|
Transitional Age Youth
Transitional age youth (alternatively: TAY, Transition Aged Youth, Transition-Age Youth, Transitional Age Youth, Transitioning Youth, Transitional Youth, and Youth in Transition) can reference both a developmental period and be a descriptor regarding eligibility for certain services. While there are variations in definitions, the age ranges do consistently overlap and include late adolescence (15-16 years of age) to early adulthood (24-26 years). This range is considered a critical period in human development characterized by several changes socially, environmentally, and cognitively. During this time, individuals can experience changes in their social roles and function, family and peer supports, exposure to substance use, educational and vocational programs, as well as changes in healthcare providers from pediatric to adult settings. History The phrase transitional aged youth (TAY and the variations listed above) originated in the foster care system but has since taken on broad a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substance Abuse And Mental Health Services Administration
The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA; pronounced ) is a branch of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. It is charged with improving the quality and availability of treatment and rehabilitative services in order to reduce illness, death, disability, and the cost to society resulting from substance abuse and mental illnesses. The Administrator of SAMHSA reports directly to the Secretary of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. SAMHSA's headquarters building is located outside of Rockville, Maryland. History SAMHSA was established in 1992 by Congress as part of a reorganization stemming from the abolition of Alcohol, Drug Abuse, and Mental Health Administration (ADAMHA). ADAMHA had been established in 1973, combining the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA), National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH). The 1992 ADAMHA Reorganization Act consolidated the tre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
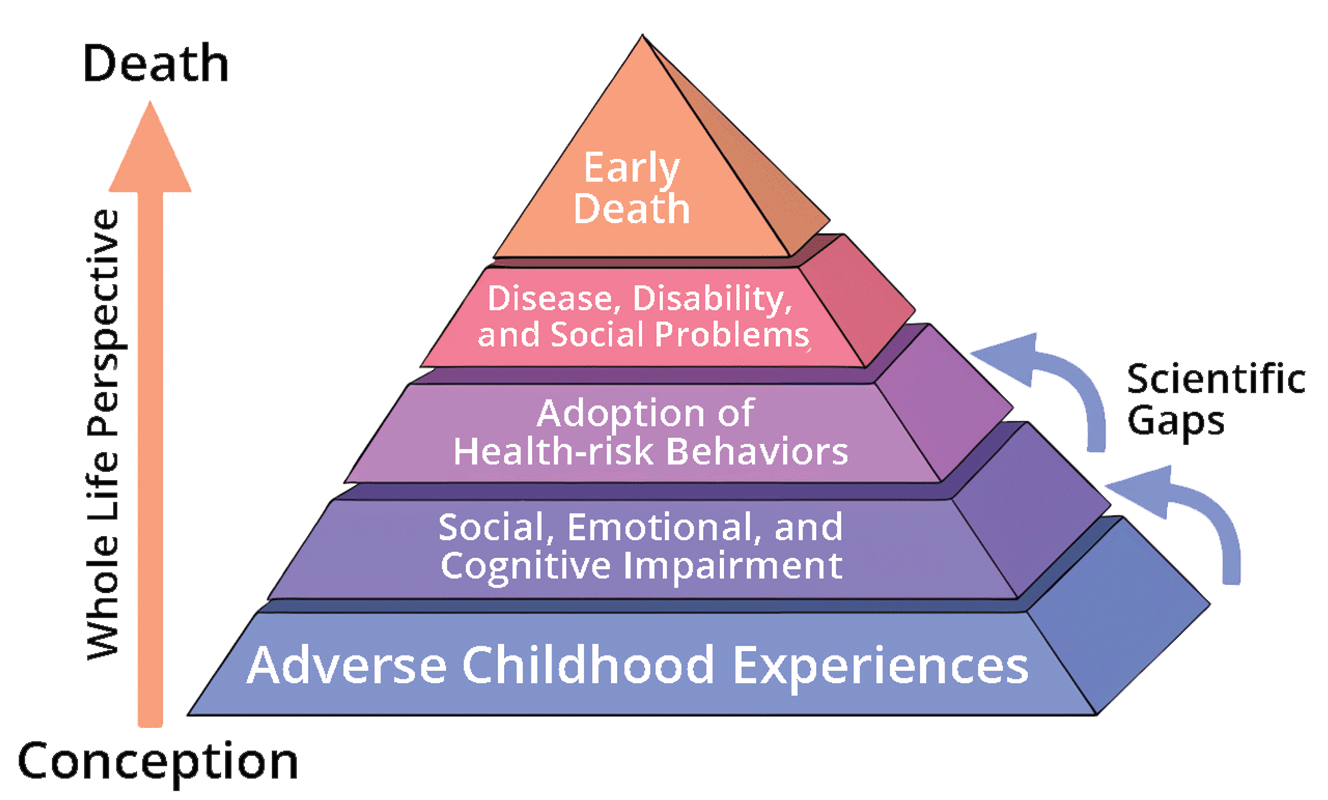
Adverse Childhood Experiences
Adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) encompass various forms of physical and emotional abuse, neglect, and household dysfunction experienced in childhood. The harms of ACEs can be long-lasting, affecting people even in their adulthood. ACEs have been linked to premature death as well as to various health conditions, including those of mental disorders. Toxic stress linked to child abuse is related to a number of neurological changes in the structure of the brain and its function. Definition and types The concept of adverse childhood experiences refers to various traumatic events or circumstances affecting children before the age of 18 and causing mental or physical harm. There are 10 types of ACEs: * physical abuse * sexual abuse * psychological abuse * physical neglect * psychological neglect * witnessing domestic abuse * having a close family member who misused drugs or alcohol * having a close family member with mental health problems * having a close family member wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coming Of Age
Coming of age is a young person's transition from being a child to being an adult. The specific age at which this transition takes place varies between societies, as does the nature of the change. It can be a simple legal convention or can be part of a ritual or spiritual event, as practiced by many societies. In the past, and in some societies today, such a change is associated with the age of sexual maturity ( puberty), especially menarche and spermarche. In others, it is associated with an age of religious responsibility. Particularly in western societies, modern legal conventions which stipulate points in around the end of adolescence and the beginning of early adulthood (most commonly 18, with the range being 16-21) when adolescents are generally no longer considered minors and are granted the full rights and responsibilities of an adult) are the focus of the transition. In either case, many cultures retain ceremonies to confirm the coming of age, and coming-of-age ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Child Development
Child development involves the Human development (biology), biological, developmental psychology, psychological and emotional changes that occur in human beings between birth and the conclusion of adolescence. Childhood is divided into 3 stages of life which include early childhood, middle childhood, and late childhood (preadolescence). Early childhood typically ranges from infancy to the age of 6 years old. During this period, development is significant, as many of life's milestones happen during this time period such as first words, learning to crawl, and learning to walk. There is speculation that middle childhood/preadolescence or ages 6–12 are the most crucial years of a child's life. Adolescence is the stage of life that typically starts around the major onset of puberty, with markers such as menarche and spermarche, typically occurring at 12–13 years of age. It has been defined as ages 10 to 19 by the World Health Organization. In the course of development, the individu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is bicameral, composed of a lower body, the House of Representatives, and an upper body, the Senate. It meets in the U.S. Capitol in Washington, D.C. Senators and representatives are chosen through direct election, though vacancies in the Senate may be filled by a governor's appointment. Congress has 535 voting members: 100 senators and 435 representatives. The U.S. vice president The vice president of the United States (VPOTUS) is the second-highest officer in the executive branch of the U.S. federal government, after the president of the United States, and ranks first in the presidential line of succession. The vice pr ... has a vote in the Senate only when senators are evenly divided. The House of Representatives has six non-voting members. The sitting of a Congress is for a two-year term, at present, beginning every other January. Elections are held every even-n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Department Of Health And Human Services
The United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) is a cabinet-level executive branch department of the U.S. federal government created to protect the health of all Americans and providing essential human services. Its motto is "Improving the health, safety, and well-being of America". Before the separate federal Department of Education was created in 1979, it was called the Department of Health, Education, and Welfare (HEW). HHS is administered by the Secretary of Health and Human Services, who is appointed by the president with the advice and consent of the United States Senate. The position is currently held by Xavier Becerra. The United States Public Health Service Commissioned Corps, the uniformed service of the PHS, is led by the Surgeon General who is responsible for addressing matters concerning public health as authorized by the secretary or by the assistant secretary for Health in addition to his or her primary mission of administering the Commiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Child Welfare Demonstration Waivers
A child ( : children) is a human being between the stages of birth and puberty, or between the developmental period of infancy and puberty. The legal definition of ''child'' generally refers to a minor, otherwise known as a person younger than the age of majority. Children generally have fewer rights and responsibilities than adults. They are classed as unable to make serious decisions. ''Child'' may also describe a relationship with a parent (such as sons and daughters of any age) or, metaphorically, an authority figure, or signify group membership in a clan, tribe, or religion; it can also signify being strongly affected by a specific time, place, or circumstance, as in "a child of nature" or "a child of the Sixties." Biological, legal and social definitions In the biological sciences, a child is usually defined as a person between birth and puberty, or between the developmental period of infancy and puberty. Legally, the term ''child'' may refer to anyone below the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family Connection Grants
Family (from la, familia) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Ideally, families offer predictability, structure, and safety as members mature and learn to participate in the community. Historically, most human societies use family as the primary locus of Attachment theory, attachment, nurturance, and socialization. Anthropologists classify most family organizations as Matrifocal family, matrifocal (a mother and her children), patrifocal (a father and his children), wikt:conjugal, conjugal (a wife, her husband, and children, also called the nuclear family), avuncular (a man, his sister, and her children), or Extended family, extended (in addition to parents and children, may include grandparents, aunts, uncles, or cousins). The field of genealogy aims to trace family lineages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinship Navigator
In anthropology, kinship is the web of social relationships that form an important part of the lives of all humans in all societies, although its exact meanings even within this discipline are often debated. Anthropologist Robin Fox says that the study of kinship is the study of what humans do with these basic facts of lifemating, gestation, parenthood, socialization, siblingship etc. Human society is unique, he argues, in that we are "working with the same raw material as exists in the animal world, but ecan conceptualize and categorize it to serve social ends." These social ends include the socialization of children and the formation of basic economic, political and religious groups. Kinship can refer both to the patterns of social relationships themselves, or it can refer to the study of the patterns of social relationships in one or more human cultures (i.e. kinship studies). Over its history, anthropology has developed a number of related concepts and terms in the study ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fostering Connections To Success And Increasing Adoptions Act Of 2008
The Fostering Connections to Success and Increasing Adoptions Act of 2008 (enacted as Public Law 110-351) was an Act of Congress in the United States signed into law by President George W. Bush on October 7, 2008. It was previously unanimously passed in both the House of Representatives and in the Senate. The law made numerous changes to the child welfare system, mostly to Title IV-E of the Social Security Act, which covers federal payments to states for foster care and adoption assistance. According to child welfare experts and advocates, the law made the most significant federal improvements to the child welfare system in over a decade. Changes The new law made a number of changes to the child welfare system, which is primarily the responsibility of the states (the Federal government supports the states through funding and legislative initiatives). Major changes include: *Allowing all states the option to provide kinship guardianship assistance payments, or payments to rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transitional Housing
Transitional housing is temporary housing for certain segments of the homeless population, including working homeless people who are earning too little money to afford long-term housing. Transitional housing is set up to transition residents into permanent, affordable housing. It is not in an emergency homeless shelter, but usually a room or apartment in a residence with support services. Description The transitional time can be short, for example one or two years, and in that time the person must file for and get permanent housing and usually some gainful employment or income, even if Social Security or assistance. Sometimes, the transitional housing residence program charges a room and board fee, maybe 30% of an individual's income, which is sometimes partially or fully refunded after the person procures a permanent place to live in. In the USA, federal funding for transitional housing programs was originally allocated in the McKinney–Vento Homeless Assistance Act of 1986.Dord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Title IV-E Independent Living Program Of 1990
A title is one or more words used before or after a person's name, in certain contexts. It may signify either generation, an official position, or a professional or academic qualification. In some languages, titles may be inserted between the first and last name (for example, ''Graf'' in German, Cardinal in Catholic usage (Richard Cardinal Cushing) or clerical titles such as Archbishop). Some titles are hereditary. Types Titles include: * Honorific titles or styles of address, a phrase used to convey respect to the recipient of a communication, or to recognize an attribute such as: ** Imperial, royal and noble ranks ** Academic degree ** Social titles, prevalent among certain sections of society due to historic or other reasons. ** Other accomplishment, as with a title of honor * Title of authority, an identifier that specifies the office or position held by an official Titles in English-speaking areas Common titles * Mr. – Adult man (regardless of marital status) * Ms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)