|
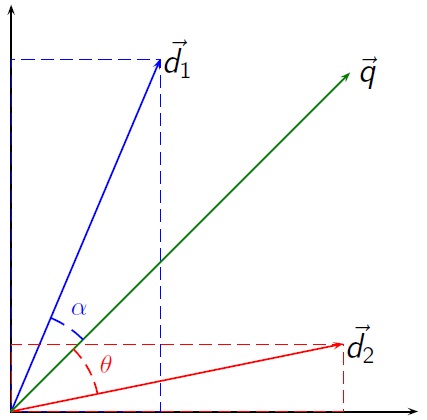
Topic-based Vector Space Model
The Topic-based Vector Space Model (TVSM) (literature extends the vector space model of information retrieval Information retrieval (IR) in computing and information science is the process of obtaining information system resources that are relevant to an information need from a collection of those resources. Searches can be based on full-text or other co ... by removing the constraint that the term-vectors be orthogonal. The assumption of orthogonal terms is incorrect regarding natural languages which causes problems with synonyms and strong related terms. This facilitates the use of stopword lists, stemming and thesaurus in TVSM. In contrast to the generalized vector space model the TVSM does not depend on concurrence-based similarities between terms. Definitions The basic premise of TVSM is the existence of a ''d'' dimensional space ''R'' with only positive axis intercepts, i.e. ''R in R+'' and ''d in N+''. Each dimension of ''R'' represents a fundamental topic. A term vector ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vector Space Model
Vector space model or term vector model is an algebraic model for representing text documents (and any objects, in general) as vectors of identifiers (such as index terms). It is used in information filtering, information retrieval, indexing and relevancy rankings. Its first use was in the SMART Information Retrieval System. Definitions Documents and queries are represented as vectors. :d_j = ( w_ ,w_ , \dotsc ,w_ ) :q = ( w_ ,w_ , \dotsc ,w_ ) Each dimension corresponds to a separate term. If a term occurs in the document, its value in the vector is non-zero. Several different ways of computing these values, also known as (term) weights, have been developed. One of the best known schemes is tf-idf weighting (see the example below). The definition of ''term'' depends on the application. Typically terms are single words, keywords, or longer phrases. If words are chosen to be the terms, the dimensionality of the vector is the number of words in the vocabulary (the number of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Retrieval
Information retrieval (IR) in computing and information science is the process of obtaining information system resources that are relevant to an information need from a collection of those resources. Searches can be based on full-text or other content-based indexing. Information retrieval is the science of searching for information in a document, searching for documents themselves, and also searching for the metadata that describes data, and for databases of texts, images or sounds. Automated information retrieval systems are used to reduce what has been called information overload. An IR system is a software system that provides access to books, journals and other documents; stores and manages those documents. Web search engines are the most visible IR applications. Overview An information retrieval process begins when a user or searcher enters a query into the system. Queries are formal statements of information needs, for example search strings in web search engines. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generalized Vector Space Model
The Generalized vector space model is a generalization of the vector space model used in information retrieval. Wong ''et al.'' presented an analysis of the problems that the pairwise orthogonality assumption of the vector space model (VSM) creates. From here they extended the VSM to the generalized vector space model (GVSM). Definitions GVSM introduces term to term correlations, which deprecate the pairwise orthogonality assumption. More specifically, the factor considered a new space, where each term vector ''ti'' was expressed as a linear combination of ''2n'' vectors ''mr'' where ''r = 1...2n''. For a document ''dk'' and a query ''q'' the similarity function now becomes: :sim(d_k,q) = \frac where ''ti'' and ''tj'' are now vectors of a ''2n'' dimensional space. Term correlation t_i \cdot t_j can be implemented in several ways. For an example, Wong et al. uses the term occurrence frequency matrix obtained from automatic indexing as input to their algorithm. The term occurren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ontology (information Science)
In computer science and information science, an ontology encompasses a representation, formal naming, and definition of the categories, properties, and relations between the concepts, data, and entities that substantiate one, many, or all domains of discourse. More simply, an ontology is a way of showing the properties of a subject area and how they are related, by defining a set of concepts and categories that represent the subject. Every academic discipline or field creates ontologies to limit complexity and organize data into information and knowledge. Each uses ontological assumptions to frame explicit theories, research and applications. New ontologies may improve problem solving within that domain. Translating research papers within every field is a problem made easier when experts from different countries maintain a controlled vocabulary of jargon between each of their languages. For instance, the definition and ontology of economics is a primary concern in Marxist econo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WordNet
WordNet is a lexical database of semantic relations between words in more than 200 languages. WordNet links words into semantic relations including synonyms, hyponyms, and meronyms. The synonyms are grouped into ''synsets'' with short definitions and usage examples. WordNet can thus be seen as a combination and extension of a dictionary and thesaurus. While it is accessible to human users via a web browser, its primary use is in automatic text analysis and artificial intelligence applications. WordNet was first created in the English language and the English WordNet database and software tools have been released under a BSD style license and are freely available for download from that WordNet website. History and team members WordNet was first created in English only in the Cognitive Science Laboratory of Princeton University under the direction of psychology professor George Armitage Miller starting in 1985 and was later directed by Christiane Fellbaum. The project was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |