|
Thermoporometry And Cryoporometry
Thermoporometry and cryoporometry are methods for measuring porosity and pore-size distributions. A small region of solid melts at a lower temperature than the bulk solid, as given by the Gibbs–Thomson equation. Thus, if a liquid is imbibed into a porous material, and then frozen, the melting temperature will provide information on the pore-size distribution. The detection of the melting can be done by sensing the transient heat flows during phase transitions using differential scanning calorimetry – DSC thermoporometry, measuring the quantity of mobile liquid using nuclear magnetic resonance – NMR cryoporometry (NMRC) or measuring the amplitude of neutron scattering from the imbibed crystalline or liquid phases – ND cryoporometry (NDC). To make a thermoporometry / cryoporometry measurement, a liquid is imbibed into the porous sample, the sample cooled until all the liquid is frozen, and then warmed until all the liquid is again melted. Measurements are made of the pha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
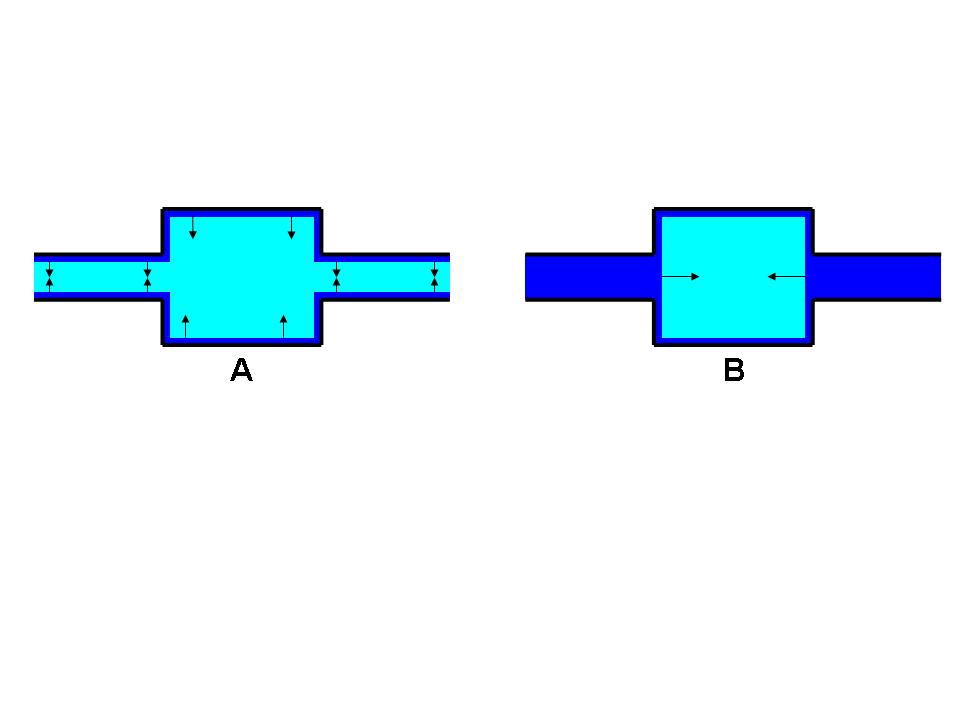
Porosity
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void (i.e. "empty") spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%. Strictly speaking, some tests measure the "accessible void", the total amount of void space accessible from the surface (cf. closed-cell foam). There are many ways to test porosity in a substance or part, such as industrial CT scanning. The term porosity is used in multiple fields including pharmaceutics, ceramics, metallurgy, materials, manufacturing, petrophysics, hydrology, earth sciences, soil mechanics, and engineering. Void fraction in two-phase flow In gas-liquid two-phase flow, the void fraction is defined as the fraction of the flow-channel volume that is occupied by the gas phase or, alternatively, as the fraction of the cross-sectional area of the channel that is occupied by the gas phase. Void fraction usually varies from location to location in the fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
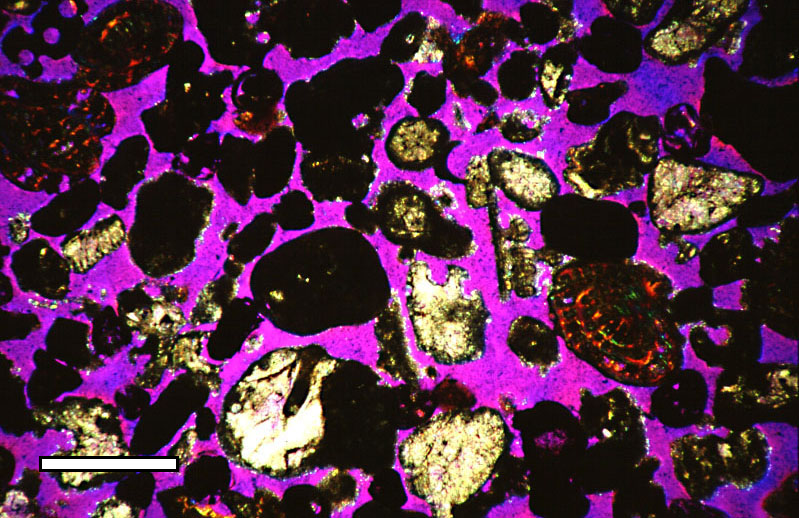
Sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks. Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates) because they are the most resistant minerals to weathering processes at the Earth's surface. Like uncemented sand, sandstone may be any color due to impurities within the minerals, but the most common colors are tan, brown, yellow, red, grey, pink, white, and black. Since sandstone beds often form highly visible cliffs and other topographic features, certain colors of sandstone have been strongly identified with certain regions. Rock formations that are primarily composed of sandstone usually allow the percolation of water and other fluids and are porous enough to store large quantities, making them valuable aquifers and petroleum reservoirs. Quartz-bearing sandstone can be changed into quartzite through metamorphism, usually r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide Removal
Carbon dioxide removal (CDR), also known as negative emissions, is a process in which carbon dioxide gas () is removed from the atmosphere and sequestered for long periods of time. Similarly, greenhouse gas removal (GGR) or negative greenhouse gas emissions is the removal of greenhouse gases (GHGs) from the atmosphere by deliberate human activities, i.e., in addition to the removal that would occur via natural carbon cycle or atmospheric chemistry processes.IPCC, 2021Annex VII: Glossary atthews, J.B.R., V. Möller, R. van Diemen, J.S. Fuglestvedt, V. Masson-Delmotte, C. Méndez, S. Semenov, A. Reisinger (eds.) IClimate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change[Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelek� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biochar
Biochar is the lightweight black residue, made of carbon and ashes, remaining after the pyrolysis of biomass. Biochar is defined by the International Biochar Initiative as "the solid material obtained from the thermochemical conversion of biomass in an oxygen-limited environment". Biochar is a stable solid that is rich in pyrogenic carbon and can endure in soil for thousands of years. The refractory stability of biochar leads to the concept of pyrogenic carbon capture and storage (PyCCS), i.e. carbon sequestration in the form of biochar. It may be a means to mitigate climate change. Biochar may increase the soil fertility of acidic soils and increase agricultural productivity. History The word "biochar" is a late 20th century English neologism derived from the Greek Language, Greek word , ''bios'', "life" and " char" ( charcoal produced by carbonisation of biomass). It is recognised as charcoal that participates in biological processes found in soil, aquatic hab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charcoal
Charcoal is a lightweight black carbon residue produced by strongly heating wood (or other animal and plant materials) in minimal oxygen to remove all water and volatile constituents. In the traditional version of this pyrolysis process, called charcoal burning, often by forming a charcoal kiln, the heat is supplied by burning part of the starting material itself, with a limited supply of oxygen. The material can also be heated in a closed retort. Modern "charcoal" briquettes used for outdoor cooking may contain many other additives, e.g. coal. This process happens naturally when combustion is incomplete, and is sometimes used in radiocarbon dating. It also happens inadvertently while burning wood, as in a fireplace or wood stove. The visible flame in these is due to combustion of the volatile gases exuded as the wood turns into charcoal. The soot and smoke commonly given off by wood fires result from incomplete combustion of those volatiles. Charcoal burns at a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes up only about 0.025 percent of Earth's crust. Three isotopes occur naturally, C and C being stable, while C is a radionuclide, decaying with a half-life of about 5,730 years. Carbon is one of the few elements known since antiquity. Carbon is the 15th most abundant element in the Earth's crust, and the fourth most abundant element in the universe by mass after hydrogen, helium, and oxygen. Carbon's abundance, its unique diversity of organic compounds, and its unusual ability to form polymers at the temperatures commonly encountered on Earth, enables this element to serve as a common element of Carbon-based life, all known life. It is the second most abundant element in the human body by mass (about 18.5%) after oxygen. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of fine and coarse aggregate bonded together with a fluid cement (cement paste) that hardens (cures) over time. Concrete is the second-most-used substance in the world after water, and is the most widely used building material. Its usage worldwide, ton for ton, is twice that of steel, wood, plastics, and aluminum combined. Globally, the ready-mix concrete industry, the largest segment of the concrete market, is projected to exceed $600 billion in revenue by 2025. This widespread use results in a number of environmental impacts. Most notably, the production process for cement produces large volumes of greenhouse gas emissions, leading to net 8% of global emissions. Other environmental concerns include widespread illegal sand mining, impacts on the surrounding environment such as increased surface runoff or urban heat island effect, and potential public health implications from toxic ingredients. Significant research and developmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cement
A cement is a binder, a chemical substance used for construction that sets, hardens, and adheres to other materials to bind them together. Cement is seldom used on its own, but rather to bind sand and gravel (aggregate) together. Cement mixed with fine aggregate produces mortar for masonry, or with sand and gravel, produces concrete. Concrete is the most widely used material in existence and is behind only water as the planet's most-consumed resource. Cements used in construction are usually inorganic, often lime or calcium silicate based, which can be characterized as hydraulic or the less common non-hydraulic, depending on the ability of the cement to set in the presence of water (see hydraulic and non-hydraulic lime plaster). Hydraulic cements (e.g., Portland cement) set and become adhesive through a chemical reaction between the dry ingredients and water. The chemical reaction results in mineral hydrates that are not very water-soluble and so are quite durable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wood
Wood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin that resists compression. Wood is sometimes defined as only the secondary xylem in the stems of trees, or it is defined more broadly to include the same type of tissue elsewhere such as in the roots of trees or shrubs. In a living tree it performs a support function, enabling woody plants to grow large or to stand up by themselves. It also conveys water and nutrients between the leaves, other growing tissues, and the roots. Wood may also refer to other plant materials with comparable properties, and to material engineered from wood, or woodchips or fiber. Wood has been used for thousands of years for fuel, as a construction material, for making tools and weapons, furniture and paper. More recently it emerged as a feedstock for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Abstraction
Water extraction (or water withdrawal) is the process of taking water from any source, either temporarily or permanently, for flood control or to obtain water for, for example, irrigation. The extracted water could also be used as drinking water after suitable treatment. Depending on the environmental legislation in the country, controls may be placed on extraction to limit the amount of water that can be removed. The over-extraction of water can lead to dry rivers or declining groundwater levels. The science of hydrogeology is used to determine safe water extraction levels. Water can go through dams that are used to regulate or stop water from coming though, creating hydroelectricity. Effects of overextraction Saltwater intrusion See also * Atmospheric water generator * Desalination * Reclaimed water Water reclamation (also called wastewater reuse, water reuse or water recycling) is the process of converting municipal wastewater (sewage) or industrial wastewater i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shale Gas
Shale gas is an unconventional natural gas that is found trapped within shale formations. Since the 1990s a combination of horizontal drilling and hydraulic fracturing has made large volumes of shale gas more economical to produce, and some analysts expect that shale gas will greatly expand worldwide energy supply. Shale gas has become an increasingly important source of natural gas in the United States since the start of this century, and interest has spread to potential gas shales in the rest of the world. China is estimated to have the world's largest shale gas reserves. A 2013 review by the United Kingdom Department of Energy and Climate Change noted that most studies of the subject have estimated that life-cycle greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from shale gas are similar to those of conventional natural gas, and are much less than those from coal, usually about half the greenhouse gas emissions of coal; the noted exception was a 2011 study by Howarth and others of C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil Extraction
Petroleum is a fossil fuel that can be drawn from beneath the earth's surface. Reservoirs of petroleum was formed through the mixture of plants, algae, and sediments in shallow seas under high pressure. Petroleum is mostly recovered from oil drilling. Seismic surveys and other methods are used to locate oil reservoirs. Oil rigs and oil platforms are used to drill long holes into the earth to create an oil well and extract petroleum. After extraction, oil is refined to make gasoline and other products such as tires and refrigerators. Extraction of petroleum can be dangerous and have led to oil spills. Locating the oil field Geologists and geophysicists use seismic surveys to search for geological structures that may form oil reservoirs. The "classic" method includes making an underground explosion nearby and observing the seismic response, which provides information about the geological structures underground. However, "passive" methods that extract information from naturally oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saunders_Quarry-1.jpg)





