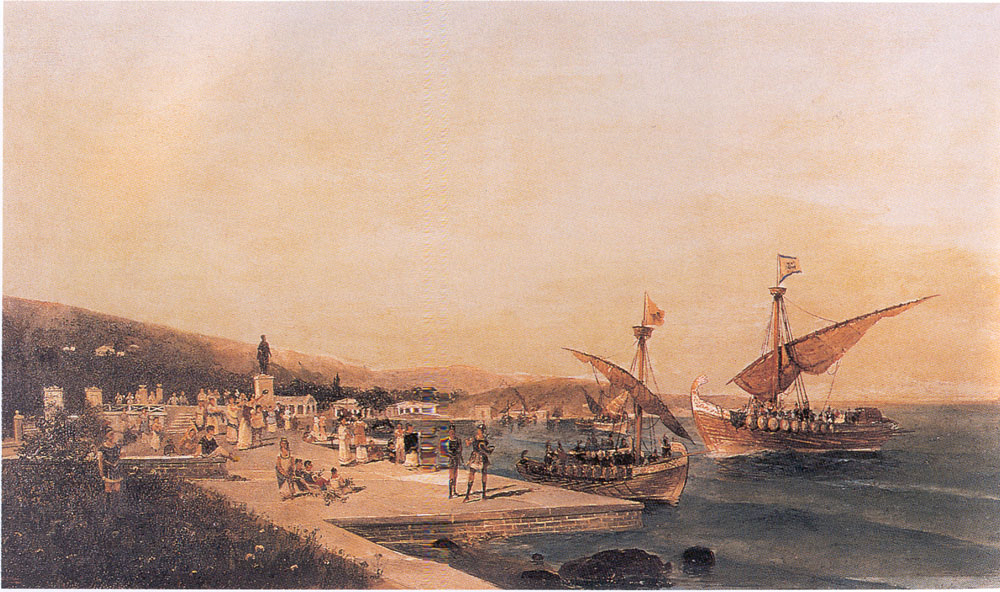|
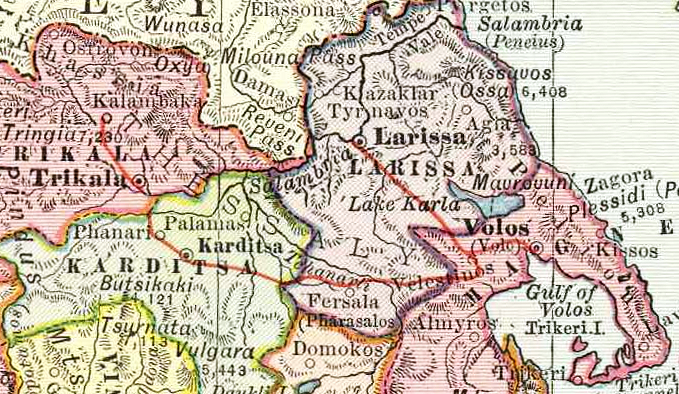
Thessaly Railways
Thessaly Railways () was a private railway company in Greece, which owned and operated the metre gauge railway network of Thessaly and Pelion railway from 1884 to 1955, when the private company was absorbed by the Hellenic State Railways state-owned company. Today the term usually refers to the section of mainline between Domokos and Rapsani and its two branches, the West Thessaly branch to Kalambaka railway station, Kalambaka and the Volos railway station, Volos branch. Network and stations The network of Thessaly Railways consisted of the following lines: * Volos—Velestinon. The line extended from Volos station to the city centre along Dimitriados Street. * Velestino-Kalampaka railway, Velestinon—Kalampaka, connecting with the Athens-Larissa-Thessaloniki standard gauge mainline at Palaiofarsalos railway station, Palaiofarsalos. This section had a maximum gradient of 3% between Velestinon and Aerinon. * Velestinon—Larissa, terminating to the Thessaly Railways station, next ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Volos Railway Station
Volos railway station () is a railway station in Volos, Greece. located within the city itself (close to the harbour). Opened on 22 April 1884 by the Thessaly Railways (now part of Hellenic Railways Organisation, OSE). Today Hellenic Train operates three daily local trains to Larissa. Previously Thessaly Railways operated a narrow gauge service to Milies from Volos, however this service now starts and terminates from Ano Lechonia railway station, Ano Lechonia (12 km from Volos). History The station was opened on 22 April 1884, an inauguration led by George I of Greece, King George. The station building (and the line) was designed by the Italy, Italian Evaristo de Chirico, (father of Giorgio de Chirico) soon after the liberation of Central Greece (geographic region), Central Greece from the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans. Part of the station still functions in this picturesque 1884 structure, reminiscent of a stately home to some. The building, built between 1882 and 1883 under E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Volos
Volos (; ) is a coastal port city in Thessaly situated midway on the Greek mainland, about north of Athens and south of Thessaloniki. It is the capital of the Magnesia (regional unit), Magnesia regional unit of the Thessaly Region. Volos is also the only outlet to the sea from Thessaly, the country's largest agricultural region. With a population of 85,803 (2021), the city is an important industrial centre, and its port provides a bridge between Europe and Asia. Volos is the newest of the Greek port cities, with a large proportion of modern buildings erected following catastrophic earthquakes in 1955. It includes the municipality, municipal units of Volos, Nea Ionia (Magnesia), Greece, Nea Ionia and Iolkos, as well as smaller suburban communities. The economy of the city is based on manufacturing, trade, services and tourism. Home to the University of Thessaly, the city also offers facilities for conferences, exhibitions and major sporting, cultural and scientific events. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Siemens Desiro
The Siemens Desiro (, , ) is a family of Diesel multiple unit, diesel or electric multiple unit passenger trains developed by Siemens Mobility, a division of the German Siemens, Siemens AG conglomerate. The main variants are the Desiro Classic, Desiro ML, Desiro UK and the later Desiro City, Desiro HC and Desiro RUS. The trains are mostly used for commuter and regional services, and their rapid acceleration makes them suitable for services with short distances between stations. The design is flexible, and has become common in many European countries. Desiro Classic Austria Austrian Federal Railways (ÖBB) is using 60 diesel-powered Desiro trains designated as ÖBB 5022. These are based on the Class 642 used by Deutsche Bahn, but have some additional safety equipment. Bulgaria In 2005 and 2006, the Bulgarian State Railways began operating Desiro trains as part of a €67 million deal with Siemens AG for a total of 25 Diesel multiple units. As of 22 March 2006, 16 trains had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
EuroSprinter
The EuroSprinter family of electric locomotives is a modular concept of locomotives for the European market built by Siemens Mobility. The internal Siemens product name is ES 64, with ES for EuroSprinter and the number 64 indicating the 6,400 kW power at rail. Additional information is given in the name on the usage (U as universal, P as prototype and F as freight) and on the number of electric power systems supported (e. g. 2 as two types, 4 as all four systems commonly used in Europe). Development The first prototype ES 64 P was built in 1992, as Deutsche Bahn AG was expected to issue a large order of locomotives as a replacement for the ageing Einheits-Elektrolokomotiven. The external appearance was similar to the earlier Siemens/Krauss-Maffei made dual voltage Spanish RENFE Class 252, delivered in 1991, which in turn used three phase asynchronous drive technology introduced with the DB Class 120. The prototype was used for extensive tests in some countries in Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
InterCity
InterCity (commonly abbreviated ''IC'' on timetables and tickets) is the train categories in Europe, classification applied to certain long-distance passenger train services in Europe. Such trains (in contrast to InterRegio, regional train, regional, local, or commuter trains) generally call at major railway station, stations only. An international variant of the InterCity trains are the EuroCity (EC) trains, which consist of high-standard coaches and are run by a variety of operators. History The Inter-City Rapid Transit Company was an Ohio interurban company, which began operations in 1930 as it had purchased its route from the Northern Ohio Traction & Light Company. It remained in operation till 1940. The use of ''Inter-City'' was reborn in the United Kingdom: A daily The Inter-City, train of that name was introduced in 1950, running between the cities of London and Birmingham. This usage can claim to be the origin of all later usages worldwide. In 1966 British Rail i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Karditsa Railway Station
Karditsa railway station () is a railway station that serves the city of Karditsa, Thessaly, Greece. Located south of the centre of Karditsa, the station opened by the Thessaly Railways, (now part of OSE). Today Hellenic Train operates 11 daily Regional trains between Kalambaka, Athens, Thessaloniki, Larissa and Palaiofarsalos. History The station open 16 June 1886 by the Thessaly Railways. The original station building (and the line) was designed by the Italian Evaristo de Chirico, (father of Giorgio de Chirico), however, this building was destroyed in the 1954 earthquake, and was rebuilt at the end of the same decade. The line was authorised by the Greek government under the law AMH’/22.6.1882. soon after the liberation of Central Greece from the Ottomans. After the First World War, the Greek state planned the ambitious construction of several new rail lines and links, including a standard gauge line from Kalambaka onto Kozani and then Veroia creating a conversion of the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
20070509-Kalampaka-620009+620010
7 (seven) is the natural number following 6 and preceding 8. It is the only prime number preceding a cube. As an early prime number in the series of positive integers, the number seven has symbolic associations in religion, mythology, superstition and philosophy. The seven classical planets resulted in seven being the number of days in a week. 7 is often considered lucky in Western culture and is often seen as highly symbolic. Evolution of the Arabic digit For early Brahmi numerals, 7 was written more or less in one stroke as a curve that looks like an uppercase vertically inverted (ᒉ). The western Arab peoples' main contribution was to make the longer line diagonal rather than straight, though they showed some tendencies to making the digit more rectilinear. The eastern Arab peoples developed the digit from a form that looked something like 6 to one that looked like an uppercase V. Both modern Arab forms influenced the European form, a two-stroke form consisting of a ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
20090613-Larissa-No72
9 (nine) is the natural number following and preceding . Evolution of the Hindu–Arabic digit Circa 300 BC, as part of the Brahmi numerals, various Indians wrote a digit 9 similar in shape to the modern closing question mark without the bottom dot. The Kshatrapa, Andhra and Gupta started curving the bottom vertical line coming up with a -look-alike. How the numbers got to their Gupta form is open to considerable debate. The Nagari continued the bottom stroke to make a circle and enclose the 3-look-alike, in much the same way that the sign @ encircles a lowercase ''a''. As time went on, the enclosing circle became bigger and its line continued beyond the circle downwards, as the 3-look-alike became smaller. Soon, all that was left of the 3-look-alike was a squiggle. The Arabs simply connected that squiggle to the downward stroke at the middle and subsequent European change was purely cosmetic. While the shape of the glyph for the digit 9 has an ascender in most modern typefa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |