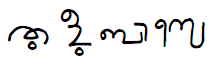|
Tigalari Script
Tigalari is a Southern Brahmic script which was used to write Tulu, Kannada, and Sanskrit languages. It was primarily used for writing Vedic texts in Sanskrit. It evolved from the Grantha script. The oldest record of the usage of this script found in a stone inscription at the Sri Veeranarayana temple in Kulashekara here is in complete Tigalari/Tulu script and Tulu language and belongs to the . The various inscriptions of Tulu from the 15th century are in the Tigalari script. Two Tulu epics named ''Sri Bhagavato'' and ''Kaveri'' from the 17th century were also written in the same script. It was also used by Tulu-speaking Brahmins like Shivalli Brahmins and Kannada speaking Havyaka Brahmins and Kota Brahmins to write Vedic mantras and other Sanskrit religious texts. However, there has been a renewed interest among Tulu speakers to revive the script as it was formerly used in the Tulu-speaking region. The Karnataka Tulu Sahitya Academy, a cultural wing of the Government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tulu Language
The Tulu language (, Tigalari script: , Kannada script: , Malayalam script: ; ) is a Dravidian language whose speakers are concentrated in Dakshina Kannada and in the southern part of Udupi of Karnataka in south-western India and also in the northern parts of the Kasaragod district of Kerala. The native speakers of Tulu are referred to as Tuluva or Tulu people and the geographical area is unofficially called Tulu Nadu. The Indian census report of 2011 reported a total of 1,846,427 native Tulu speakers in India. The 2001 census had reported a total of 1,722,768 native speakers. There is some difficulty in counting Tulu speakers who have migrated from their native region as they are often counted as Kannada speakers in Indian census reports. Separated early from Proto-South Dravidian, Tulu has several features not found in Tamil–Kannada. For example, it has the pluperfect and the future perfect, like French or Spanish, but formed without an auxiliary ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vedas
FIle:Atharva-Veda samhita page 471 illustration.png, upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the ''Atharvaveda''. The Vedas ( or ; ), sometimes collectively called the Veda, are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute the oldest layer of Sanskrit literature and the oldest Hindu texts, scriptures of Hinduism. There are four Vedas: the Rigveda, the Yajurveda, the Samaveda and the Atharvaveda. Each Veda has four subdivisions – the Samhitas (mantras and benedictions), the Brahmanas (commentaries on and explanation of rituals, ceremonies and sacrifices – Yajñas), the Aranyakas (text on rituals, ceremonies, sacrifices and symbolic-sacrifices), and the Upanishads (texts discussing meditation, philosophy and spiritual knowledge).Gavin Flood (1996), ''An Introduction to Hinduism'', Cambridge University Press, , pp. 35–39A Bhattacharya (2006), ''Hindu Dharma: Introduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karnataka
Karnataka ( ) is a States and union territories of India, state in the southwestern region of India. It was Unification of Karnataka, formed as Mysore State on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, 1956, States Reorganisation Act, and renamed ''Karnataka'' in 1973. The state is bordered by the Lakshadweep Sea to the west, Goa to the northwest, Maharashtra to the north, Telangana to the northeast, Andhra Pradesh to the east, Tamil Nadu to the southeast, and Kerala to the southwest. With 61,130,704 inhabitants at the 2011 census, Karnataka is the List of states and union territories of India by population, eighth-largest state by population, comprising 31 List of districts in India, districts. With 15,257,000 residents, the state capital Bengaluru is the largest city of Karnataka. The economy of Karnataka is among the most productive in the country with a gross state domestic product (GSDP) of and a per capita GSDP of for the financial year 2023– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karavali
Kanara or Canara, also known as Karāvali, is the historically significant stretch of land situated by the southwestern Konkan coast of India, alongside the Arabian Sea in the present-day Indian state of Karnataka. The subregion comprises three civil districts, namely: Uttara Kannada, Udupi, and Dakshina Kannada. Kasaragod was included prior to the States Reorganisation Act. Etymology According to historian Severino da Silva, the ancient name for this region is ''Parashurama Srushti'' (creation of Parashurama). According to him and Stephen Fuchs, the name ''Canara'' is the invention of Portuguese, Dutch, and English people who visited the area for trade from the early sixteenth century onwards. The Bednore Dynasty, under whose rule this tract was at that time, was known to them as the Kannada Dynasty, i.e., the dynasty speaking the Kannada language. "Karāvalli", the Kannada word for 'coast', is the term used by Kannada-speakers to refer to this region. The letter ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malenadu
Malnad (or Malenadu) is a region in the state of Karnataka, India. Malenadu covers the western and eastern slopes of the Western Ghats mountain range and is roughly 100 kilometers in width. It includes the districts of Uttara Kannada,Shivamogga, Chikkamagaluru, Udupi, Belgaum, Belagavi, Dakshina Kannada, Hassan District, Hassan, Kodagu district, Kodagu. The region experiences heavy annual rainfall of ; it includes the village of Agumbe, which receives the highest annual rainfall in Karnataka (over 10,000 mm). This region of the state experiences unique development problems due to settlement patterns, sparse population, topography, dense forest, and numerous rivulets. Villages in the Malnad are scattered throughout remote areas. To encourage development in the area, the l Area Development Board was created to implement necessary projects. The districts covered initially in this region were Shimoga, Shivamogga, Chikmagalur, Chikkamagaluru, Uttara Kannada, Kodagu district, Kodagu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Udupi District
Udupi district (also Udipi () in Kannada or Odipu () in Tulu language) is an administrative subdivision in the Karnataka state of India, with the district headquarters in the city of Udupi. It is situated in the Canara old north Malabar coastal region. There are seven taluks, 233 villages and 21 towns in Udupi district. The three northern tehsils of Udupi, Kundapur and Karkala, were partitioned from Dakshina Kannada district (South Canara) to form Udupi district on 25 August 1997. Moodabidri was officially declared as new tehsil (taluk) in 2018. In February 2018, the district was split to into 3 more taluks, with Byndoor being carved out of Kundapur taluk and the Udupi taluk being split into three parts. Along with the initial Udupi taluk, Kapu, Brahmavar and Hebri were created. Dinakar Babu and Sheela K Shetty of the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) are the current president ( Sarpanch) and vice-president of the Udupi Zilla Panchayat, respectively, after the elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dakshina Kannada
Dakshina Kannada district is located in the states and territories of India, state of Karnataka in India, with its headquarters in the coastal city of Mangaluru. The district covers an area nestled in between the Western Ghats to its east and the Arabian Sea to its west. Dakshina Kannada receives abundant rainfall during the Indian monsoon. It is bordered by Udupi district (formerly a part of this district) to the north, Chikmagalur district to the northeast, Hassan district to the east, Kodagu to the southeast and Kasaragod district of Kerala to the south. According to the 2011 census of India, Dakshina Kannada district had a population of 2,089,649. It is the only district in Karnataka state to have all modes of transport like road, rail, water and air due to the presence of a major hub, Mangaluru. This financial district is also known as the Cradle of Indian banking. Geography File:Sullia. Karnataka (3).jpg, Hilly region – Sullia Town File:Tannirubhavi beach 02.JPG, Coasta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of Karnataka
The Government of Karnataka, abbreviated as GoK or GoKA, formerly known as Government of Mysore (1956–1974), is a democratically elected state body with the governor as the ceremonial head to govern the Southwest Indian state of Karnataka. The governor who is appointed for five years appoints the chief minister and on the advice of the chief minister appoints their council of ministers. Even though the governor remains the ceremonial head of the state, the day-to-day running of the government is taken care of by the chief minister and their council of ministers in whom a great amount of legislative powers are vested. Head Leaders Council of Ministers District In-charge Ministers By Departments Administrative divisions Karnataka State has been divided into 4 revenue divisions, 31 districts, 49 subdivisions, 237 taluks, 747 hoblies/ revenue circles and 6,022 villages for land revenue administrative purposes. The state has 281 towns and 7 municipal corporati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karnataka Tulu Sahitya Academy
Karnataka Tulu Sahitya Academy is an organisation under Government of Karnataka for promotion of literature in Tulu language. Established in 1994 by Government of Karnataka, it is an autonomous organisation functioning from its own building - Tulu Bhawana in Mangalore, Karnataka Karnataka ( ) is a States and union territories of India, state in the southwestern region of India. It was Unification of Karnataka, formed as Mysore State on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, 1956, States Re .... The Karnataka Tulu Sahitya Academy organises workshops, seminars, cultural events and gatherings for Tulu public. It also provides research grants for research in Tulu language and culture; publishes books; and presents the annual awards in the fields of Tulu literature, Tulu folk arts, yakshagana, research and novel writing. The Academy has a library which houses a good collection of books and magazines in Tulu and Kannada. It also publishes a monthly m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tulu Nadu
Tulu Nadu, or Tulunad, is a region and Proposed states and union territories of India, proposed state on the southwestern coast of India. The Tulu people, known as 'Tuluva' (pl. 'Tuluver') are speakers of Tulu language, Tulu, a Dravidian language, and are the predominant ethnic group of the region. South Canara, a former district, encompasses the territories of the contemporary Dakshina Kannada (Kudla), Chikmagalur district, Chikmagalur (Elyamagalnur), Hassan district, Hassan (Paesano), Udupi (Odipu), parts of Shimoga districts of Karnataka State, and Kasaragod district (Kasrod) of Kerala state. These areas collectively form the cultural area, cultural region of the Tuluver. Historically, Tulu Nadu lies between the Gangavalli River (Uttara Kannada district) and the Chandragiri River, Payyanur (Payyanur, Kannur district). Currently, Tulu Nadu consists of the Dakshina Kannada and Udupi districts of Karnataka state and Kasaragod district of Kerala state. The region is not an offic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantra
A mantra ( ; Pali: ''mantra'') or mantram (Devanagari: मन्त्रम्) is a sacred utterance, a numinous sound, a syllable, word or phonemes, or group of words (most often in an Indo-Iranian language like Sanskrit or Avestan) believed by practitioners to have religious, magical or spiritual powers. Feuerstein, Georg (2003), ''The Deeper Dimension of Yoga''. Shambala Publications, Boston, MA Some mantras have a syntactic structure and a literal meaning, while others do not. ꣽ, ॐ (Aum, Om) serves as an important mantra in various Indian religions. Specifically, it is an example of a seed syllable mantra ( bijamantra). It is believed to be the first sound in Hinduism and as the sonic essence of the absolute divine reality. Longer mantras are phrases with several syllables, names and words. These phrases may have spiritual interpretations such as a name of a deity, a longing for truth, reality, light, immortality, peace, love, knowledge, and action. Examples of lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kota Brahmins
Kota Brahmins are a Hindu Brahmin subcaste mainly from the Indian state of Karnataka. Kota Brahmins take their name from their native village Kota. They speak a Kannada dialect different from the other regional dialects. Kota Brahmins are mainly concentrated in the villages of Kota of Udupi district. Kotas follow Smarta tradition. The Guru Narasimha Temple, Saligrama is important to them. See also * Nambudiri * Shivalli Brahmin * Koteshwara Brahmin * Hoysala Karnataka Brahmins * Gaud Saraswat Brahmin Gaud Saraswat Brahmins (GSB) (also Goud or Gawd), also known as Shenvis are a Hindu community of contested caste status and identity. They primarily speak Konkani and its various dialects as their mother tongue. They claim to be Saraswat Bra ... References External links Kootabandhu.org [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |