|
Transport In Poland
Transport in Poland involves air, water, road and rail transportation. The country has a large network of municipal public transport, such as buses, trams and the metro. As a country located at the 'cross-roads' of Europe, Poland is a nation with a large and increasingly modern network of transport infrastructure. The country's most important waterway is the Vistula river. The largest seaports are the Port of Gdańsk, the Port of Gdynia and the Port of Szczecin. Air travel is generally used for international travel, with many flights originating at Warsaw Chopin Airport. Railways connect all of Poland's major cities and the state-owned Polish State Railways (PKP) corporation, through its subsidiaries, runs a great number of domestic and international services of varying speed and comfort. In addition to this, five out of sixteen Polish voivodeships have their own regional rail service providers. Rail transport Poland is served by an extensive network of railways. In mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-speed Rail
High-speed rail (HSR) is a type of rail transport network utilising trains that run significantly faster than those of traditional rail, using an integrated system of specialised rolling stock and dedicated railway track, tracks. While there is no single definition or standard that applies worldwide, lines built to handle speeds of at least or upgraded lines of at least are generally considered to be high-speed. The first high-speed rail system, the Tōkaidō Shinkansen, began operations in Honshu, Japan, in 1964. Due to the streamlined spitzer (bullet), spitzer-shaped nose cone of the 0 Series Shinkansen, trains, the system also became known by its English nickname bullet train. Japan's example was followed by several European countries, initially in High-speed rail in Italy, Italy with the Florence–Rome high-speed railway, Direttissima line, followed shortly thereafter by High-speed rail in France, France, High-speed rail in Germany, Germany, and High-speed rail in Spain, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puławy
Puławy (, also written Pulawy) is a city in eastern Poland, in Lesser Poland's Lublin Voivodeship, at the confluence of the Vistula and Kurówka River, Kurówka Rivers. Puławy is the capital of Puławy County. The city's 2019 population was Census in Poland, estimated at 47,417. Its coat of arms is based on Coat of arms of Lithuania, Pogonia. Puławy was first mentioned in documents of the 15th century. At that time it was spelled ''Pollavy'', its name probably coming from a Vistula River Ford (crossing), ford located nearby. The town is a local center of science, industry and tourism, together with nearby Nałęczów and Kazimierz Dolny. Puławy is home to Poland's first permanent museum and is a Vistula River port. The town has two bridges and four rail stations, and serves as a road junction. Nearby Dęblin has a military airport. Location and transport Puławy lies in the western part of Lublin Voivodeship, at the edge of the picturesque Lesser Polish Gorge of the Vistul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minsk
Minsk (, ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach (Berezina), Svislach and the now subterranean Nyamiha, Niamiha rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative status in Belarus and is the administrative centre of Minsk region and Minsk district. it has a population of about two million, making Minsk the Largest cities in Europe, 11th-most populous city in Europe. Minsk is one of the administrative capitals of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) and the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU). First mentioned in 1067, Minsk became the capital of the Principality of Minsk, an appanage of the Principality of Polotsk, before being annexed by the Grand Duchy of Lithuania in 1242. It received town privileges in 1499. From 1569, it was the capital of Minsk Voivodeship, an administrative division of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It was part of the territories annexed by the Russian Empire in 1793, as a consequence of the Second Part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terespol
Terespol (; ) is a border town in eastern Poland on the border with Belarus. It lies on the border river Bug, directly opposite the city of Brest, Belarus. It has 5,794 inhabitants as of 2014. Overview Since 1999 Terespol has been within Biała Podlaska County in Lublin Voivodeship. Between 1975 and 1998 it belonged to Biała Podlaska Voivodeship. The town is a busy border crossing between Poland and Belarus on the European route E30 which links Berlin-Warsaw-Minsk-Moscow. Another crossing into Brest is located at Kukuryki northwest of Terespol. There was also a local train between Brest and Terespol. It comes 3 times a day. The trip took 18 minutes and was a very comfortable way of crossing border between Belarus and Poland. Due to the Coronavirus pandemic, the train was cancelled at the beginning of 2020 and has been suspended for an indefinite period. Terespol features in a novel by the Yiddish Nobel Prize-winning writer Isaac Bashevis Singer, '' The Family Moskat'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siedlce
Siedlce () ( ) is a city in the Masovian Voivodeship in eastern Poland with 77,354 inhabitants (). The city is situated between two small rivers, the Muchawka and the Helenka, and lies along the European route E30, around east of Warsaw. It is the fourth largest city of the Masovian Voivodeship, and the seat of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Siedlce. Siedlce is a local educational, cultural and sports center, with a university, a notable rugby club and two important museums. It also hosts a garrison of the Polish Armed Forces. First recorded in the medieval period, Siedlce is a former residential city of prominent Polish magnate families of Czartoryski and Ogiński, under whose patronage it became an important cultural center in Poland. The city contains several landmarks in various styles, especially Baroque and Neoclassical, including the Ogiński Palace and Park ensemble. From 1975 to 1998, the city was the capital of a separate Siedlce Voivodeship. History The city, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
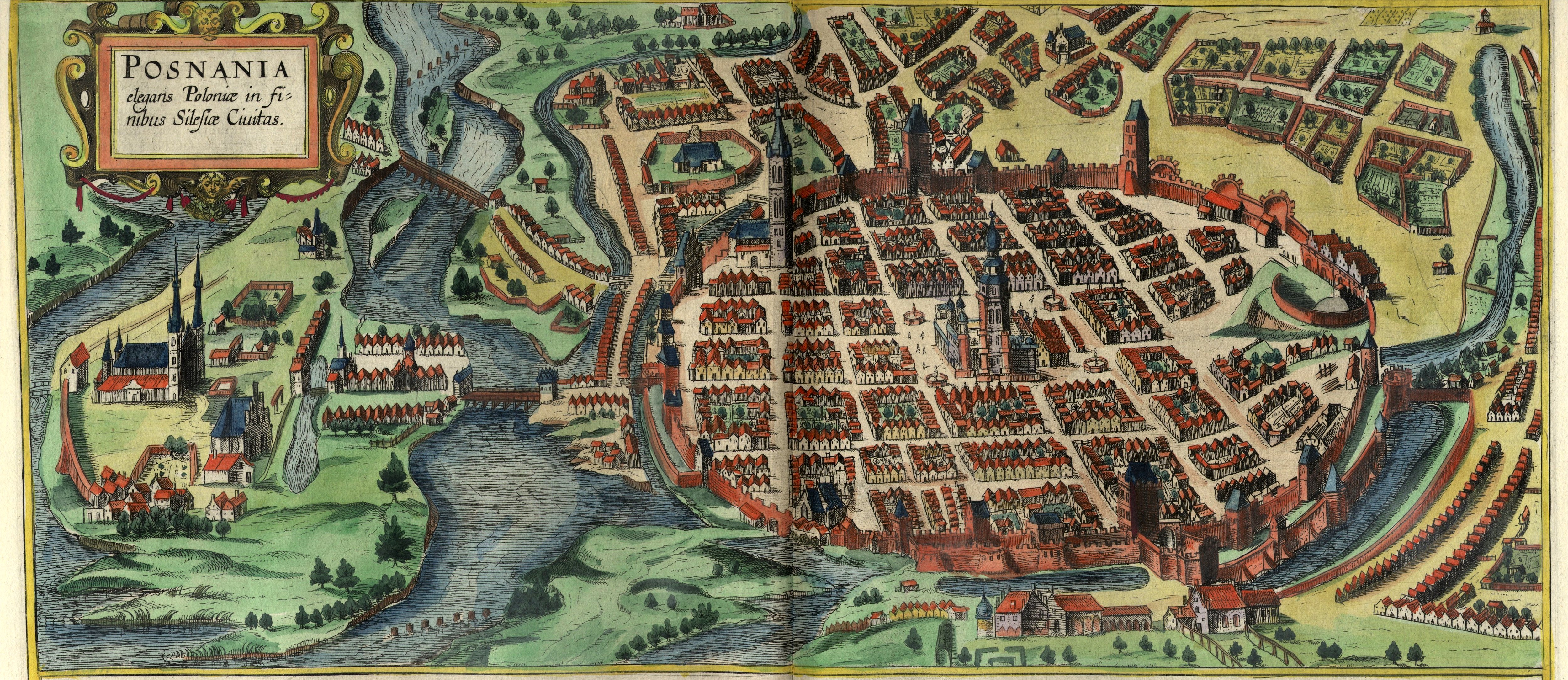
Poznań
Poznań ( ) is a city on the Warta, River Warta in west Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business center and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint John's Fair, Poznań, Saint John's Fair (''Jarmark Świętojański''), traditional St. Martin's croissant, Saint Martin's croissants and a local dialect. Among its most important heritage sites are the Renaissance in Poland, Renaissance Old Town, Poznań Town Hall, Town Hall and Poznań Cathedral. Poznań is the fifth-largest List of cities and towns in Poland#Cities, city in Poland. As of 2023, the city's population is 540,146, while the Poznań metropolitan area (''Metropolia Poznań'') comprising Poznań County and several other communities is inhabited by over 1.029 million people. It is one of four historical capitals of medieval Poland and the ancient capital of the Greater Poland region, currently the administrative capital of the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kutno
Kutno is a city in central Poland with 42,704 inhabitants (2021) and an area of . It is the capital of Kutno County in the Łódź Voivodeship. Founded in the medieval period, Kutno was a local center of crafts and trade, owing its growth to its location on the Royal Route connecting Warsaw with Poznań and Dresden in the 18th century, and the railway from Warsaw to Toruń and Bydgoszcz since the 19th century. During the invasion of Poland in 1939, Polish armies under General Tadeusz Kutrzeba conducted an offensive in and around Kutno, that was later named the Battle of the Bzura. Based on its central location and the intersection of multiple rail lines, Kutno is an important railroad junction in Poland. Two main lines cross there (Łódź – Toruń and Warsaw – Poznań – Berlin). Another connection also starts in Kutno, which connects the town to Płock. Kutno is the location of the European Little League Baseball Center and hosts the annual Kutno Rose Festival. Geograph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Train Control System
The European Train Control System (ETCS) is a train protection system designed to replace the many incompatible systems used by European railways, and railways outside of Europe. ETCS is the signalling and control component of the European Rail Traffic Management System (ERTMS). ETCS consists of 2 major parts: #trackside equipment #on-board (on train) equipment ETCS can allow all trackside information to be passed to the driver cab, removing the need for trackside signals. This is the foundation for future automatic train operation (ATO). Trackside equipment aims to exchange information with the vehicle for safely supervising train circulation. The information exchanged between track and trains can be either continuous or intermittent according to the ERTMS/ETCS level of application and to the nature of the information itself. The need for a system like ETCS stems from more and longer running trains resulting from economic integration of the European Union (EU) and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Investment Bank
The European Investment Bank (EIB) is the European Union's investment bank and is owned by the 27 member states. It is the largest multilateral financial institution in the world. The EIB finances and invests both through equity and debt solutions companies and projects that achieve the policy aims of the European Union through loans, equity and guarantees. The EIB focuses on the areas of climate, environment, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), development, cohesion and infrastructure. It has played a large role in providing finance during crises including the 2008 financial crisis and the COVID-19 pandemic. Over 60 years since its inception in 1958 to 2018 the EIB has invested over 1.1 trillion euros. It primarily funds projects that "cannot be entirely financed by the various means available in the individual Member States". The EIB is one of the biggest financiers of Sustainable finance, green finance in the world. In 2007, the EIB became the first institution in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pendolino
Pendolino (from Italian language, Italian "pendulum", and ''-ino,'' a diminutive suffix) is an Italian family of high-speed tilting trains (and non-tilting) used in Italy, Spain, Germany, Poland, Portugal, Slovenia, Finland, the Czech Republic, Slovakia (Czech railways are operating), the UK, the US, Switzerland, China, and Greece. It was also used in Russia from December 12, 2010, until March 26, 2022. Based on the design of the Italian ETR 401, it was further developed and manufactured by Fiat Ferroviaria, which was later acquired by Alstom in 2000. The idea of a tilting train became popular in the 1960s and 1970s, when various rail operators, impressed by the high-speed rail services being introduced in France and Japan, wondered how they could similarly speed up travel without building a dedicated parallel rail network (as those two countries were doing). By tilting, the train could go around Minimum railway curve radius, curves designed for slower trains at higher speeds wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alstom
Alstom SA () is a French multinational rolling stock manufacturer which operates worldwide in rail transport markets. It is active in the fields of passenger transportation, signaling, and locomotives, producing high-speed, suburban, regional and urban trains along with trams. The company and its name (originally spelled Alsthom) was formed by a merger between the electric engineering division of Société Alsacienne de Constructions Mécaniques (Als) and Compagnie Française Thomson-Houston (thom) in 1928. Significant acquisitions later included the Constructions Électriques de France (1932), shipbuilder Chantiers de l'Atlantique (1976), and parts of ACEC (late 1980s). A merger with parts of the British General Electric Company formed GEC Alsthom in 1989. Throughout the 1990s, the company expanded its holdings in the rail sector, acquiring German rolling stock manufacturer Linke-Hofmann-Busch and Italian rail signaling specialist Sasib Railways. In 1998, GEC Alsthom was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |