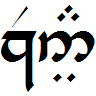|
The War Of The Jewels
''The War of the Jewels'' (1994) is the 11th volume of Christopher Tolkien's series ''The History of Middle-earth'', analysing the unpublished manuscripts of his father J. R. R. Tolkien. It is the second of two volumes—''Morgoth's Ring'' being the first—to explore the later 1951 '' Silmarillion'' drafts (those written after the completion of ''The Lord of the Rings''). Book Inscription There is an inscription in tengwar on the title page of each volume of ''The History of Middle-earth'', written by Christopher Tolkien and describing the contents of the book. The inscription in Volume XI reads "In this book are recorded the last writings of John Ronald Reuel Tolkien concerning the wars of Beleriand, here also is told the story of how Húrin Thali brought ruin to the Men of Brethil, with much else concerning the Edain and Dwarves and the names of many peoples in the speech of the Elves." Contents The volume includes: * The second part of the 1951 ''Silmarillion'' dra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christopher Tolkien
Christopher John Reuel Tolkien (21 November 1924 – 16 January 2020) was an English academic editor, becoming a French citizen in later life. The son of author and academic J. R. R. Tolkien, Christopher Tolkien edited much of his father's posthumously published work, including '' The Silmarillion'' and the 12-volume (plus one volume of indexes) series '' The History of Middle-Earth''. Tolkien also drew the original maps for his father's '' The Lord of the Rings''. Outside his father's unfinished works, he edited three tales by Geoffrey Chaucer (with Nevill Coghill) and his father's translation of '' Sir Gawain and the Green Knight''. Early life Tolkien was born in Leeds, England, the third of four children and youngest son of John Ronald Reuel and Edith Mary Tolkien (''née'' Bratt). He was educated at the Dragon School ( Oxford) and later at The Oratory School. He entered the Royal Air Force in mid-1943 and was sent to South Africa for flight training, comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guy Gavriel Kay
Guy Gavriel Kay (born November 7, 1954) is a Canadian writer of fantasy fiction. The majority of his novels take place in fictional settings that resemble real places during real historical periods, such as Constantinople during the reign of Justinian I or Spain during the time of El Cid. Kay has expressed a preference to avoid genre categorization of these works as historical fantasy. , Kay has published 15 novels and a book of poetry. , his fiction has been translated into at least 22 languages. Kay is also a qualified lawyer in Canada. Biography Kay was born in Weyburn, Saskatchewan, in 1954. He was raised and educated in Winnipeg, Manitoba, and received a bachelor's degree in philosophy from the University of Manitoba in 1975. When Christopher Tolkien needed an assistant to edit his father J. R. R. Tolkien's unpublished work, he chose Kay, then a student of philosophy at the University of Manitoba, because of a family connection. Kay moved to Oxford in 1974 to assist C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1994 Books
File:1994 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The 1994 Winter Olympics are held in Lillehammer, Norway; The Kaiser Permanente building after the 1994 Northridge earthquake; A model of the MS Estonia, which sank in the Baltic Sea; Nelson Mandela casts his vote in the 1994 South African general election, in which he was elected South Africa's first president, and which effectively brought Apartheid to an end; NAFTA, which was signed in 1992, comes into effect in Canada, the United States, and Mexico; The first passenger rail service to utilize the newly-opened Channel tunnel; The 1994 FIFA World Cup is held in the United States; Skulls from the Rwandan genocide, in which over half a million Tutsi people were massacred by Hutus., 300x300px, thumb rect 0 0 200 200 1994 Winter Olympics rect 200 0 400 200 Northridge earthquake rect 400 0 600 200 Sinking of the MS Estonia rect 0 200 300 400 Rwandan genocide rect 300 200 600 400 Nelson Mandela rect 0 400 200 600 199 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
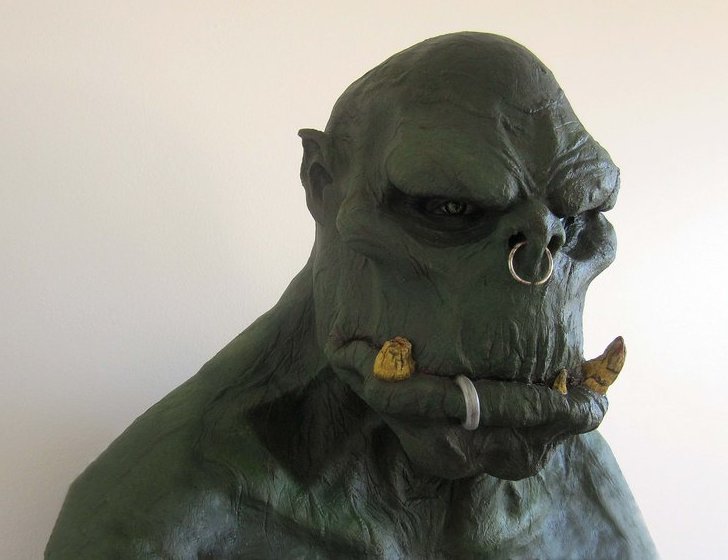
Orc (Middle-earth)
An Orc (or Ork) is a fictional humanoid monster like a goblin. Orcs were brought into modern usage by the fantasy writings of J. R. R. Tolkien, especially ''The Lord of the Rings''. In Tolkien's works, Orcs are a brutish, aggressive, ugly, and malevolent race of monsters, contrasting with the benevolent Elves. There is a suggestion, among several somewhat contradictory origin stories, that they are a corrupted race of elves. Mythological monsters with names similar to "orc" can be found in the Old English poem ''Beowulf'', in Early Modern poetry, and in Northern European folk tales and fairy tales. Tolkien stated that he took the name from ''Beowulf''. The orc appears on lists of imaginary creatures in two of Charles Kingsley's mid-1860s novels. Tolkien's concept of orcs has been adapted into the fantasy fiction of other authors, and into games of many different genres such as ''Dungeons & Dragons'', '' Magic: The Gathering'', and '' Warcraft''. Etymology Old Engl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sundering Of The Elves
In J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, the Elves or Quendi are a sundered (divided) people. They awoke at Cuiviénen on the continent of Middle-earth, where they were divided into three tribes: Minyar (the Firsts), Tatyar (the Seconds) and Nelyar (the Thirds). After some time, they were summoned by Oromë to live with the Valar in Valinor, on Aman. That summoning and the Great Journey that followed split the Elves into two main groups (and many minor ones), which were never fully reunited. Tolkien stated that the stories were made to create a world for his elvish languages, not the reverse. The Tolkien scholar Tom Shippey writes that '' The Silmarillion'' derived from the linguistic relationship between the two languages, Quenya and Sindarin, of the divided Elves. The Tolkien scholar Verlyn Flieger states that Tolkien used the Indo-European type of proto-language as his model. In her view, the sundering of the Elves reflects the progressive decline and fall in Middle-earth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sindarin
Sindarin is one of the fictional languages devised by J. R. R. Tolkien for use in his fantasy stories set in Arda, primarily in Middle-earth. Sindarin is one of the many languages spoken by the Elves. The word is a Quenya word. Called in English "Grey-Elvish" or "Grey-Elven", it was the language of the Grey Elves of Beleriand. These were Elves of the Third Clan who remained behind in Beleriand after the Great Journey. Their language became estranged from that of their kin who sailed over sea. Sindarin derives from an earlier language called Common Telerin, which evolved from Common Eldarin, the tongue of the Eldar before their divisions, e.g., those Elves who decided to follow the Vala Oromë and undertook the Great March to Valinor. Even before that the Eldar Elves spoke the original speech of all Elves, or Primitive Quendian. In the Third Age (the setting of ''The Lord of the Rings''), Sindarin was the language most commonly spoken by most Elves in the Western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telerin
J. R. R. Tolkien constructed many Elvish languages; the best known are Quenya and Sindarin. These were the various languages spoken by the Elves of Middle-earth as they developed as a society throughout the Ages. In his pursuit for realism and in his love of language, Tolkien was especially fascinated with the development and evolution of language through time. Tolkien created two almost fully developed languages and a dozen more in various beginning stages as he studied and reproduced the way that language adapts and morphs. A philologist by profession, he spent much time on his constructed languages. In the collection of letters he had written, posthumously published by his son, Christopher John Tolkien, he stated that he began stories set within this secondary world, the realm of Middle-earth, not with the characters or narrative as one would assume, but with a created set of languages. The stories and characters serve as conduits to make those languages come to life. Inventin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quenya
Quenya ()Tolkien wrote in his "Outline of Phonology" (in '' Parma Eldalamberon'' 19, p. 74) dedicated to the phonology of Quenya: is "a sound as in English ''new''". In Quenya is a combination of consonants, ibidem., p. 81. is a constructed language, one of those devised by J. R. R. Tolkien for the Elves in his Middle-earth fiction. Tolkien began devising the language around 1910, and restructured its grammar several times until it reached its final state. The vocabulary remained relatively stable throughout the creation process. He successively changed the language's name from ''Elfin'' and ''Qenya'' to the eventual ''Quenya''. Finnish had been a major source of inspiration, but Tolkien was also fluent in Latin and Old English, and was familiar with Greek, Welsh (the latter being the primary inspiration for Sindarin, Tolkien's other major Elvish language), and other ancient Germanic languages, particularly Gothic, during his development of Quenya. A notable feature of T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Eldarin
Quenya ()Tolkien wrote in his "Outline of Phonology" (in ''Parma Eldalamberon'' 19, p. 74) dedicated to the phonology of Quenya: is "a sound as in English ''new''". In Quenya is a combination of consonants, ibidem., p. 81. is a constructed language, one of those devised by J. R. R. Tolkien for the Elves in his Middle-earth fiction. Tolkien began devising the language around 1910, and restructured its grammar several times until it reached its final state. The vocabulary remained relatively stable throughout the creation process. He successively changed the language's name from ''Elfin'' and ''Qenya'' to the eventual ''Quenya''. Finnish had been a major source of inspiration, but Tolkien was also fluent in Latin and Old English, and was familiar with Greek, Welsh (the latter being the primary inspiration for Sindarin, Tolkien's other major Elvish language), and other ancient Germanic languages, particularly Gothic, during his development of Quenya. A notable feature of Tolk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eagle (Middle-earth)
In J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth, the Eagles or Great Eagles, " The Council of Elrond", "Of the Ruin of Doriath" were immense birds that were sapient and could speak. The Great Eagles resembled actual eagles, but were much larger. Thorondor is said to have been the greatest of all birds, with a wingspan of ., "Of the Return of the Noldor" Elsewhere, the eagles have varied in nature and size both within Tolkien's writings and in later adaptations. Scholars have noticed that the Eagles appear as agents of '' eucatastrophe'' or ''deus ex machina'' throughout Tolkien's writings, from '' The Silmarillion'' and the accounts of Númenor to ''The Hobbit'' and ''The Lord of the Rings''. Where Elves are good, and fully sentient, and Orcs bad, Eagles and other races are in between; the Hobbit Bilbo Baggins fears he will become their supper, torn up like a rabbit, and is indeed served rabbit for supper. The scholar Marjorie Burns notes, too, that Gandalf's association with Eagles is re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melian (Middle-earth)
Melian is a fictional character in J.R.R. Tolkien's Middle-earth Tolkien's legendarium, legendarium. She appears in ''The Silmarillion'', ''The Children of Húrin'', ''Beren and Lúthien'', and in several stories within ''The History of Middle-earth'' series. An early version of Melian is found in ''The Book of Lost Tales II'', part of ''The History of Middle-earth'', where her characterization differs significantly. The final version of the character is presented as a Maia (Middle-earth), Maia, a lesser class of powerful divine beings in Tolkien's legendarium known as the Ainu (Middle-earth), Ainur, who takes the form of an Elf and becomes the loyal queen consort of Elu Thingol. Melian is a pivotal character in the First Age of Middle-earth, and an essential part of the ancestral backgrounding of the interracial romances between her daughter Lúthien and the Man (Middle-earth), mortal Man Beren, as well as that of her descendants The Tale of Aragorn and Arwen, Aragorn and Arwen. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |