|
Timur's Conquests
The Timurid conquests and invasions started in the late 14th century with Timur's control over the Chagatai Khanate and ended at the start of the 15th century with the death of Timur. Due to the sheer scale of Timur's wars, and due to the fact that he was generally undefeated in battle, he has been regarded as one of the most successful military commanders of all time. These wars resulted in Timur's supremacy over Central Asia, Persia, the Caucasus, the Levant, and parts of South Asia and Eastern Europe, and they also resulted in the formation of the short-lived Timurid Empire. Timur gained power over the Western Chagatai Khanate (Transoxiana) after defeating Amir Husayn, the regent of the Chagatai Khanate, at the Siege of Balkh (1370), Battle of Balkh but the laws laid down by Genghis Khan prevented him from becoming Khagan in his own right because he was not a Descendants of Genghis Khan, direct descendant of Genghis Khan by birth.Marozzi, Justin (2004). Tamerlane: Sword of Is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timurid Empire
The Timurid Empire was a late medieval, culturally Persianate, Turco-Mongol empire that dominated Greater Iran in the early 15th century, comprising modern-day Iran, Iraq, Afghanistan, much of Central Asia, the South Caucasus, and parts of contemporary Pakistan, North India, and Turkey. The empire was culturally hybrid, combining Turkic, Mongolic, and Persian influences, with the last members of the dynasty being regarded as "ideal Perso-Islamic rulers". The empire was founded by Timur (also known as Tamerlane), a warlord of Turco-Mongol lineage, who established the empire between 1370 and his death in 1405. He envisioned himself as the great restorer of the Mongol Empire of Genghis Khan, regarded himself as Genghis's heir, and associated closely with the Borjigin. Timur continued vigorous trade relations with Ming China and the Golden Horde, with Chinese diplomats like Ma Huan and Chen Cheng regularly traveling west to Samarkand to buy and sell goods. The empire led ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shahrukh Mirza
Shah Rukh or Shahrukh Mirza (, ''Šāhrokh''; 20 August 1377 – 13 March 1447) was the ruler of the Timurid Empire between 1405 and 1447. He was the son of the Central Asian conqueror Timur (Tamerlane), who founded the Timurid dynasty in 1370. However, Shah Rukh ruled only over the eastern portion of the empire established by his father, comprising most of Persia and Transoxiana, the western territories having been lost to invaders in the aftermath of Timur's death. In spite of this, Shah Rukh's empire remained a cohesive dominion of considerable extent throughout his reign, as well as a dominant power in Asia. Shah Rukh controlled the main trade routes between Asia and Europe, including the legendary Silk Road, and became immensely wealthy as a result. He chose to have his capital not in Samarqand as his father had done, but in Herat. This was to become the political centre of the Timurid empire and residence of his principal successors, though both cities benefited from the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as ''Ulug Ulus'' ( in Turkic) was originally a Mongols, Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the division of the Mongol Empire after 1259, it became a functionally separate khanate. It is also known as the Kipchak Khanate or the Ulus of Jochi, and replaced the earlier, less organized Cuman–Kipchak confederation. After the death of Batu Khan (the founder of the Blue Horde) in 1255, his dynasty flourished for a full century, until 1359, though the intrigues of Nogai Khan, Nogai instigated a partial civil war in the late 1290s. The Horde's military power peaked during the reign of Özbeg Khan (1312–1341), who adopted Islam. The territory of the Golden Horde at its peak extended from Siberia and Central Asia to parts of Eastern Europe from the Ural Mountains, Urals to the Danube in the west, and from the Black Sea to the Caspian Sea in the south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
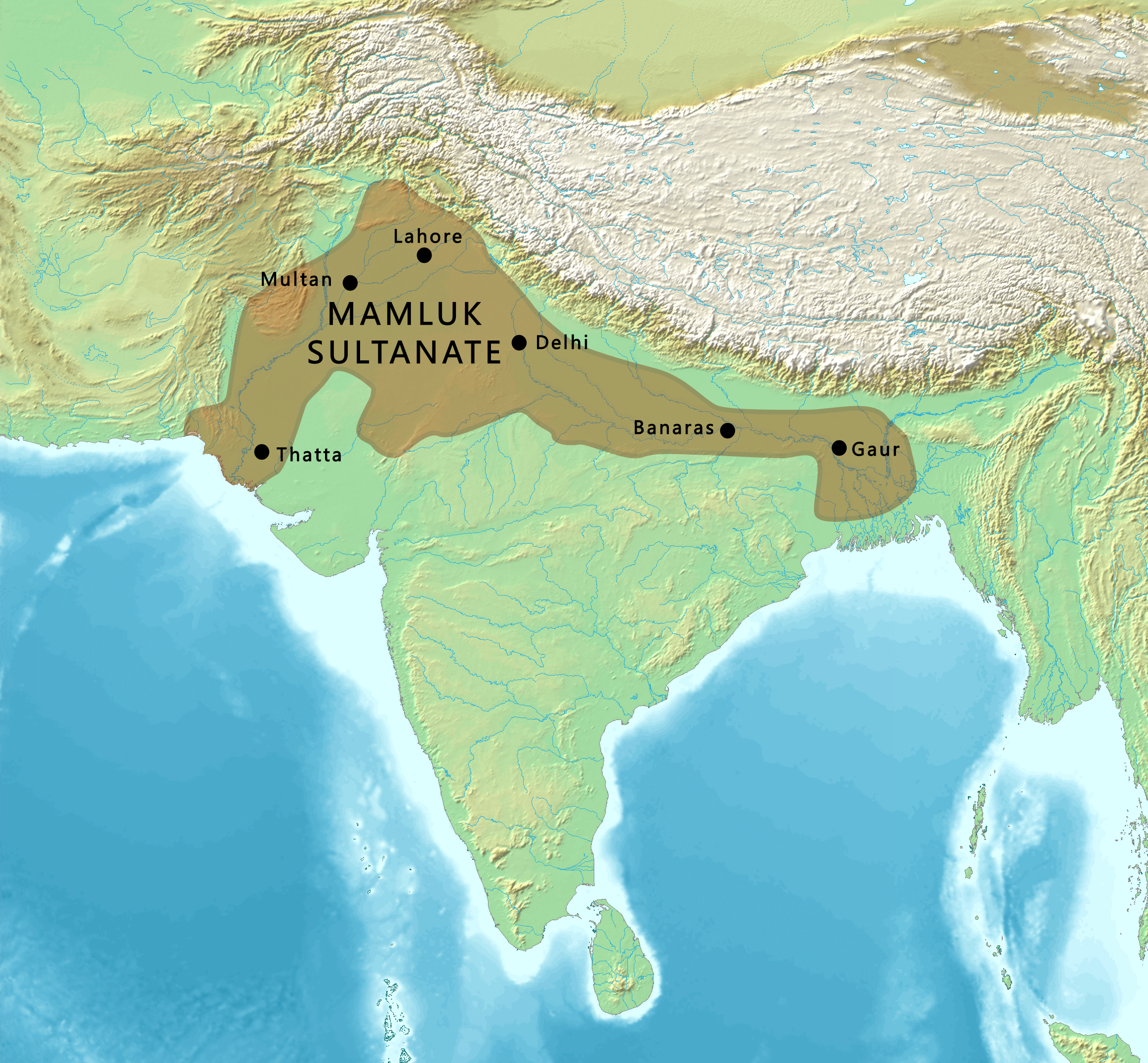
Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate or the Sultanate of Delhi was a Medieval India, late medieval empire primarily based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for more than three centuries.Delhi Sultanate Encyclopædia Britannica The sultanate was established around in the former Ghurid Empire, Ghurid territories in India. The sultanate's history is generally divided into five periods: Mamluk dynasty (Delhi), Mamluk (1206–1290), Khalji dynasty, Khalji (1290–1320), Tughlaq dynasty, Tughlaq (1320–1414), Sayyid dynasty, Sayyid (1414–1451), and Lodi dynasty, Lodi (1451–1526). It covered large swaths of territory in modern-day India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, as well as some parts of southern Nepal. The foundation of the Sultanate was established by the Ghurid conqueror Muhammad of Ghor, Muhammad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Central Europe, between the early 16th and early 18th centuries. The empire emerged from a Anatolian beyliks, ''beylik'', or principality, founded in northwestern Anatolia in by the Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. His successors Ottoman wars in Europe, conquered much of Anatolia and expanded into the Balkans by the mid-14th century, transforming their petty kingdom into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the Fall of Constantinople, conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed II. With its capital at History of Istanbul#Ottoman Empire, Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul) and control over a significant portion of the Mediterranean Basin, the Ottoman Empire was at the centre of interacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mamluk Sultanate (Cairo)
The Mamluk Sultanate (), also known as Mamluk Egypt or the Mamluk Empire, was a state that ruled medieval Egypt, Egypt, the Levant and the Hejaz from the mid-13th to early 16th centuries, with Cairo as its capital. It was ruled by a military caste of mamluks (freed slave soldiers) headed by a sultan. The sultanate was established with the overthrow of the Ayyubid dynasty in Egypt in 1250 and was Ottoman–Mamluk War (1516–1517), conquered by the Ottoman Empire in 1517. Mamluk history is generally divided into the Turkic peoples, Turkic or Bahri Mamluks, Bahri period (1250–1382) and the Circassians, Circassian or Burji Mamluks, Burji period (1382–1517), called after the predominant ethnicity or corps of the ruling Mamluks during these respective eras. The first rulers of the sultanate hailed from the mamluk regiments of the Ayyubid sultan as-Salih Ayyub (), usurping power from his successor in 1250. The Mamluks under Sultan Qutuz and Baybars Battle of Ain Jalut, routed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suzerainty
A suzerain (, from Old French "above" + "supreme, chief") is a person, state (polity)">state or polity who has supremacy and dominant influence over the foreign policy">polity.html" ;"title="state (polity)">state or polity">state (polity)">state or polity who has supremacy and dominant influence over the foreign policy and economic relations of another subordinate party or polity, but allows internal autonomy to that subordinate. Where the subordinate polity is called a vassal, vassal state or tributary state, the dominant party is called the suzerain. The rights and obligations of a vassal are called ''vassalage'', and the rights and obligations of a suzerain are called suzerainty. Suzerainty differs from sovereignty in that the dominant power does not exercise centralized governance over the vassals, allowing tributary states to be technically self-ruling but enjoy only limited independence. Although the situation has existed in a number of historical empires, it is con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transoxiana
Transoxiana or Transoxania (, now called the Amu Darya) is the Latin name for the region and civilization located in lower Central Asia roughly corresponding to eastern Uzbekistan, western Tajikistan, parts of southern Kazakhstan, parts of Turkmenistan and southern Kyrgyzstan. The name was first coined by Alexander the Great in the 4th century BC when Alexander's troops conquered the region. The region may have had a similar Greek name in the days of Alexander the Great, but the earlier name is no longer known. Geographically, it is the region between the rivers Amu Darya to its south and the Syr Darya to its north. The region of Transoxiana was one of the satrapies (provinces) of the Achaemenid Empire of Persia under the name Sogdia. It was defined within the classical world of Persia to distinguish it from Iran proper, especially its northeastern province of Khorasan, a term originating with the Sasanians, although early Arab historians and geographers tended to subs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
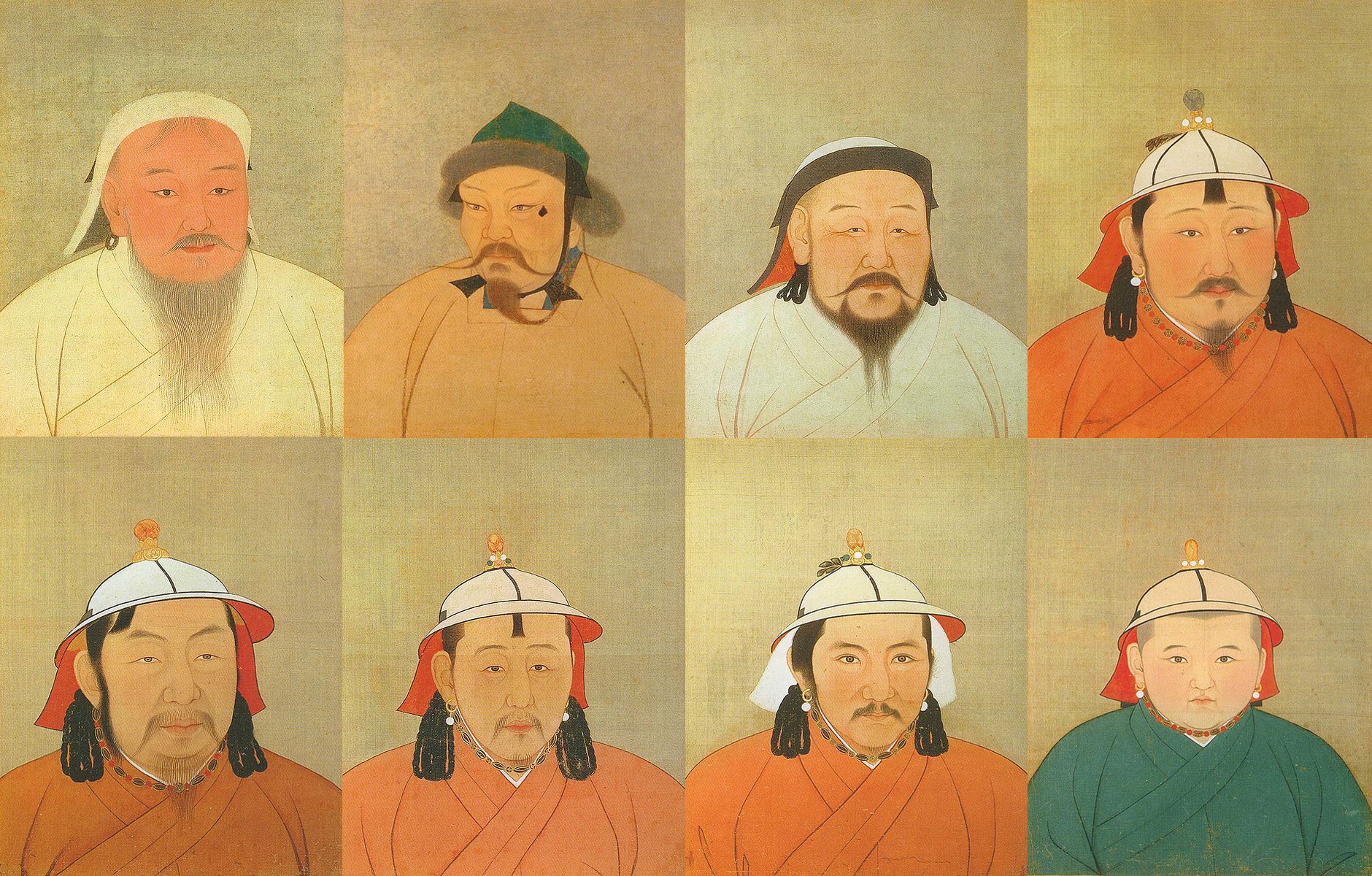
Great Khan
Khagan or Qaghan ( Middle Mongol:; or ''Khagan''; ) or zh, c=大汗, p=Dàhán; ''Khāqān'', alternatively spelled Kağan, Kagan, Khaghan, Kaghan, Khakan, Khakhan, Khaqan, Xagahn, Qaghan, Chagan, Қан, or Kha'an is a title of imperial rank in Turkic, Mongolic, and some other languages, equal to the status of emperor and someone who rules a khaganate (empire). The female equivalent is Khatun. It may also be translated as " Khan of Khans", equivalent to King of Kings. In Bulgarian, the title became known as ''Khan'', while in modern Turkic, the title became ''Khaan'' with the ''g'' sound becoming almost silent or non-existent; the ''ğ'' in modern Turkish ''Kağan'' is also silent. After the division of the Mongol Empire, monarchs of the Yuan dynasty and the Northern Yuan held the title of ''Khagan''. ''Kağan, Hakan'' and ''Kaan'', Turkish equivalents of the title are common Turkish names in Turkey. The common western rendering as Great Khan (or ''Grand Khan'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saray Mulk Khanum
Saray Mulk Khanum ( Chagatai: سرای ملک خانم; 1341 – 1408) was the empress consort of the Timurid Empire as the chief consort of Timur, also known as Tamerlane the Great, the founder of the Timurid Empire as well as the Timurid dynasty. By birth, she was a princess of Moghulistan as a daughter of Qazan Khan ibn Yasaur and was also a direct descendant of Genghis Khan. Family and lineage Saray Mulk Khanum was born a princess of Moghulistan in 1341 to Qazan Khan ibn Yasaur, the last Khan of the Chagatai Khanate. Saray's grandfather was Khan Yasa'ur, her father's predecessor and a great-great-grandson of Chagatai Khan. She was therefore, a direct descendant of Genghis Khan, the Great Khan (Emperor) and founder of the Mongol Empire. Saray was thus, a member of the House of Borjigin, the most renowned family clan in Eurasia. Being the daughter of a Khan, Saray held the title of Khanum ("daughter of a Khan or princess") by birth. Marriage to Timur Before her mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amir
Emir (; ' (), also transliterated as amir, is a word of Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person possessing actual or ceremonial authority. The title has a history of use in West Asia, East Africa, West Africa, Central Asia, and South Asia. In the modern era, when used as a formal monarchical title, it is roughly synonymous with "prince", applicable both to a son of a hereditary monarch, and to a reigning monarch of a sovereign principality, namely an emirate. The feminine form is emira ( '), with the same meaning as "princess". Prior to its use as a monarchical title, the term "emir" was historically used to denote a "commander", "general", or "leader" (for example, Amir al-Mu'min). In contemporary usage, "emir" is also sometimes used as either an honorary or formal title for the head of an Islamic, or Arab (regardless of religion) organisation or movement. Qatar and Kuwait are the only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |