|
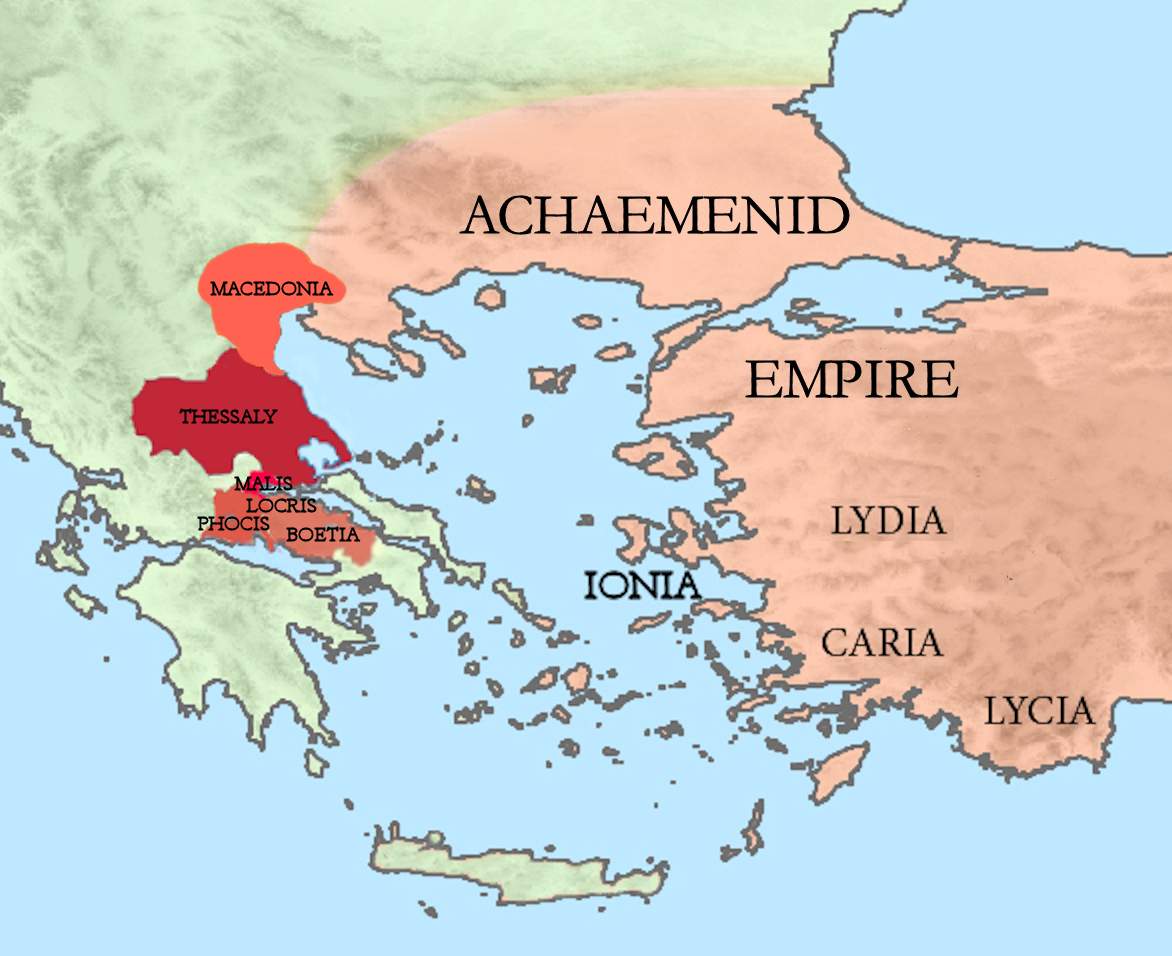
Thorax Of Larissa
Thorax ( Greek: ) of Larissa in Thessaly was a member of the powerful family of the Aleuadae. He was a son of an Aleuas who was a friend of the poet Simonides. Thorax and his brothers, Eurypylus and Thrasydaeus, wishing to confirm or to increase their power, were among those who urged Xerxes to invade Greece, and promised him their assistance in the enterprise. In Xerxes' retreat, after the Battle of Salamis, Thorax formed one of his escort, after which he still continued to show his zeal in the cause of the invaders, and was present with Mardonius at the Battle of Plataea in 479 BC. When the Persians had been finally driven from Greece, Leotychidas, king of Sparta, led an army into Thessaly to punish those who had sided with the barbarians, but the Aleuadae bribed him to refrain from making reprisals against their kin.Herodotus Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek ( el, label= Modern Greek, Ελληνικά, Elliniká, ; grc, Ἑλληνική, Hellēnikḗ) is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Italy (Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The alphabet arose from the Phoenician script and was in turn the basis of the Latin, Cyrillic, Armenian, Coptic, Gothic, and many other writing systems. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mardonius (general)
Mardonius ( peo, 𐎶𐎼𐎯𐎢𐎴𐎡𐎹 ; grc-gre, Μαρδόνιος ; died 479 BC) was a leading Persian military commander during the Persian Wars with Greece in the early 5th century BC who died at the Battle of Plataea. Early years Mardonius was the son of Gobryas, a Persian nobleman who had assisted the Achaemenid prince Darius when he claimed the throne. The alliance between the new king and his friend was cemented by diplomatic marriages: Darius married Gobryas' daughter, and Gobryas married Darius' sister. Furthermore, Mardonius married Darius' daughter Artozostra. Thus, Darius the Great was simultaneously Mardonius' uncle, father-in-law, and half-brother-in-law. Persian Wars with the Greeks First Persian invasion of Greece Darius appointed Mardonius as one of his generals and, after the Ionian Revolt, sent him in 492 BC to punish the Greek city-state of Athens for assisting the Ionians. On his way to Athens, he used his army in the Ionian cities to depose th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5th-century BC Greek People
The 5th century is the time period from 401 ( CDI) through 500 ( D) ''Anno Domini'' (AD) or Common Era (CE) in the Julian calendar. The 5th century is noted for being a period of migration and political instability throughout Eurasia. It saw the collapse of the Western Roman Empire, which came to an end in 476 AD. This empire had been ruled by a succession of weak emperors, with the real political might being increasingly concentrated among military leaders. Internal instability allowed a Visigoth army to reach and ransack Rome in 410. Some recovery took place during the following decades, but the Western Empire received another serious blow when a second foreign group, the Vandals, occupied Carthage, capital of an extremely important province in Africa. Attempts to retake the province were interrupted by the invasion of the Huns under Attila. After Attila's defeat, both Eastern and Western empires joined forces for a final assault on Vandal North Africa, but this campaign was a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Thessalian Statesmen
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500. The three-age system periodizes ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages varies between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was already exponentially increasing due to the Neolithic Revolution, which was in full progress. While in 10,000 BC, the world population s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Larissaeans
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500. The three-age system periodizes ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages varies between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was already exponentially increasing due to the Neolithic Revolution, which was in full progress. While in 10,000 BC, the world population stood a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria ( Italy). He is known for having written the ''Histories'' – a detailed account of the Greco-Persian Wars. Herodotus was the first writer to perform systematic investigation of historical events. He is referred to as " The Father of History", a title conferred on him by the ancient Roman orator Cicero. The ''Histories'' primarily cover the lives of prominent kings and famous battles such as Marathon, Thermopylae, Artemisium, Salamis, Plataea, and Mycale. His work deviates from the main topics to provide a cultural, ethnographical, geographical, and historiographical background that forms an essential part of the narrative and provides readers with a wellspring of additional information. Herodotus has been criticized for his inclusion of "legends and fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparta
Sparta (Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement on the banks of the Eurotas River in Laconia, in south-eastern Peloponnese. Around 650 BC, it rose to become the dominant military land-power in ancient Greece. Given its military pre-eminence, Sparta was recognized as the leading force of the unified Greek military during the Greco-Persian Wars, in rivalry with the rising naval power of Athens. Sparta was the principal enemy of Athens during the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), from which it emerged victorious after the Battle of Aegospotami. The decisive Battle of Leuctra in 371 BC ended the Spartan hegemony, although the city-state maintained its political independence until its forced integration into the Achaean League in 192 BC. The city neverthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leotychidas
Leotychidas II ( grc-gre, Λεωτυχίδας; Doric: ; c. 545 – c. 469 BC) was king of Sparta between 491–476 BC, alongside Cleomenes I and later Leonidas I and Pleistarchus. He led Spartan forces during the Persian Wars from 490 BC to 478 BC. Born in Sparta around 545 BC, Leotychidas was a descendant of the Royal House of the Eurypontids (through Menamus, Agesilaus, Hippocratides, Leotychides, Anaxilaus, Archidamos, Anaxandridas I and Theopompus) and came to power in 491 BC with the help of the Agiad King Cleomenes I by challenging the legitimacy of the birth of Demaratus for the Eurypontid throne of Sparta. Later that year, he joined Cleomenes' second expedition to Aegina, where ten hostages were seized and given to Athens. However, after Cleomenes' death in 488 BC, Leotychidas was almost surrendered to Aegina. In the spring of 479 BC, following the death of his co-ruler Leonidas at the Battle of Thermopylae, Leotychidas commanded a Greek fleet consisting of 110 ships ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Plataea
The Battle of Plataea was the final land battle during the second Persian invasion of Greece. It took place in 479 BC near the city of Plataea in Boeotia, and was fought between an alliance of the Ancient Greece, Greek city-states (including Sparta, History of Athens, Athens, Corinth and Megara), and the Achaemenid Empire, Persian Empire of Xerxes I (allied with Greece's Boeotians, Thessalians, and Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedonians). The previous year the Persian invasion force, led by the Persian king in person, had scored victories at the battles of Battle of Thermopylae, Thermopylae and Battle of Artemisium, Artemisium and conquered Thessaly, Phocis, Boeotia, Euboea and Attica. However, at the ensuing Battle of Salamis, the allied Greek navy had won an unlikely but decisive victory, preventing the conquest of the Peloponnesus. Xerxes then retreated with much of his army, leaving his general Mardonius (nephew of Darius I), Mardonius to finish off the Greeks the followi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Salamis
The Battle of Salamis ( ) was a naval battle fought between an alliance of Greek city-states under Themistocles and the Persian Empire under King Xerxes in 480 BC. It resulted in a decisive victory for the outnumbered Greeks. The battle was fought in the straits between the mainland and Salamis, an island in the Saronic Gulf near Athens, and marked the high point of the second Persian invasion of Greece. To block the Persian advance, a small force of Greeks blocked the pass of Thermopylae, while an Athenian-dominated Allied navy engaged the Persian fleet in the nearby straits of Artemisium. In the resulting Battle of Thermopylae, the rearguard of the Greek force was annihilated, while in the Battle of Artemisium the Greeks suffered heavy losses and retreated after the loss at Thermopylae. This allowed the Persians to conquer Phocis, Boeotia, Attica and Euboea. The Allies prepared to defend the Isthmus of Corinth while the fleet was withdrawn to nearby Salamis Islan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larissa
Larissa (; el, Λάρισα, , ) is the capital and largest city of the Thessaly region in Greece. It is the fifth-most populous city in Greece with a population of 144,651 according to the 2011 census. It is also capital of the Larissa regional unit. It is a principal agricultural centre and a national transport hub, linked by road and rail with the port of Volos, the cities of Thessaloniki and Athens. The municipality of Larissa has 162,591 inhabitants, while the regional unit of Larissa reached a population of 284,325 (). Legend has it that Achilles was born here. Hippocrates, the "Father of Medicine", died here. Today, Larissa is an important commercial, transportation, educational, agricultural and industrial centre of Greece. Geography There are a number of highways including E75 and the main railway from Athens to Thessaloniki (Salonika) crossing through Thessaly. The region is directly linked to the rest of Europe through the International Airport of Central Greec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xerxes I Of Persia
Xerxes I ( peo, 𐎧𐏁𐎹𐎠𐎼𐏁𐎠 ; grc-gre, Ξέρξης ; – August 465 BC), commonly known as Xerxes the Great, was the fourth King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, ruling from 486 to 465 BC. He was the son and successor of Darius the Great () and his mother was Atossa, a daughter of Cyrus the Great (), the founder of the Achaemenid empire. Like his father, he ruled the empire at its territorial peak. He ruled from 486 BC until his assassination in 465 BC at the hands of Artabanus, the commander of the royal bodyguard. Xerxes I is notable in Western history for his invasion of Greece in 480 BC. His forces temporarily overran mainland Greece north of the Isthmus of Corinth until losses at Salamis and Plataea a year later reversed these gains and ended the second invasion decisively. However, Xerxes successfully crushed revolts in Egypt and Babylon. Xerxes also oversaw the completion of various construction projects at Susa and Persepolis. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |