|
Tonicella Lineata
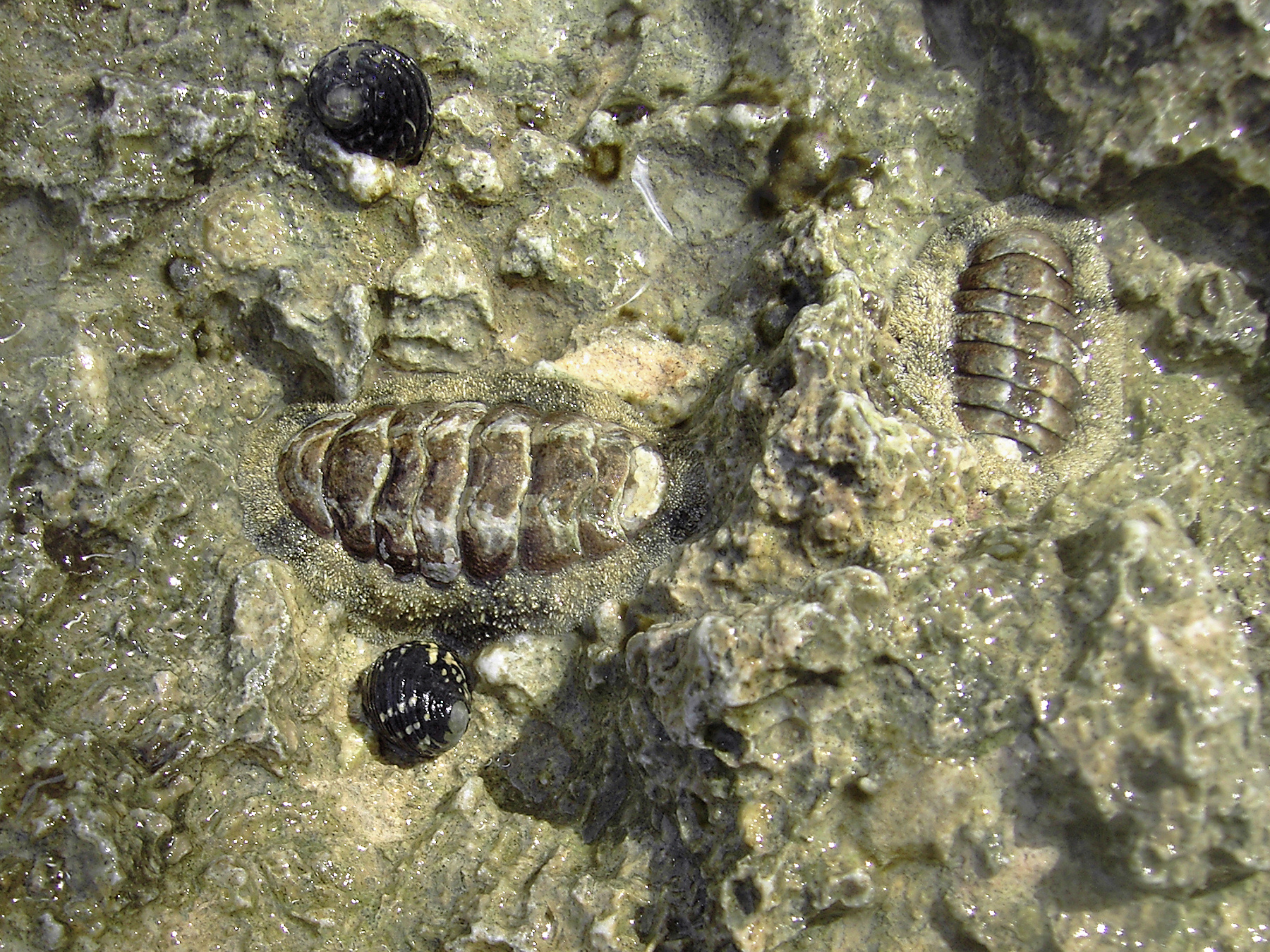
''Tonicella lineata'', commonly known as the lined chiton, is a species of chiton from the North Pacific. Size and description ''Tonicella lineata'' is a very colorful chiton, having blue, purple or black straight or zig-zag lines on each of the eight valves. The background color of the valves is often brown or red, but can also be bright blue or yellow to orange. The girdle is hairless and brown to red or pink, often with regular yellow or white patches. This species grows to 5 cm in length. Similar species '' Tonicella lokii'' is extremely similar but has radiating bands on the girdle. '' Tonicella undocaerulea'' is very similar but lacks a dark border to the concentric blue lines on the anterior plate. '' Mopalia spectabilis'' looks superficially similar due to its bright blue wavy lines on the valves, but has a hairy girdle.Baldwin, A. (2007). Illustrated Keys to the chitons (Polyplacophora). Accessed from: It can also be confused with '' Tonicella insignis'' ( Reeve, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiton
Chitons () are marine molluscs of varying size in the class Polyplacophora ( ), formerly known as Amphineura. About 940 extant and 430 fossil species are recognized. They are also sometimes known as sea cradles or coat-of-mail shells or suck-rocks, or more formally as loricates, polyplacophorans, and occasionally as polyplacophores. Chitons have a shell composed of eight separate shell plates or valves. These plates overlap slightly at the front and back edges, and yet articulate well with one another. Because of this, the shell provides protection at the same time as permitting the chiton to flex upward when needed for locomotion over uneven surfaces, and even allows the animal to curl up into a ball when dislodged from rocks. The shell plates are encircled by a skirt known as a girdle. Habitat Chitons live worldwide, from cold waters through to the tropics. They live on hard surfaces, such as on or under rocks, or in rock crevices. Some species live quite high in the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea in the south. The Japanese archipelago consists of four major islands—Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu—and List of islands of Japan, thousands of smaller islands, covering . Japan has a population of over 123 million as of 2025, making it the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh-most populous country. The capital of Japan and List of cities in Japan, its largest city is Tokyo; the Greater Tokyo Area is the List of largest cities, largest metropolitan area in the world, with more than 37 million inhabitants as of 2024. Japan is divided into 47 Prefectures of Japan, administrative prefectures and List of regions of Japan, eight traditional regions. About three-quarters of Geography of Japan, the countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ctenidium (mollusc)
A ctenidium is a respiratory organ or gill which is found in many molluscs. This structure exists in bivalves, cephalopods, polyplacophorans (chitons), and in aquatic gastropods such as freshwater snails and marine snails. Certain molluscs, such as the bivalves, possess paired ctenidia, but others, such as members of the Ampullariidae, bear a single ctenidium. A ctenidium is shaped like a comb or a feather, with a central part from which many filaments or plate-like structures protrude, lined up in a row. Some aquatic gastropods possess a single row of filaments on their ctenidium, known as the monopectinate condition, and others have a pair of filament rows, known as the bipectinate or aspidobranch condition. The ctenidium hangs into the mantle cavity and increases the area available for gas exchange. The apple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptasterias Haxactis
''Leptasterias'' is a genus of starfish in the family Asteriidae. Members of this genus are characterised by having six arms although five-armed specimens sometimes occur. ''L. muelleri'' is the type species. The taxonomy of the genus is confusing and ''Leptasterias hexactis'' seems to be a species complex. Some species brood their eggs. Description and biology ''Leptasterias'' is a genus of starfish in the family Asteriidae and order Forcipulatida. It is often noted that members in the genus have six arms, however, occasionally five-armed specimen can occur. They are also characterized by having several cryptic species complexes. They are often found in the waters of Alaska to central California in rocky intertidal and subtidal habitats. They are typically small in size, measuring less than 6 cm from ray tip to ray tip. They mature around the age of two. They are known for being lecithotrophic, providing the embryo with no nutrition other than the yolk in its egg. The fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pisaster Ochraceus
''Pisaster ochraceus'', generally known as the purple sea star, ochre sea star, or ochre starfish, is a common seastar found among the waters of the Pacific Ocean. Identified as a keystone species, ''P. ochraceus'' is considered an important indicator for the health of the intertidal zone. Description This sea star has five stout rays that range in length from 10 to 25 centimeters (4 to 10 in). The rays are arranged around an ill-defined central disk. While most individuals are purple, they can be orange, orange-ochre, yellow, reddish, or brown. The aboral surface contains many small spines (ossicles) that are arranged in a netlike or pentagonal pattern on the central disk. The ossicles are no higher than 2 mm.Kozloff, E. N. (1996). Marine Invertebrates of the Pacific Northwest. Seattle: University of Washington Press.McFadden, M. (2002)Pisaster ochraceus Retrieved May 10, 2010 In ''Pisaster'' the tube feet have suckers on their distal ends which allow them to attach to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strongylocentrotus Purpuratus
''Strongylocentrotus purpuratus'' is a species of sea urchin in the family Strongylocentrotidae commonly known as the purple sea urchin. It lives along the eastern edge of the Pacific Ocean extending from Ensenada, Mexico, to British Columbia, Canada. This sea urchin species is deep purple in color, and lives in lower inter-tidal and nearshore sub-tidal communities. Its eggs are orange when secreted in water. January, February, and March function as the typical active reproductive months for the species. Sexual maturity is reached around two years. It normally grows to a diameter of about 10 cm (4 inches), consisting of an exoskeleton called a test. They may live as long as 70 years. ''Strongylocentrotus purpuratus'' is used as a model organism and its genome was the first echinoderm genome to be sequenced. Role in biomedical research The initial discovery of three distinct eukaryotic DNA-dependent RNA polymerases was made using ''S. purpuratus'' as a model org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oregon
Oregon ( , ) is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is a part of the Western U.S., with the Columbia River delineating much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of its eastern boundary with Idaho. The 42nd parallel north, 42° north parallel delineates the southern boundary with California and Nevada. The western boundary is formed by the Pacific Ocean. Oregon has been home to many Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous nations for thousands of years. The first European traders, explorers, and settlers began exploring what is now Oregon's Pacific coast in the early to mid-16th century. As early as 1564, the Spanish expeditions to the Pacific Northwest, Spanish began sending vessels northeast from the Philippines, riding the Kuroshio Current in a sweeping circular route across the northern part of the Pacific. In 1592, Juan de Fuca undertook detailed mapping a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isopods
Isopoda is an Order (biology), order of crustaceans. Members of this group are called isopods and include both Aquatic animal, aquatic species and Terrestrial animal, terrestrial species such as woodlice. All have rigid, segmented exoskeletons, two pairs of Antenna (biology), antennae, seven pairs of jointed limbs on the Thorax#In_arthropods, thorax, and five pairs of branching appendages on the Abdomen#In other animals, abdomen that are used in Respiration (physiology), respiration. Females brood their young in a pouch under their thorax called the Brood pouch (Peracarida), marsupium. Isopods have various feeding methods: some eat dead or decaying plant and animal matter, others are Grazing (behaviour), grazers or filter feeders, a few are Predation, predators, and some are internal or external parasites, mostly of fish. Aquatic species mostly live on the seabed or the bottom of freshwater body of water, bodies of water, but some Taxon, taxa can swim for short distance. Terre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algae
Algae ( , ; : alga ) is an informal term for any organisms of a large and diverse group of photosynthesis, photosynthetic organisms that are not plants, and includes species from multiple distinct clades. Such organisms range from unicellular microalgae, such as cyanobacteria, ''Chlorella'', and diatoms, to multicellular macroalgae such as kelp or brown algae which may grow up to in length. Most algae are aquatic organisms and lack many of the distinct cell and tissue types, such as stomata, xylem, and phloem that are found in embryophyte, land plants. The largest and most complex marine algae are called seaweeds. In contrast, the most complex freshwater forms are the Charophyta, a Division (taxonomy), division of green algae which includes, for example, ''Spirogyra'' and stoneworts. Algae that are carried passively by water are plankton, specifically phytoplankton. Algae constitute a Polyphyly, polyphyletic group because they do not include a common ancestor, and although Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sublittoral Zone
The neritic zone (or sublittoral zone) is the relatively shallow part of the ocean above the drop-off of the continental shelf, approximately in depth. From the point of view of marine biology it forms a relatively stable and well-illuminated environment for marine life, from plankton up to large fish and corals, while physical oceanography sees it as where the oceanic system interacts with the coast. Definition (marine biology), context, extra terminology In marine biology, the neritic zone, also called coastal waters, the coastal ocean or the sublittoral zone, refers to the zone of the ocean where sunlight reaches the ocean floor, that is, where the water is never so deep as to take it out of the photic zone. It extends from the low tide mark to the edge of the continental shelf, with a relatively shallow depth extending to about 200 meters (660 feet). Above the neritic zone lie the intertidal (or eulittoral) and supralittoral zones; below it the continental slope begi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intertidal
The intertidal zone or foreshore is the area above water level at low tide and underwater at high tide; in other words, it is the part of the littoral zone within the tidal range. This area can include several types of habitats with various species of life, such as sea stars, sea urchins, and many species of coral with regional differences in biodiversity. Sometimes it is referred to as the ''littoral zone'' or '' seashore'', although those can be defined as a wider region. The intertidal zone also includes steep rocky cliffs, sandy beaches, bogs or wetlands (e.g., vast mudflats). This area can be a narrow strip, such as in Pacific islands that have only a narrow tidal range, or can include many meters of shoreline where shallow beach slopes interact with high tidal excursion. The peritidal zone is similar but somewhat wider, extending from above the highest tide level to below the lowest. Organisms in the intertidal zone are well-adapted to their environment, facing high level ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puget Sound
Puget Sound ( ; ) is a complex estuary, estuarine system of interconnected Marine habitat, marine waterways and basins located on the northwest coast of the U.S. state of Washington (state), Washington. As a part of the Salish Sea, the sound (geography), sound has one major and two minor connections to the Strait of Juan de Fuca, which in turn connects to the open Pacific Ocean. The major connection is Admiralty Inlet; the minor connections are Deception Pass and the Swinomish Channel. Puget Sound extends approximately from Deception Pass in the north to Olympia, Washington, Olympia in the south. Its average depth is and its maximum depth, off Jefferson Point between Indianola, Washington, Indianola and Kingston, Washington, Kingston, is . The depth of the main basin, between the southern tip of Whidbey Island and Tacoma, Washington, Tacoma, is approximately . In 2009, the term Salish Sea was established by the United States Board on Geographic Names as the collective wate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |