|
Track Geometry Car
A track geometry car (also known as a track recording car) is an automated track inspection vehicle on a rail transport system used to test several parameters of the track geometry without obstructing normal railroad operations. Some of the parameters generally measured include position, curvature, alignment of the track, smoothness, and the crosslevel of the two rails. The cars use a variety of sensors, measuring systems, and data management systems to create a profile of the track being inspected. History Track geometry cars emerged in the 1920s when rail traffic became sufficiently dense that manual and visual inspections were no longer practical. Furthermore, the increased operating speeds of trains of that era required more meticulously maintained tracks. In 1925, the Chemins de fer de l'Est put a track geometry car into operation carrying an accelerograph developed by Emile Hallade, the inventor of the Hallade method. The accelerograph could record horizontal and verti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TRT Notting Hill Gate
The Turkish Radio and Television Corporation (TRT; Turkish: ) is the national public broadcasting, public broadcaster of Turkey, founded in 1964. TRT was for many years the only television and radio broadcaster in Turkey. Before the introduction of commercial radio in 1990, and subsequently commercial television in 1992, it held a monopoly on broadcasting. More recent deregulation of the Turkish television broadcasting market produced analogue terrestrial television. Today, TRT broadcasts around the world, including in Europe, the Middle East, Africa, Asia, the United States, and Australia. Around 70% of TRT's funding comes from a license tax on television and radio receivers. Additionally, a 2% TRT tax was added to the electricity bills until January 2022. As these are hypothecation (taxation), hypothecated taxes, as opposed to the money allocated to general government funds, the principle is similar to that of the television licence levied in a number of other countries, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiel
Kiel ( ; ) is the capital and most populous city in the northern Germany, German state of Schleswig-Holstein. With a population of around 250,000, it is Germany's largest city on the Baltic Sea. It is located on the Kieler Förde inlet of the Bay of Kiel and lies in the southeast of the Jutland Peninsula, on the mouth of the Schwentine River, approximately northeast of Hamburg. The world's busiest artificial waterway, the Kiel Canal, has a terminus in Kiel's Holtenau district. This canal connects the Baltic to the North Sea, with its other end in Brunsbüttel. Most of Kiel is part of Holstein. The boroughs north of the Schwentine also belong to Wagria, while those north of the Kiel Canal are historically part of Southern Schleswig. Kiel is one of Germany's major maritime centres, known for a variety of international sailing events, including the annual Kiel Week, which is the biggest sailing event in the world. Kiel is also known for the Kiel mutiny, Kiel Mutiny, when sailors re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
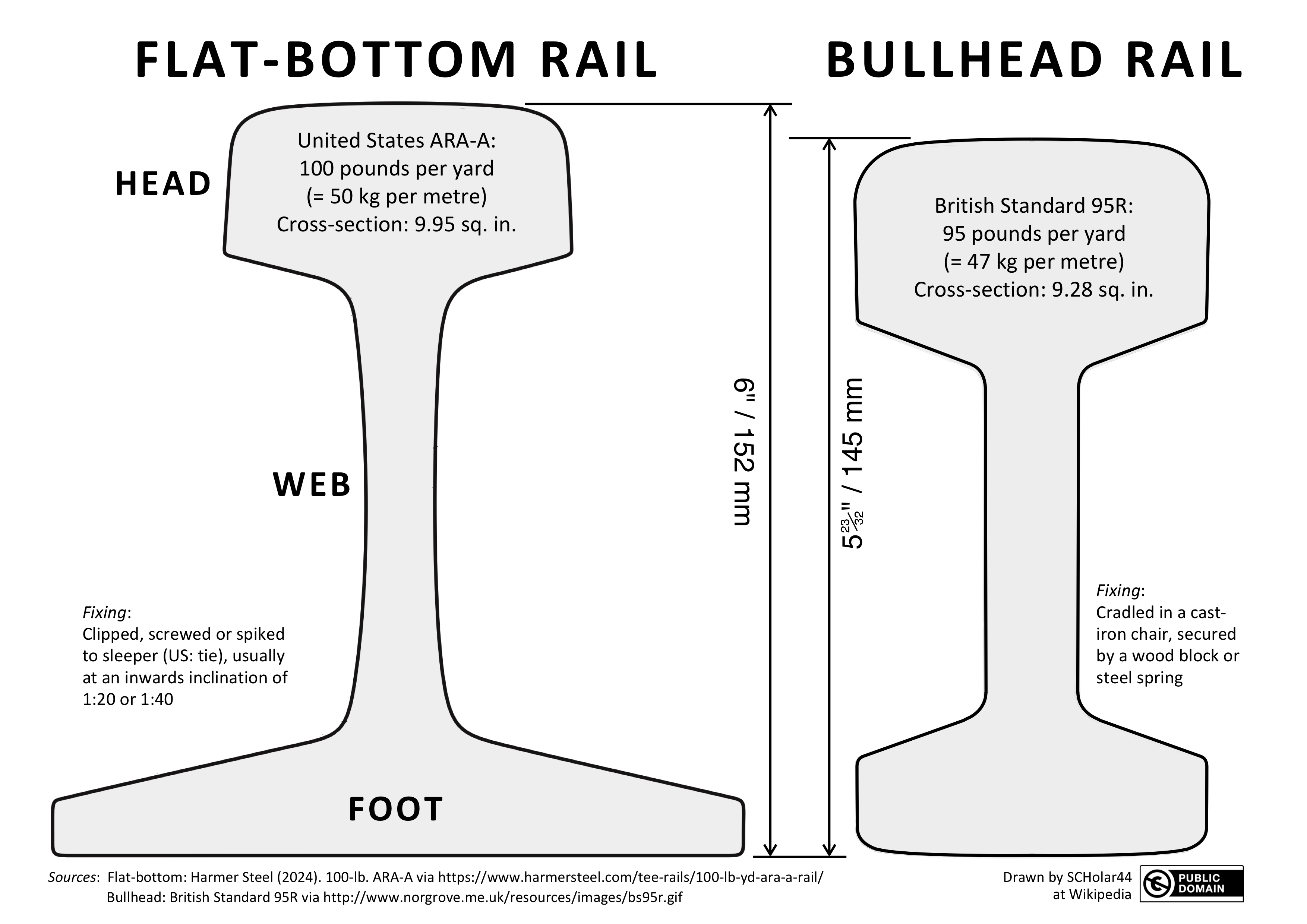
Rail Profile
The rail profile is the cross-sectional shape of a Railway track#Rail, rail as installed on a railway or railroad, perpendicular to its length. Early rails were made of wood, cast iron or wrought iron. All modern rails are hot rolled steel with a cross section Profile (engineering), (profile) approximate to an I-beam, but asymmetric about a horizontal axis (however see #Grooved rail, grooved rail below). The head is profiled to resist wear and to give a good ride, and the foot profiled to suit the fixing system. Unlike some other uses of iron and steel, railway rails are subject to very high stresses and are made of very high quality steel. It took many decades to improve the quality of the materials, including the change from iron to steel. Minor flaws in the steel that may pose no problems in other applications can lead to broken rails and dangerous derailments when used on railway tracks. By and large, the heavier the rails and the rest of the track work, the heavier an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York City Subway
The New York City Subway is a rapid transit system in New York City serving the New York City boroughs, boroughs of Manhattan, Brooklyn, Queens, and the Bronx. It is owned by the government of New York City and leased to the New York City Transit Authority, an affiliate agency of the Government of New York (state), state-run Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA). Opened on October 27, 1904, the New York City Subway is one of the world's oldest public transit systems, one of the most-used, and the one with the second-most stations after the Beijing Subway, with New York City Subway stations, 472 stations in operation (423, if stations connected by transfers are counted as single stations). The system has operated 24/7 service every day of the year throughout most of its history, barring emergencies and disasters. By annual ridership, the New York City Subway is the busiest rapid transit system in both the Western Hemisphere and the Western world, as well as the List of m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Profile
The rail profile is the cross-sectional shape of a Railway track#Rail, rail as installed on a railway or railroad, perpendicular to its length. Early rails were made of wood, cast iron or wrought iron. All modern rails are hot rolled steel with a cross section Profile (engineering), (profile) approximate to an I-beam, but asymmetric about a horizontal axis (however see #Grooved rail, grooved rail below). The head is profiled to resist wear and to give a good ride, and the foot profiled to suit the fixing system. Unlike some other uses of iron and steel, railway rails are subject to very high stresses and are made of very high quality steel. It took many decades to improve the quality of the materials, including the change from iron to steel. Minor flaws in the steel that may pose no problems in other applications can lead to broken rails and dangerous derailments when used on railway tracks. By and large, the heavier the rails and the rest of the track work, the heavier an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard-gauge Railway
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of . The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), international gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge in Europe, and SGR in East Africa. It is the most widely used track gauge around the world, with about 55% of the lines in the world using it. All high-speed rail lines use standard gauge except those in Russia, Finland, Uzbekistan, and some line sections in Spain. The distance between the inside edges of the heads of the rails is defined to be 1,435 mm except in the United States, Canada, and on some heritage British lines, where it is defined in U.S. customary/ British Imperial units as exactly "four feet eight and one half inches", which is equivalent to 1,435.1mm. History As railways developed and expanded, one of the key issues was the track gauge (the distance, or width, between the inner sides of the rail heads) to be used, as the wheels of the rolling stock (locomoti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Track Gauge
In rail transport, track gauge is the distance between the two rails of a railway track. All vehicles on a rail network must have Wheelset (rail transport), wheelsets that are compatible with the track gauge. Since many different track gauges exist worldwide, gauge differences often present a barrier to wider operation on railway networks. The term derives from the metal bar, or gauge, that is used to ensure the distance between the rails is correct. Railways also deploy two other gauges to ensure compliance with a required standard. A ''loading gauge'' is a two-dimensional profile that encompasses a cross-section of the track, a rail vehicle and a maximum-sized load: all rail vehicles and their loads must be contained in the corresponding envelope. A ''structure gauge'' specifies the outline into which structures (bridges, platforms, lineside equipment etc.) must not encroach. Uses of the term The most common use of the term "track gauge" refers to the transverse distance be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overhead Line
An overhead line or overhead wire is an electrical cable that is used to transmit electrical energy to electric locomotives, Electric multiple unit, electric multiple units, trolleybuses or trams. The generic term used by the International Union of Railways for the technology is ''overhead line''. It is known variously as overhead catenary, overhead contact line (OCL), overhead contact system (OCS), overhead equipment (OHE), overhead line equipment (OLE or OHLE), overhead lines (OHL), overhead wiring (OHW), traction wire, and trolley wire. An overhead line consists of one or more wires (or Overhead conductor rail, rails, particularly in tunnels) situated over rail tracks, raised to a high electrical potential by connection to feeder stations at regularly spaced intervals along the track. The feeder stations are usually fed from a High voltage, high-voltage Electricity distribution, electrical grid. Overview Electric trains that collect their current from overhead lines use a de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degree Of Curvature
Degree of curve or degree of curvature is a measure of curvature of a circular arc used in civil engineering for its easy use in layout surveying. Definition The Degree (angle), degree of curvature is defined as the central angle to the ends of an agreed length of either an Arc (curvature), arc or a Chord (geometry), chord; various lengths are commonly used in different areas of practice. This angle is also the Body relative direction, change in forward direction as that portion of the curve is traveled. In an ''n''-degree curve, the forward Bearing (angle), bearing changes by ''n'' degree (angle), degrees over the standard length of arc or chord. Usage Curvature is usually measured in radius of curvature. A small circle can be easily laid out by just using radius of curvature, but degree of curvature is more convenient for calculating and laying out the curve if the radius is as large as a kilometer or mile, as is needed for large scale works like roads and railroads. By using ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cant (road/rail)
The cant of a Rail transport, railway track or camber angle, camber of a road (also referred to as superelevation, cross slope or cross fall) is the rate of change in elevation (height) between the two rails or edges of the road. This is normally greater where the railway or road is curved; raising the outer rail or the outer edge of the road creates a banked turn, thus allowing vehicles to travel round the curve at greater speeds than would be possible if the surface were level. Rail Superelevation in railway tracks ;Importance of superelevation In curved railway tracks, the outer rail is elevated, providing a banked turn. This allows trains to navigate curves at higher speeds and reduces the pressure of the wheel flanges against the rails, minimizing friction and wear. The difference in elevation between the outer and inner rails is referred to as cant in most countries. ;How superelevation works The main functions of cant are the following: * Improve distribution of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Track Geometry
Track geometry is concerned with the properties and relations of points, lines, curves, and surfaces in the three-dimensional positioning of railroad Track (rail transport), track. The term is also applied to measurements used in design, construction and maintenance of track. Track geometry involves standards, speed limits and other regulations in the areas of track gauge, alignment, elevation, curvature and track surface. Standards are usually separately expressed for Horizontal plane, horizontal and Vertical direction, vertical layouts although track geometry is three-dimensional. Layout Horizontal layout Horizontal layout is the track layout on the horizontal plane. This can be thought of as the Multiview orthographic projection#Plan, plan view which is a view of a 3-dimensional track from the position above the track. In track geometry, the horizontal layout involves the layout of three main track types: ''tangent track'' (straight line), ''curved track'', and ''track transit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Track Class
Rail speed limits in the United States are regulated by the Federal Railroad Administration. Railroads also implement their own limits and enforce speed limits. Speed restrictions are based on a number of factors including curvature, signaling, track condition, and the presence of grade crossings. Like road speed limits in the United States, speed limits for tracks and trains are measured in miles per hour (mph). Signal speeds Federal regulators set train speed limits based on the signaling systems in use. Passenger trains were limited to 59 mph (95 km/h) and freight trains to 49 mph (79 km/h) on tracks without block signals, known as "dark territory." Trains without an automatic cab signal, train stop, or train control system were not allowed to exceed 79 mph (127 km/h). This rule, issued in 1947 and effective by the end of 1951, was a response to a serious 1946 crash in Naperville, Illinois, involving two trains. Following a 1987 train collision in Maryland, freight train ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |