', the biological category ''protist'' is used for convenience. Others classify any unicellular eukaryotic microorganism as a protist. The study of protists is termed protistology. History The classification of a third kingdom separate from animals and plants was first proposed by John Hogg in 1860 as the kingdom Protoctista; in 1866 Ernst Haeckel also proposed a third kingdom Protista as "the kingdom of primitive forms". Originally these also included prokaryotes, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |