|
Trindade And Martim Vaz
Trindade and Martim Vaz (, ) is an archipelago located in the South Atlantic Ocean about east off the coast of the Brazilian state of Espírito Santo, of which it forms a part. The archipelago has a total area of and a navy-supported research station of up to 8 persons. The archipelago consists of five islands and several rock (landform), rocks and stack (geology), stacks; Trindade is the largest island, with an area of ; about east of it are the tiny Martim Vaz islets, with a total area of . The islands are of volcanic origin and have rugged terrain; the date of last eruption in the island is unknown, but occurred on the southeastern tip of the island at Vulcão de Paredão. They are largely barren, except for the southern part of Trindade. They were discovered in 1502 by Portuguese explorer Estêvão da Gama (c. 1470), Estêvão da Gama and stayed Portuguese until they became part of Brazil at its Independence of Brazil, independence in 1822. From 1895 to 1896, Trindade was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinidad And Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago, officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean, comprising the main islands of Trinidad and Tobago, along with several List of islands of Trinidad and Tobago, smaller islets. The capital city is Port of Spain, while its largest and most populous municipality is Chaguanas. Despite its proximity to South America, Trinidad and Tobago is generally considered to be part of the Caribbean. Trinidad and Tobago is located northeast off the coast of Venezuela, south of Grenada, and 288 kilometres (155 nautical miles) southwest of Barbados. Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous peoples inhabited Trinidad for centuries prior to Spanish Empire, Spanish colonization, following the arrival of Christopher Columbus in 1498. Spanish governor José María Chacón surrendered the island to a British fleet under Sir Ralph Abercromby's command in 1797. Trinidad and Tobago were ceded to Britain in 1802 under t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
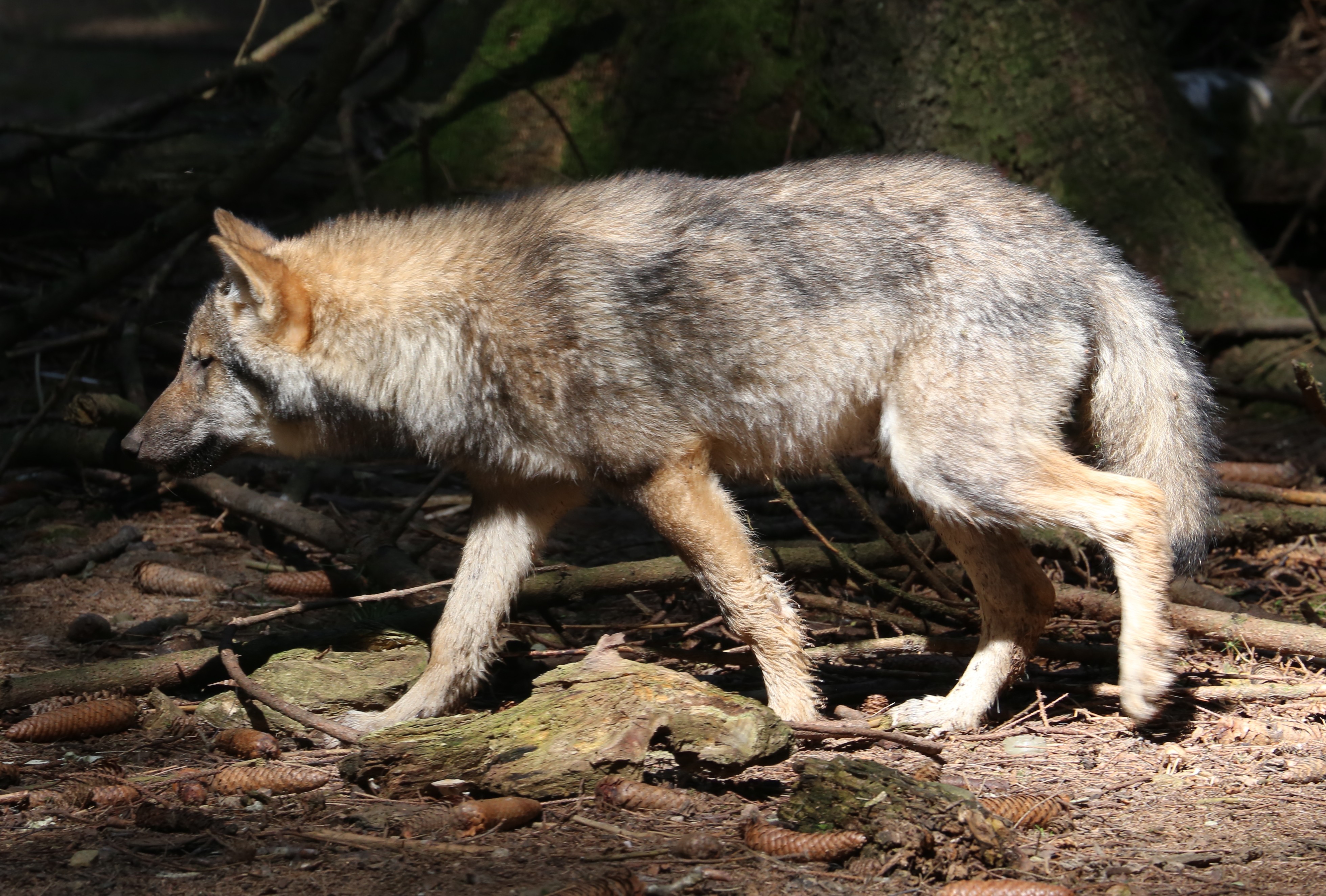
Local Extinction
Local extinction, also extirpation, is the termination of a species (or other taxon) in a chosen geographic area of study, though it still exists elsewhere. Local extinctions are contrasted with extinction, global extinctions. Local extinctions mark a change in the ecology of an area. It has sometimes been followed by a replacement of the species taken from other locations, such as with wolf reintroduction. Discussion Glacial period, Glaciation is one factor that leads to local extinction. This was the case during the Quaternary glaciation, Pleistocene glaciation event in North America. During this period, most of the native North American species of earthworm were killed in places covered by glaciation. This left them open for colonization by European earthworms brought over in soil from Europe. Species naturally become extinct from islands over time; this can be either local extinction if the species also occurs elsewhere, or in cases of endemism, island endemism, outright ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippe D'Auvergne
} Vice admiral (Royal Navy), Vice-Admiral Philippe d'Auvergne (13 November 1754 – 18 September 1816) was a Royal Navy officer who served in the American War of Independence and French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. D'Auvergne also worked as a spymaster for British intelligence, engaging in plots to destabilise the First French Republic's control over Brittany and Normandy which included printing counterfeit money to cause hyperinflation. Early life Philippe D'Auvergne was born in Jersey, where his family had lived for four centuries. His mother Elizabeth Le Geyt (d. 1754), the daughter of Philippe Le Geyt, Bailiff (Channel Islands), Lieut-Bailiff of Jersey from 1729 to 1746, died giving birth to him. His father, Charles Dauvergne (1724-1797), was an ex-British Army officer, advisor to British Cabinet Committees and aide-de-camp to various Governors; they included John Huske, Governor from 1749 to 1761, who left Charles £2,000 when he died in January 1761. His younger hal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cutter (boat)
A cutter is any of various types of watercraft. The term can refer to the sail plan, rig (sail plan) of a sailing vessel (but with regional differences in definition), to a governmental enforcement agency vessel (such as a coast guard or border force cutter), to a type of ship's boat which can be used under sail or oars, or, historically, to a type of fast-sailing vessel introduced in the 18th century, some of which were used as small warships. As a sailing rig, a cutter is a single-masted boat, with two or more headsails. On the eastern side of the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, the two headsails on a single mast is the fullest extent of the modern definition. In U.S. waters, a greater level of complexity applies, with the placement of the mast and the rigging details of the bowsprit taken into account so a boat with two headsails may be classed as a sloop. Government agencies use the term "cutter" for vessels employed in patrolling their territorial waters and other enforcement a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilha Da Trindade - 2022 (52551543050) , an island and populated place of the coast of mainland Mozambique
{{geodis ...
Ilha (Portuguese for "island") may refer to the following places in Portugal or Mozambique: *Ilha (Santana), a parish in the municipality of Santana, Madeira *Ilha (Pombal), a former parish in the municipality of Pombal *Island of Mozambique The Island of Mozambique () lies off northern Mozambique, between the Mozambique Channel and Mossuril Bay, and is part of Nampula Province. Prior to 1898, it was the capital of colonial Portuguese East Africa. With its rich history and sandy b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monarchy Of The United Kingdom
The monarchy of the United Kingdom, commonly referred to as the British monarchy, is the form of government used by the United Kingdom by which a hereditary monarch reigns as the head of state, with their powers Constitutional monarchy, regulated by the British constitution. The term may also refer to the role of the British royal family, royal family within the Politics of the United Kingdom, UK's broader political structure. The monarch since 8 September 2022 is King Charles III, who ascended the throne on Death and state funeral of Elizabeth II, the death of Queen Elizabeth II, his mother. The monarch and British royal family, their immediate family undertake various official, ceremonial, diplomatic and representational duties. Although formally the monarch has authority over the Government of the United Kingdom, governmentwhich is known as "His Majesty's Government (term), His/Her Majesty's Government"this power may only be used according to laws enacted in Parliament of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
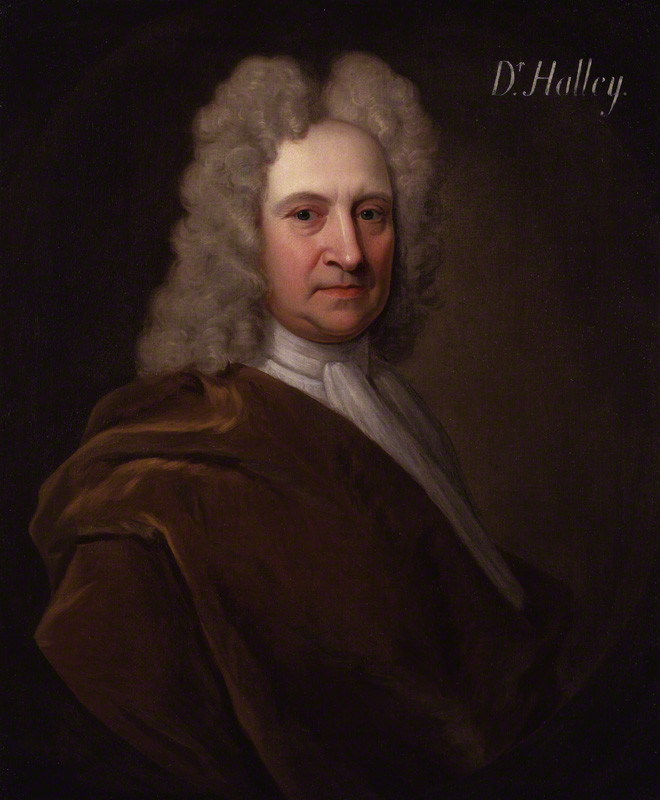
Edmund Halley
Edmond (or Edmund) Halley (; – ) was an English astronomer, mathematician and physicist. He was the second Astronomer Royal in Britain, succeeding John Flamsteed in 1720. From an observatory he constructed on Saint Helena in 1676–77, Halley catalogued the southern celestial hemisphere and recorded a transit of Mercury across the Sun. He realised that a similar transit of Venus could be used to determine the distances between Earth, Venus, and the Sun. Upon his return to England, he was made a fellow of the Royal Society, and with the help of King Charles II, was granted a master's degree from Oxford. Halley encouraged and helped fund the publication of Isaac Newton's influential ''Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica'' (1687). From observations Halley made in September 1682, he used Newton's law of universal gravitation to compute the periodicity of Halley's Comet in his 1705 ''Synopsis of the Astronomy of Comets''. It was named after him upon its predicted ret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese Empire
The Portuguese Empire was a colonial empire that existed between 1415 and 1999. In conjunction with the Spanish Empire, it ushered in the European Age of Discovery. It achieved a global scale, controlling vast portions of the Americas, Africa and various islands in Asia and Oceania. It was one of the most powerful empires of the early modern period, while at its greatest extent in 1820, covering 5.5 million square km ( million square miles), making it among the List of largest empires, largest empires in history. Composed of colonialism, colonies, Factory (trading post)#Portuguese feitorias (c. 1445), factories, and later Territory#Overseas territory, overseas territories, it was the longest-lived colonial empire in history, from the conquest of Ceuta in North Africa in 1415 to the handover of Macau to China in 1999. The power and influence of the Kingdom of Portugal would eventually expand across the globe. In the wake of the Reconquista, Portuguese maritime exploration, Port ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Whaling Commission
The International Whaling Commission (IWC) is a specialised regional fishery management organisation, established under the terms of the 1946 International Convention for the Regulation of Whaling (ICRW) to "provide for the proper conservation of whale stocks and thus make possible the orderly development of the whaling industry". As the decision-making body of the convention, the IWC reviews and revises measures laid down in the "Schedule to the Convention", which govern the conduct of whaling throughout the world. These measures include: confer complete protection of certain species; designate specific areas as whale sanctuaries; set limits on the numbers and size of whales which may be taken; prescribe open and closed seasons and areas for whaling; and prohibit the capture of suckling calves and female whales accompanied by calves. The Commission also mandates the compilation of catch reports and other statistical and biological records, and is actively involved in whale res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
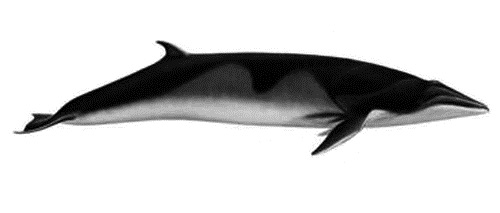
Humpback Whale
The humpback whale (''Megaptera novaeangliae'') is a species of baleen whale. It is a rorqual (a member of the family Balaenopteridae) and is the monotypic taxon, only species in the genus ''Megaptera''. Adults range in length from and weigh up to . The humpback has a distinctive body shape, with long pectoral fins and tubercles on its head. It is known for Cetacean surfacing behaviour, breaching and other distinctive surface behaviors, making it popular with whale watching, whale watchers. Males produce a complex Whale sound, song that typically lasts from 4 to 33 minutes. Found in oceans and list of seas, seas around the world, humpback whales typically animal migration, migrate between feeding areas towards the poles and breeding areas near the equator. They feed in Polar region, polar waters and migrate to tropics, tropical or subtropical waters to breed and give birth. Their diet consists mostly of krill and small fish, and they usually Bubble-net feeding, use bubbles to c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trindade Petrel
The Trindade petrel (''Pterodroma arminjoniana''), also known as the Round island petrel, is a species of seabird and a member of the gadfly petrels. The bird is in size, with an wingspan. The petrel has various color morphs: dark and light, as well as intermediates between the two. Previously, two separate populations were considered conspecific, one occurring in the south Pacific, sometimes seen in Hawaii; the other occurring in the south Atlantic, nesting off Brazil, with regular sightings in the Gulf Stream off the southeastern United States. The little-known Pacific birds were then split and determined distinct as the Herald petrel, ''Pterodroma heraldica''. It uses oceanic islands and atolls, nesting on cliff ledges, ridges or rocky slopes. On some islands, nesting birds are threatened by feral cats and rats. Due to ongoing habitat loss and small breeding range, this species is evaluated as vulnerable on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species The International Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |