|
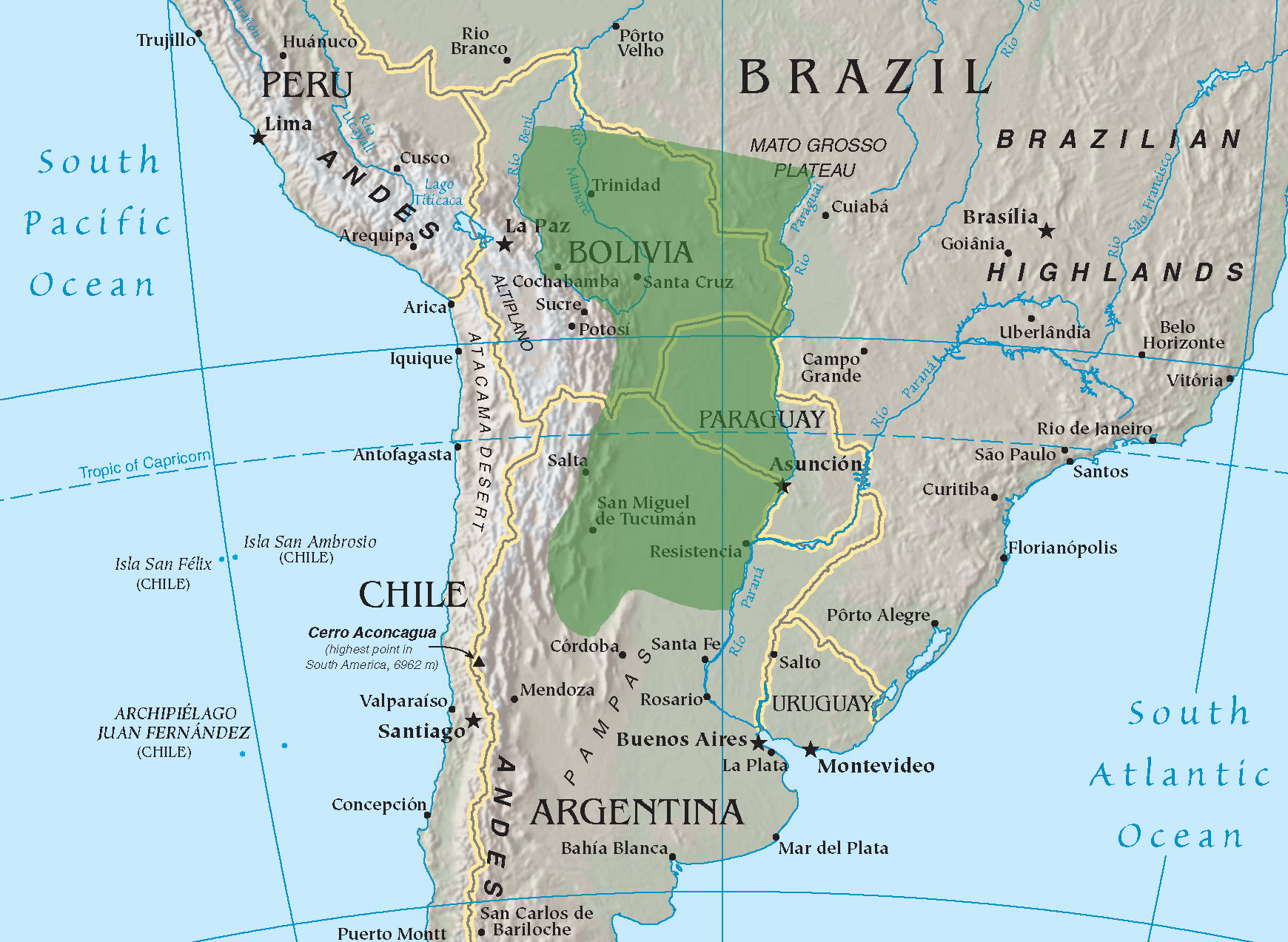
Toba People
The Toba people, also known as the Qom people, are one of the largest Indigenous groups in Argentina who historically inhabited the region known today as the Gran Chaco, Pampas of the Central Chaco. During the 16th century, the Qom inhabited a large part of what is today northern Argentina, in the current provinces of Salta Province, Salta, Chaco Province, Chaco, Santiago del Estero Province, Santiago del Estero, Formosa Province, Formosa and the province of Gran Chaco Province, Gran Chaco in the southeast of the Tarija Department, Department of Tarija in Bolivia (which the Qom have inhabited since the 20th century). Currently, many Toba, due to persecution in their rural ancestral regions, live in the suburbs of Orán, Salta, San Ramón de la Nueva Orán, Salta, Tartagal, Salta, Tartagal, Resistencia, Chaco, Resistencia, Charata, Formosa, Rosario, Santa Fe, Rosario and Santa Fe, Argentina, Santa Fe and in Greater Buenos Aires. Nearly 130,000 people currently identify themselves as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resistencia, Chaco
Resistencia () is the capital and largest city of the Provinces of Argentina, province of Chaco Province, Chaco in north-eastern Argentina. According to the 2010 census, the population of the city proper was 291,720 inhabitants. It is the anchor of a larger metropolitan area, Greater Resistencia, which comprises at least three more municipalities for a total population of 387,340 as of 2010. This conurbation is the largest in the province, and the List of cities in Argentina by population, eleventh most populous in the country. It is located along the Negro River (Chaco), Negro River, a tributary of the much larger Paraná river, Paraná River, opposite the city of Corrientes, Corrientes Province. The area was originally inhabited by Guaycuru aboriginals such as the Toba people, Tobas. Their resistance to evangelisation postponed substantial European settlement until the late 19th century. Not until 1865 was a proper settlement established, and on January 27, 1878, Resistencia was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Buenos Aires
Greater Buenos Aires (, GBA), also known as the Buenos Aires Metropolitan Area (, AMBA), refers to the urban agglomeration comprising the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires Buenos Aires, controlled by the government of the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires, is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Argentina. It is located on the southwest of the Río de la Plata. Buenos Aires is classified as an Alpha− glob ... and the adjacent 24 ''partidos of Buenos Aires, partidos'' (districts) in the Buenos Aires Province, Province of Buenos Aires. Thus, it does not constitute a single administrative unit. The conurbation spreads south, west and north of Buenos Aires city. To the east, the Río de la Plata, River Plate serves as a natural boundary. Urban sprawl, especially between 1945 and 1980, created a vast metropolitan area of over 3,800 km² (1,500 mi²) – or 19 times the area of Buenos Aires proper. The 24 suburban ''partidos'' (counties) grew more than sixfold in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Land Rights
Indigenous land rights are the rights of Indigenous peoples to land and natural resources therein, either individually or collectively, mostly in colonised countries. Land and resource-related rights are of fundamental importance to Indigenous peoples for a range of reasons, including: the religious significance of the land, self-determination, identity, and economic factors. Land is a major economic asset, and in some Indigenous societies, using natural resources of earth and sea form (or could form) the basis of their household economy, so the demand for ownership derives from the need to ensure their access to these resources. Land can also be an important instrument of inheritance or a symbol of social status. In many Indigenous societies, such as among the many Aboriginal Australian peoples, the land is an essential part of their spirituality and belief systems. Indigenous land claims have been addressed with varying degrees of success on the national and inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as inactive or latent tuberculosis. A small proportion of latent infections progress to active disease that, if left untreated, can be fatal. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with hemoptysis, blood-containing sputum, mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms. Tuberculosis is Human-to-human transmission, spread from one person to the next Airborne disease, through the air when people who have active TB in their lungs cough, spit, speak, or sneeze. People with latent TB do not spread the disease. A latent infection is more likely to become active in those with weakened I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discrimination
Discrimination is the process of making unfair or prejudicial distinctions between people based on the groups, classes, or other categories to which they belong or are perceived to belong, such as race, gender, age, class, religion, or sexual orientation. Discrimination typically leads to groups being unfairly treated on the basis of perceived statuses based on ethnic, racial, gender or religious categories. It involves depriving members of one group of opportunities or privileges that are available to members of another group. Discriminatory traditions, policies, ideas, practices and laws exist in many countries and institutions in all parts of the world, including some, where such discrimination is generally decried. In some places, countervailing measures such as quotas have been used to redress the balance in favor of those who are believed to be current or past victims of discrimination. These attempts have often been met with controversy, and sometimes been called re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients which adversely affects the body's tissues and form. Malnutrition is a category of diseases that includes undernutrition and overnutrition. Undernutrition is a lack of nutrients, which can result in stunted growth, wasting, and being underweight. A surplus of nutrients causes overnutrition, which can result in obesity or toxic levels of micronutrients. In some developing countries, overnutrition in the form of obesity is beginning to appear within the same communities as undernutrition. Most clinical studies use the term 'malnutrition' to refer to undernutrition. However, the use of 'malnutrition' instead of 'undernutrition' makes it impossible to distinguish between undernutrition and overnutrition, a less acknowledged form of malnutrition. Accordingly, a 2019 report by The Lance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poverty
Poverty is a state or condition in which an individual lacks the financial resources and essentials for a basic standard of living. Poverty can have diverse Biophysical environment, environmental, legal, social, economic, and political causes and effects. When evaluating poverty in statistics or economics there are two main measures: ''absolute poverty'' which compares income against the amount needed to meet basic needs, basic personal needs, such as food, clothing, and Shelter (building), shelter; secondly, ''relative poverty'' measures when a person cannot meet a minimum level of living standards, compared to others in the same time and place. The definition of ''relative poverty'' varies from one country to another, or from one society to another. Statistically, , most of the world's population live in poverty: in Purchasing Power Parity, PPP dollars, 85% of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napalpí Massacre
The Napalpí massacre occurred on 19 July 1924, in Napalpí a rural village in the Chaco Province of Northeast Argentina. It involved the massacre of 400 Indigenous people of the Toba and Mocoví ethnicity by the Argentine Police and ranchers. Historical context Forty years earlier, the Argentine Army had been involved in a military campaign to subjugate the Indigenous people, mostly Guaycuru of several different ethnic groups, of the Argentine Chaco called the Conquest of Chaco. The campaign resulted in the death of thousands of Indigenous people, the displacement of many more, and the social and cultural destruction of numerous ethnic groups from the provinces of Chaco and Formosa. The Argentine forces established a line of fortresses in order to gain lands for European settlers. The land was mainly used by the settlers to grow cotton. The native people were confined in compounds, where they were subjected to a regime of exploitation bordering on slavery. One of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massacre
A massacre is an event of killing people who are not engaged in hostilities or are defenseless. It is generally used to describe a targeted killing of civilians Glossary of French words and expressions in English#En masse, en masse by an armed group or person. The word is a Loanword, loan of a French term for "butchery" or "carnage". Other terms with overlapping scope include war crime, pogrom, mass killing, mass murder, and extrajudicial killing. Etymology ''Massacre'' derives from late 16th century Middle French word ''macacre'' meaning "slaughterhouse" or "butchery". Further origins are dubious, though the word may be related to Latin ''macellum'' "provisions store, butcher shop". The Middle French word ''macecr'' "butchery, carnage" is first recorded in the late 11th century. Its primary use remained the context of animal slaughter (in hunting terminology referring to the head of a stag) well into the 18th century. The use of ''macecre'' "butchery" of the mass killing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Assimilation
Cultural assimilation is the process in which a minority group or culture comes to resemble a society's Dominant culture, majority group or fully adopts the values, behaviors, and beliefs of another group. The melting pot model is based on this concept. A related term is cultural integration, which describes the process of becoming economically and socially integrated into another society while retaining elements of one’s original culture. This approach is also known as cultural pluralism, and it forms the basis of a cultural mosaic model that upholds the preservation of cultural rights. Another closely related concept is acculturation, which occurs through cultural diffusion and involves changes in the cultural patterns of one or both groups, while still maintaining distinct characteristics. There are various types of cultural assimilation, including full assimilation and forced assimilation. Full assimilation is common, as it occurs spontaneously. Assimilation can also invol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesuit Reduction
Reductions (, also called ; ) were settlements established by Spanish rulers and Roman Catholic missionaries in Spanish America and the Spanish East Indies (the Philippines). In Portuguese-speaking Latin America, such reductions were also called ''aldeias''. The Spanish and Portuguese relocated, forcibly in many cases, indigenous inhabitants (''Indians'' or ''Indios'') of their colonies into urban settlements modeled on those in Spain and Portugal. The Royal Academy of Spain defines (reduction) as "a grouping into settlement of indigenous people for the purpose of evangelization and assimilation." In colonial Mexico, reductions were called "congregations" (''congregaciones''). Forced resettlements aimed to concentrate indigenous people into communities, facilitating civil and religious control over populations. The concentration of the indigenous peoples into towns facilitated the organization and exploitation of their labor. The practice began during Spanish colonization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unfree Labour
Forced labour, or unfree labour, is any work relation, especially in modern or early modern history, in which people are employed against their will with the threat of destitution, detention, or violence, including death or other forms of extreme hardship to either themselves or members of their families. Unfree labour includes all forms of slavery, penal labour, and the corresponding institutions, such as debt slavery, serfdom, corvée and labour camps. Definition Many forms of unfree labour are also covered by the term forced labour, which is defined by the International Labour Organization (ILO) as all involuntary work or service exacted under the menace of a penalty.Andrees and Belser, "Forced labor: Coercion and exploitation in the private economy", 2009. Rienner and ILO. However, under the ILO Forced Labour Convention of 1930, the term forced or compulsory labour does not include: *"any work or service exacted in virtue of compulsory military service laws fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |