|
Theotokos Of The Pharos
The Church of the Virgin of the Pharos (, ''Theotokos tou Pharou'') was a Byzantine chapel built in the southern part of the Great Palace of Constantinople, and named after the tower of the lighthouse (''pharos'') that stood next to it. It housed one of the most important collections of Christian relics in the city, and functioned as the chief palatine chapel of the Byzantine emperors. History The church was probably built sometime in the 8th century, as it is first attested in the chronicle of Theophanes the Confessor for 769: it was there that the future emperor Leo IV (r. 775–780) married Irene of Athens.Maguire (2004), p. 55 Emperor Leo V (r. 813–820) was assassinated there. The church was located close to the ceremonial heart of the palace, the throne room of the ''Chrysotriklinos'' and the adjoining imperial apartments.Klein (2006), p. 80 Following the end of iconoclasm, it was extensively rebuilt and redecorated by Emperor Michael III (r. 842–867). As restored, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantinople Imperial District
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empires between its consecration in 330 until 1930, when it was renamed to Istanbul. Initially as New Rome, Constantinople was founded in 324 during the reign of Constantine the Great on the site of the existing settlement of Byzantium, and shortly thereafter in 330 became the capital of the Roman Empire. Following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the late 5th century, Constantinople remained the capital of the Eastern Roman Empire (also known as the Byzantine Empire; 330–1204 and 1261–1453), the Latin Empire (1204–1261), and the Ottoman Empire (1453–1922). Following the Turkish War of Independence, the Turkish capital then moved to Ankara. Although the city had been known as Istanbul since 1453, it was officially renamed as Is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apse
In architecture, an apse (: apses; from Latin , 'arch, vault'; from Ancient Greek , , 'arch'; sometimes written apsis; : apsides) is a semicircular recess covered with a hemispherical Vault (architecture), vault or semi-dome, also known as an ''exedra''. In Byzantine architecture, Byzantine, Romanesque architecture, Romanesque, and Gothic architecture, Gothic Architecture of cathedrals and great churches, Christian church architecture, church (including cathedral and abbey) architecture, the term is applied to a semi-circular or polygonal termination of the main building at the liturgical east and west, liturgical east end (where the altar is), regardless of the shape of the roof, which may be flat, sloping, domed, or hemispherical. Smaller apses are found elsewhere, especially in shrines. Definition An apse is a semicircular recess, often covered with a hemispherical vault. Commonly, the apse of a church, cathedral or basilica is the semicircular or polygonal termination to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
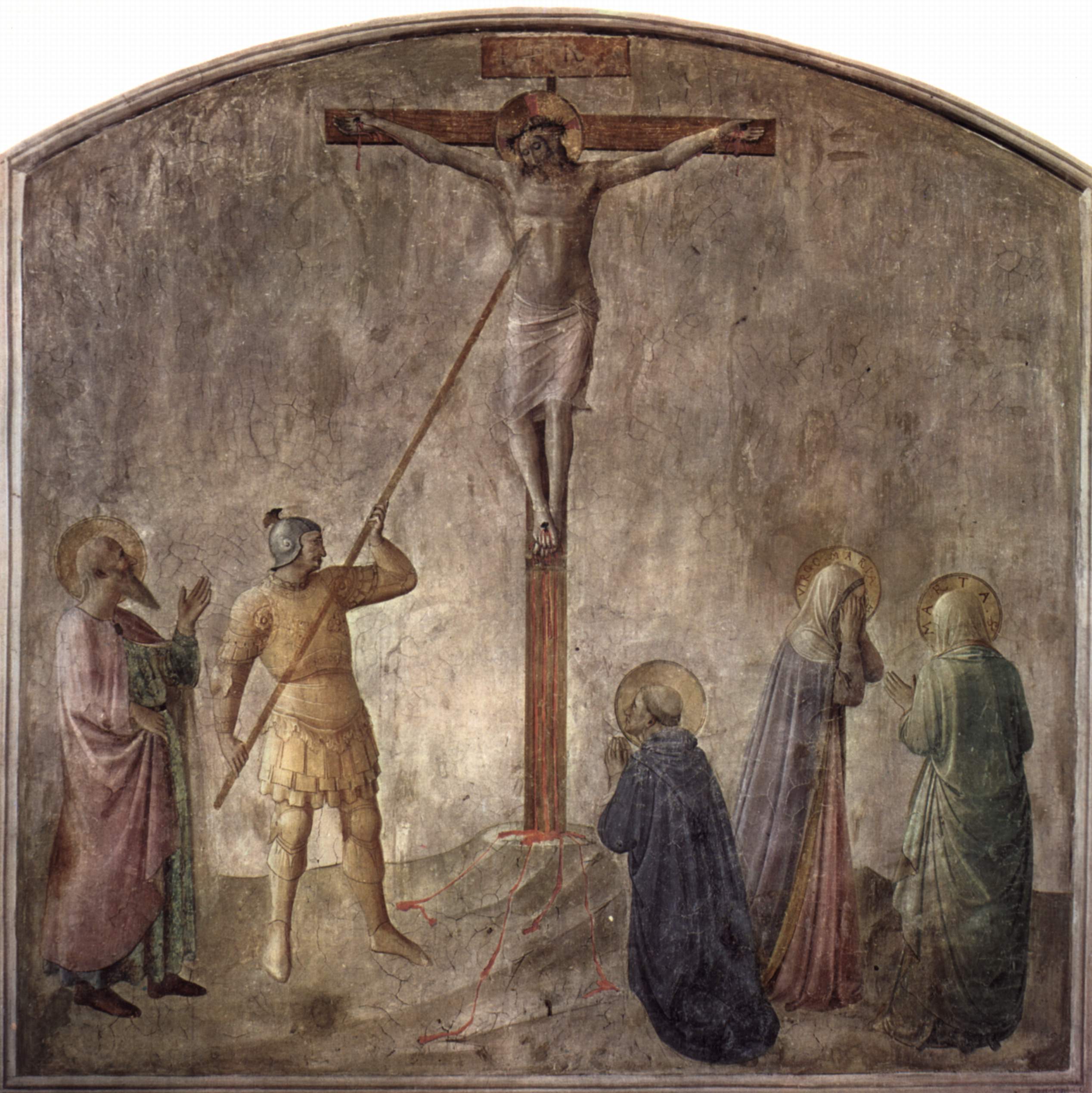
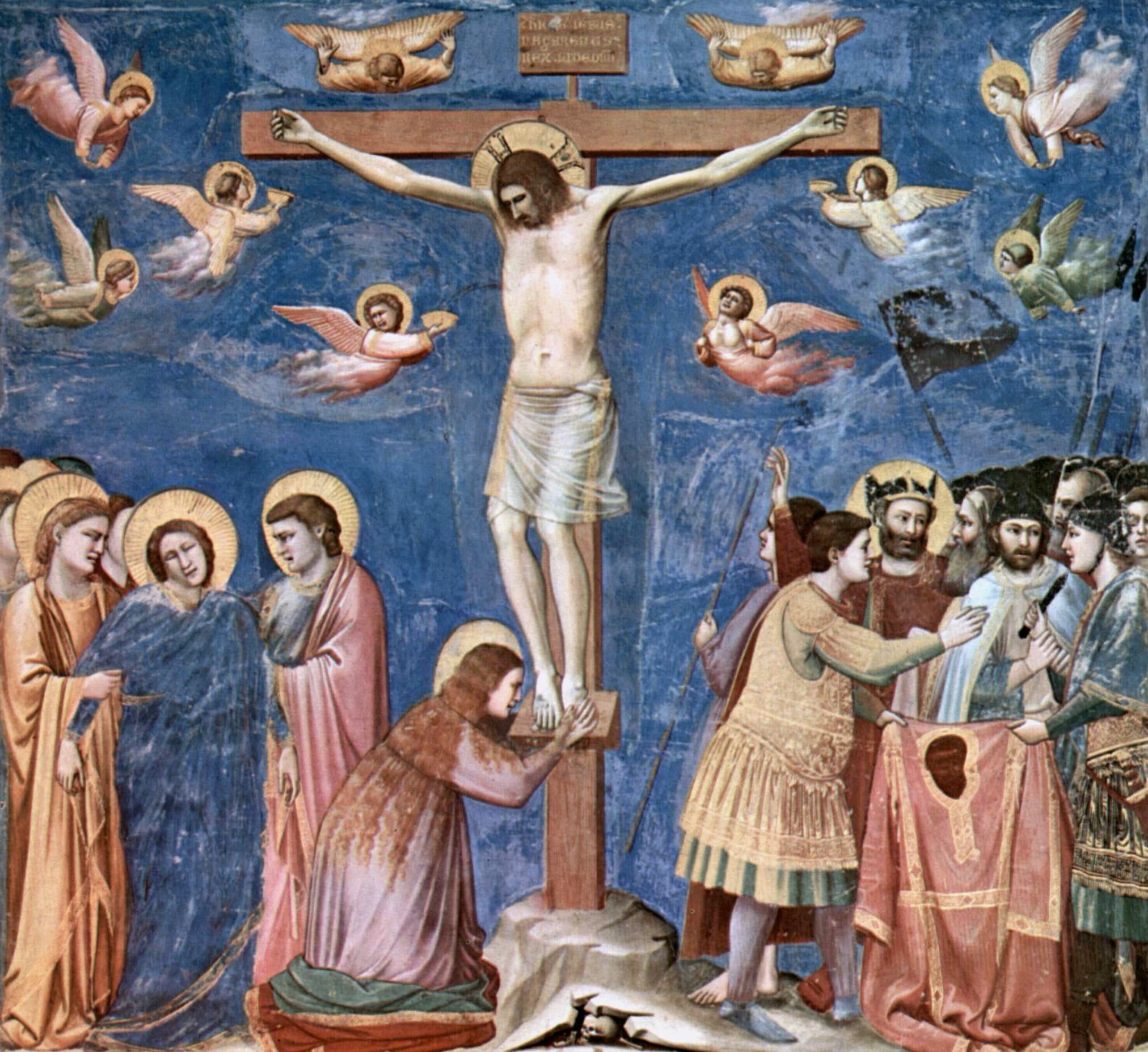
Christ
Jesus ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the Jesus in Christianity, central figure of Christianity, the Major religious groups, world's largest religion. Most Christians consider Jesus to be the Incarnation (Christianity), incarnation of God the Son and awaited Messiah#Christianity, messiah, or Christ (title), Christ, a descendant from the Davidic line that is prophesied in the Old Testament. Virtually all modern scholars of classical antiquity, antiquity agree that Historicity of Jesus, Jesus existed historically. Accounts of Life of Jesus, Jesus's life are contained in the Gospels, especially the four canonical Gospels in the New Testament. Since the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment, Quest for the historical Jesus, academic research has yielded various views on the historical reliability of the Gospels and how closely they reflect the hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St John The Baptist
John the Baptist ( – ) was a Jewish preacher active in the area of the Jordan River in the early first century AD. He is also known as Saint John the Forerunner in Eastern Orthodoxy and Oriental Orthodoxy, John the Immerser in some Baptist Christian traditions, and as the prophet Yahya ibn Zakariya in Islam. He is sometimes referred to as John the Baptiser. John is mentioned by the Roman Jewish historian Josephus, and he is revered as a major religious figure in Christianity, Islam, the Baháʼí Faith, the Druze faith, and Mandaeism; in the last of these he is considered to be the final and most vital prophet. He is considered to be a prophet of God by all of the aforementioned faiths, and is honoured as a saint in many Christian denominations. According to the New Testament, John anticipated a messianic figure greater than himself; in the Gospels, he is portrayed as the precursor or forerunner of Jesus. According to the Gospel of Matthew, Jesus himself identifies John a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Of Edessa
According to Christian tradition, the Image of Edessa was a holy relic consisting of a square or rectangle of cloth upon which a miraculous image of the face of Jesus Christ had been imprinted—the first icon (). The image is also known as the Mandylion (, 'cloth' or 'towel'), in Eastern Orthodoxy, it is also known as Acheiropoieton (, ). In the tradition recorded in the early 4th century by Eusebius of Caesarea, King Abgar of Edessa wrote to Jesus, asking him to come cure him of an illness. Abgar received a reply letter from Jesus, declining the invitation, but promising a future visit by one of his disciples. One of the seventy disciples, Thaddeus of Edessa, is said to have come to Edessa, bearing the words of Jesus, by the virtues of which the king was miraculously healed. Eusebius said that he had transcribed and translated the actual letter in the Syriac chancery documents of the king of Edessa, but who makes no mention of an image. The report of an image, which accrued t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
True Cross
According to Christian tradition, the True Cross is the real instrument of Jesus' crucifixion, cross on which Jesus of Nazareth was Crucifixion of Jesus, crucified. It is related by numerous historical accounts and Christian mythology, legends that Helena, mother of Constantine I, Helen, the mother of Roman emperor Constantine the Great, recovered the True Cross at the Holy Sepulchre in Jerusalem, when she travelled to the Holy Land in the years 326–328. The late fourth-century historians Gelasius of Caesarea and Tyrannius Rufinus wrote that while Helen was there, she discovered the hiding place of three crosses that were believed to have been used at the crucifixion of Jesus and the two thieves, Penitent thief, Dismas and Impenitent thief, Gestas, who were executed with him. To one cross was affixed the Titulus (inscription), titulus bearing Jesus' name, but according to Rufinus, Helen was unsure of its legitimacy until a miracle revealed that it was the True Cross. This event ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Lance
The Holy Lance, also known as the Spear of Longinus (named after Longinus, Saint Longinus), the Spear of Destiny, or the Holy Spear, is alleged to be the lance that pierced the side of Jesus as he hung on the cross during his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion. As with other Arma Christi, instruments of the Passion, the lance is only briefly mentioned in the Christian Bible, but later became the subject of extrabiblical traditions (Apocrypha) in the Christianity in the Middle Ages, medieval church. Relics purported to be the lance began to appear as early as the 6th century, originally in Jerusalem. By the Late Middle Ages, relics identified as the spearhead of the Holy Lance (or fragments thereof) had been described throughout Europe. Several of these artifacts are still preserved to this day. Holy Lance relics have typically been used for religious ceremonies, but at times some of them have been considered to be guarantees of victory in battle. For example, Henry the Fowler's l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyril Mango
Cyril Alexander Mango (14 April 1928 – 8 February 2021) was a British scholar of the history, art, and architecture of the Byzantine Empire. He is celebrated as one of the leading Byzantinists of the 20th century. Mango was Koraes Professor of Modern Greek and Byzantine History, Language and Literature at King's College London, the University of Oxford Bywater and Sotheby Professor Emeritus of Byzantine and Modern Greek Language and Literature and emeritus professorial fellow of Exeter College, Oxford. Early life and education Mango was born on 14 April 1928 in Istanbul, Turkey, the youngest of three sons of Alexander A. Mango, a descendant of a Genoese family who came to Istanbul via Chios, and Adelaide, known as Ada, (''née'' Damonov) Mango, a refugee from Baku. One of his brothers, Andrew Mango, who lived and worked in London becoming head of the South East European Service of the BBC World Service, was also a respected scholar and author on Turkey. His other brothe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nea Ekklesia
The Nea Ekklēsia (, "New Church"; known in English as "The Nea") was a church built by Byzantine Emperor Basil I the Macedonian in Constantinople between 876 and 880. It was the first monumental church built in the Byzantine capital after the Hagia Sophia in the 6th century, and marks the beginning of the middle period of Byzantine architecture. It continued in use until the Palaiologan period. Used as a gunpowder magazine by the Ottomans, the building was destroyed in 1490 after being struck by lightning. No traces of it survive, and information about it derives from historical accounts and depictions. History Emperor Basil I was the founder of the Macedonian dynasty, the most successful in Byzantine history. Basil regarded himself as a restorer of the empire, a new Justinian, and initiated a great building program in Constantinople in emulation his great predecessor. The ''Nea'' was to be Basil's Hagia Sophia, with its very name, "New Church", implying the beginning of a new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daphne Palace
The Palace of Daphne () was one of the major wings of the Great Palace of Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire (modern Istanbul, Turkey). According to George Codinus, it was named after a statue of the nymph Daphne, brought from Rome. The exact layout and appearance of the palace is unclear, since it lies under the Sultan Ahmed Mosque, and the only surviving evidence comes from literary sources.Westbrook (2007) Jonathan Bardill, however, has suggested that the peristyle with mosaics adjoining an apsed hall, excavated by the Walker Trust excavations in 1935-7 and 1952-4, could be the Augusteus of the Daphne Palace. History and description The Daphne belonged to the earliest building phase of the palace complex, that of Constantine I, who rebuilt the city of Byzantium into Constantinople, his new capital, as well as his immediate successors. Justin II () expanded the original building, which remained the main residential area for the emperors until the 8th century. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homilies
A homily (from Greek ὁμιλία, ''homilía'') is a commentary that follows a reading of scripture, giving the "public explanation of a sacred doctrine" or text. The works of Origen and John Chrysostom (known as Paschal Homily) are considered exemplary forms of Christian homily. In Catholic, Anglican, Lutheran, and Eastern Orthodox churches, a homily is usually given during Mass (Divine Liturgy or Holy Qurbana for Orthodox and Eastern Catholic Churches, and Divine Service for the Lutheran Church) at the end of the Liturgy of the Word. Many people consider it synonymous with a sermon. The English word homily is derived from the Ancient Greek word ὁμιλία ''homilia'', which means intercourse or interaction with other people (derived from the word ''homilos,'' meaning "a gathering"). The word is used in ("wicked ''homiliai'' corrupt good morals"). The related verb is used in (as ''homiloun''), and in (as ''homilei''), both used in the sense of "speaking with". The word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photios I Of Constantinople
Photius I of Constantinople (, ''Phōtios''; 815 – 6 February 893), also spelled ''Photius''Fr. Justin Taylor, essay "Canon Law in the Age of the Fathers" (published in Jordan Hite, T.O.R., and Daniel J. Ward, O.S.B., "Readings, Cases, Materials in Canon Law - A Textbook for Ministerial Students, Revised Edition" ollegeville, Minn., The Liturgical Press, 1990, p. 61 (), was the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople from 858 to 867 and from 877 to 886. He is recognized in the Eastern Orthodox Church as Saint Photius the Great. Photius I is widely regarded as the most powerful and influential church leader of Constantinople subsequent to John Chrysostom's archbishopric around the turn of the fifth century. He is also viewed as the most important intellectual of his time – "the leading light of the ninth-century renaissance". He was a central figure in both the conversion of the Slavs to Christianity and the Photian schism, and is considered " e great systematic compiler ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |