|
Trichomanes Speciosum
''Vandenboschia speciosa'', synonym ''Trichomanes speciosum'', commonly known as the Killarney fern, is a species of fern found widely in Western Europe. It is most abundant in Ireland, Great Britain, Brittany, Galicia, Canary Islands, Madeira and the Azores, but is also found in other locations including France, Spain, Portugal and Italy. It is a relict endemic European species with a disjunct distribution, having had a much wider distribution before the climate changes of the Tertiary and Quaternary periods. This fern has an unusual life cycle, with a perennial gametophyte phase with an active vegetative reproduction. The gametophyte has the ability to tolerate darker and drier habitats than does the sporophyte. The sporophyte form is found in only 16 locations in the UK although the gametophyte form is more widespread. Once found on Arran, it was thought to be extinct in Scotland due to the activities of Victorian collectors, but the species has been discovered on Skye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Ludwig Willdenow
Carl Ludwig Willdenow (22 August 1765 – 10 July 1812) was a German botanist, pharmacist, and plant Taxonomy (biology), taxonomist. He is considered one of the founders of phytogeography, the study of the geographic distribution of plants. Willdenow was also a mentor of Alexander von Humboldt, one of the earliest and best known phytogeographers. He also influenced Christian Konrad Sprengel, who pioneered the study of plant pollination and floral biology. Biography Willdenow was born in Berlin and studied medicine and botany at the University of Halle. After studying pharmaceutics at Wieglieb College, Langensalza and in medicine at Halle, he returned to Berlin to work at his father's pharmacy located in the Unter den Linden. His early interest in botany was kindled by his uncle Johann Gottlieb Gleditsch, J. G. Gleditsch and he started a herbarium collection in his teenage years. In 1794, he became a member of the Berlin Academy of Sciences. He was a director of the Botanica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), as well as the current and most recent of the twelve periods of the Phanerozoic eon. It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million years ago to the present. The Quaternary Period is divided into two epochs: the Pleistocene (2.58 million years ago to 11.7 thousand years ago) and the Holocene (11.7 thousand years ago to today); a proposed third epoch, the Anthropocene, was rejected in 2024 by IUGS, the governing body of the ICS. The Quaternary is typically defined by the Quaternary glaciation, the cyclic growth and decay of continental ice sheets related to the Milankovitch cycles and the associated climate and environmental changes that they caused. Research history In 1759 Giovanni Arduino proposed that the geological strata of northern Italy could be divided into four succ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of Scotland
The flora of Scotland is an assemblage of native plant species including over 1,600 vascular plants, more than 1,500 lichens and nearly 1,000 bryophytes. The total number of vascular species is low by world standards but lichens and bryophytes are abundant and the latter form a population of global importance. Various populations of rare fern exist, although the impact of 19th-century collectors threatened the existence of several species. The flora is generally typical of the north-west European part of the Palearctic realm and prominent features of the Scottish flora include boreal Caledonian forest (much reduced from its natural extent), heather moorland and coastal machair."Flowering Plants and Ferns" SNH. Retrieved 26 April 2008 In addition to the native species of vascular plants there are nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of Ireland
Ireland is in the Atlantic European Province of the Circumboreal Region, a floristic region within the Holarctic. Composition of the flora Ireland has a small flora for a European country because of its small size, lack of geological and ecological variation and its Pleistocene history. There are 3,815 species of plant listed for Ireland:G.T. Higgins, J.R. Martin, P.M. PerriNATIONAL SURVEY OF NATIVE WOODLAND IN IRELANDMarch 2004 *Phylum Anthocerotophyta – hornworts: 3 species *Phylum Bryophyta – mosses: 556 species *Phylum Charophyta – charophytes: 244 species *Phylum Chlorophyta – green algae: 148 species *Phylum Lycopodiophyta – clubmosses: 9 species *Phylum Magnoliophyta – flowering plants: 2,196 species *Phylum Marchantiophyta – liverworts: 229 species *Phylum Pinophyta – pines: 12 species *Phylum Pteridophyta – ferns: 79 species *Phylum Rhodophyta – red algae: 339 species An additional 2,512 species of fungus occur in Ireland. *Phylum Acrasiomycota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of England
Flora (: floras or florae) is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring ( indigenous) native plants. The corresponding term for animals is ''fauna'', and for fungi, it is '' funga''. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora as in the terms '' gut flora'' or '' skin flora'' for purposes of specificity. Etymology The word "flora" comes from the Latin name of Flora, the goddess of plants, flowers, and fertility in Roman mythology. The technical term "flora" is then derived from a metonymy of this goddess at the end of the sixteenth century. It was first used in poetry to denote the natural vegetation of an area, but soon also assumed the meaning of a work cataloguing such vegetation. Moreover, "Flora" was used to refer to the flowers of an artificial garden in the seventeenth century. The distinction between vegetation (the general appearance of a community) and flora (the taxonomic composition of a community) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferns Of Europe
The ferns (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta) are a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. They differ from mosses by being vascular, i.e., having specialized tissues that conduct water and nutrients, and in having life cycles in which the branched sporophyte is the dominant phase. Ferns have complex leaves called megaphylls that are more complex than the microphylls of clubmosses. Most ferns are leptosporangiate ferns. They produce coiled fiddleheads that uncoil and expand into fronds. The group includes about 10,560 known extant species. Ferns are defined here in the broad sense, being all of the Polypodiopsida, comprising both the leptosporangiate ( Polypodiidae) and eusporangiate ferns, the latter group including horsetails, whisk ferns, marattioid ferns, and ophioglossoid ferns. The fern crown group, consisting of the leptosporangiates and eusporangiates, is estimated to have originated in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hymenophyllales
The Hymenophyllaceae, the filmy ferns and bristle ferns, are a family of two to nine genera (depending on classification system) and about 650 known species of ferns, with a subcosmopolitan distribution, but generally restricted to very damp places or to locations where they are wetted by spray from waterfalls or springs. Fossil evidence shows that ferns of the family Hymenophyllaceae have existed since at least the Upper Triassic. Description They often appear as very dark green or even black clumps and may be mistaken for a robust moss or liverwort. The rhizome is usually thin and wiry and the fronds variously pinnate with a single strand ("nerve") of vascular tissue. As in most ferns, young fronds have circinate vernation. In most species, the frond, apart from the vascular tissue, is only a single cell thick, and they do not have any stomata. The cuticle is also greatly reduced or absent, leaving filmy ferns poikilohydric and very susceptible to desiccation where a reliable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vulnerable Species
A vulnerable species is a species which has been Conservation status, categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as being threatened species, threatened with extinction unless the circumstances that are threatened species, threatening its survival and reproduction improve. Vulnerability is mainly caused by habitat loss or destruction of the species' home. Vulnerable habitat or species are monitored and can become increasingly threatened. Some species listed as "vulnerable" may be common in captivity (animal), captivity, an example being the military macaw. In 2012 there were 5,196 animals and 6,789 plants classified as vulnerable, compared with 2,815 and 3,222, respectively, in 1998. Practices such as cryoconservation of animal genetic resources have been enforced in efforts to conserve vulnerable breeds of livestock specifically. Criteria The International Union for Conservation of Nature uses several criteria to enter species in this category. A taxon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
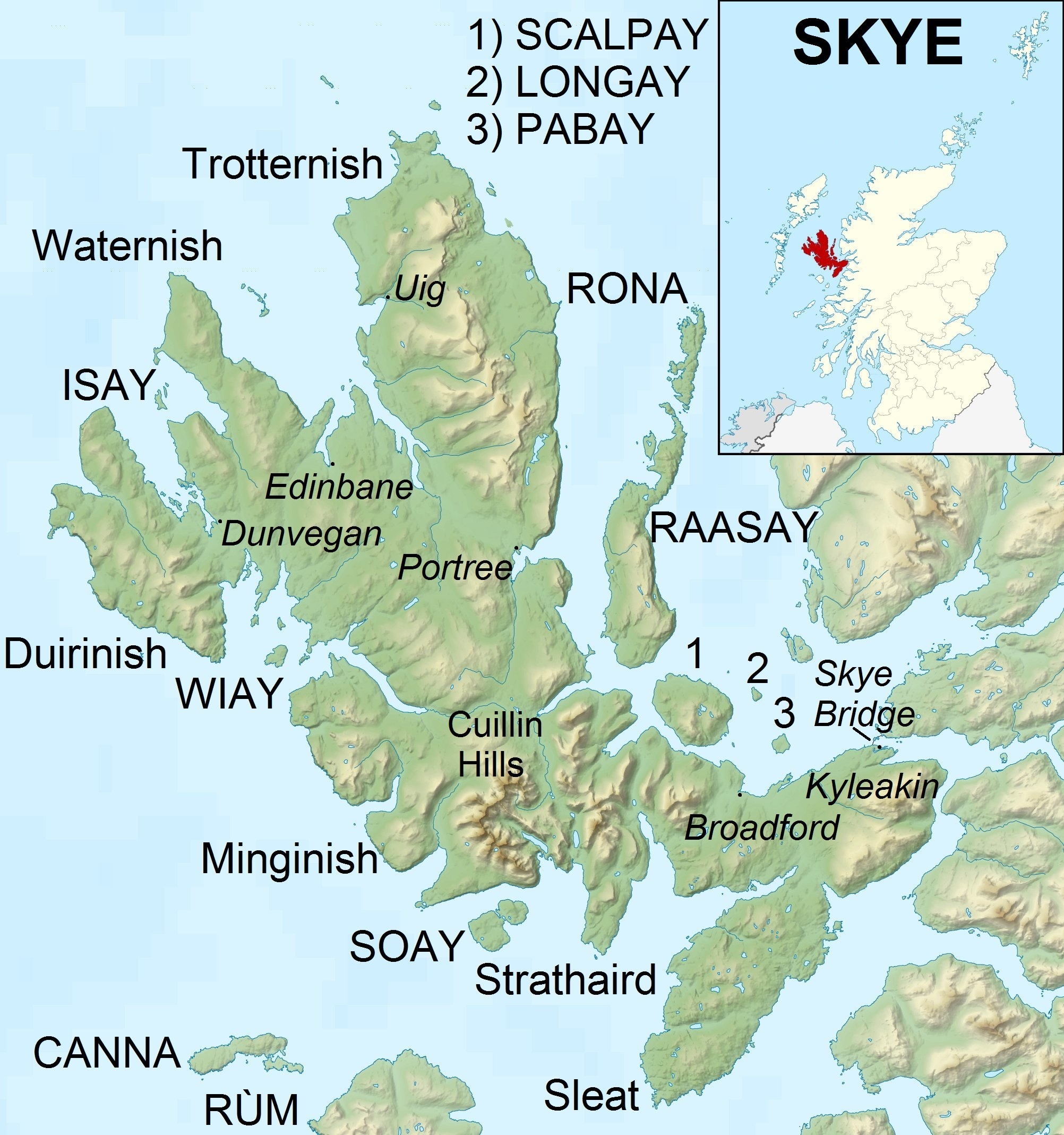
Skye
The Isle of Skye, or simply Skye, is the largest and northernmost of the major islands in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. The island's peninsulas radiate from a mountainous hub dominated by the Cuillin, the rocky slopes of which provide some of the most dramatic mountain scenery in the country. Slesser (1981) p. 19. Although has been suggested to describe a winged shape, no definitive agreement exists as to the name's origin."Gaelic Culture" . VisitScotland. Retrieved 5 January 2013. The island has been occupied since the period, and over its history has been occupied at various times by Celtic tribes includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pteridomania
Pteridomania or fern fever was a Victorian craze for ferns. Decorative arts of the period presented the fern motif in pottery, glass, metal, textiles, wood, printed paper, and sculpture, with ferns "appearing on everything from christening presents to gravestones and memorials". Description ''Pteridomania'', meaning ''Fern Madness'' or ''Fern Craze'', a compound of '' Pteridophytes'' and ''mania'', was coined in 1855 by Charles Kingsley in his book ''Glaucus, or the Wonders of the Shore'': According to one author: Collection and cultivation The collection of ferns drew enthusiasts from different social classes, leading naturalist Peter D A Boyd to write that "even the farm labourer or miner could have a collection of British ferns which he had collected in the wild and a common interest sometimes brought people of very different social backgrounds together". For some a fashionable hobby and for others a more serious scientific pursuit, fern collecting became commer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjacent Islands of Scotland, islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. To the south-east, Scotland has its Anglo-Scottish border, only land border, which is long and shared with England; the country is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the north-east and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. The population in 2022 was 5,439,842. Edinburgh is the capital and Glasgow is the most populous of the cities of Scotland. The Kingdom of Scotland emerged as an independent sovereign state in the 9th century. In 1603, James VI succeeded to the thrones of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland, forming a personal union of the Union of the Crowns, three kingdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isle Of Arran
The Isle of Arran (; ) or simply Arran is an island off the west coast of Scotland. It is the largest island in the Firth of Clyde and the seventh-largest Scottish island, at . Counties of Scotland, Historically part of Buteshire, it is in the Subdivisions of Scotland, unitary council area of North Ayrshire. In the 2011 census it had a resident population of 4,629. Though culturally and physically similar to the Hebrides, it is separated from them by the Kintyre, Kintyre peninsula. Often referred to as "Scotland in Miniature", the Island is divided into highland and lowland areas by the Highland Boundary Fault and has been described as a "geologist's paradise".Haswell-Smith (2004) pp. 11–17. Arran has been continuously inhabited since the early Neolithic period. Numerous prehistory, prehistoric remains have been found. From the 6th century onwards, Goidelic languages, Goidelic-speaking peoples from Ireland colonised it and it became a centre of religious activity. In the trou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |