|
The Ruin (Dafydd Ap Gwilym Poem)
"The Ruin" (Welsh: Yr Adfael) is a ''cywydd'' by the 14th-century Welsh poet Dafydd ap Gwilym, widely seen as the greatest of the Welsh poets. In it the poet, considering a ruined house and remembering the love-affair he once conducted there, reflects on the transience of all worldly pleasures. "The Ruin" is commonly supposed to have been written in Dafydd's old age. It has been called one of his most poignant poems, and it was included in ''The Penguin Book of Welsh Verse'', ''The Oxford Book of Welsh Verse'', '' The Oxford Book of Welsh Verse in English'' and ''The Longman Anthology of British Literature''. Synopsis The poet considers the prospect of a ruined building which was once an inhabited house, and reflects on former days when one of the residents was a woman who loved him and whom he loved, and on the days of pleasure they knew. The house itself replies, lamenting the damage that the winds have wreaked on it. The poet again contrasts the derelict state of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cywydd
The cywydd (; plural ) is one of the most important metrical forms in traditional Welsh poetry ( cerdd dafod). There are a variety of forms of the cywydd, but the word on its own is generally used to refer to the ("long-lined couplet") as it is by far the most common type. The first recorded examples of the cywydd date from the early 14th century, when it is believed to have been developed. This was the favourite metre of the Poets of the Nobility, the poets working from the fourteenth to the seventeenth centuries, and it is still used today. The cywydd consists of a series of seven-syllable lines in rhyming couplets, with all lines written in cynghanedd. One of the lines must finish with a stressed syllable, while the other must finish with an unstressed syllable. The rhyme may vary from couplet to couplet, or may remain the same. There is no rule about how many couplets there must be in a cywydd. The and the related , and the all occur in the list of the twenty four trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conquest Of Wales By Edward I
The conquest of Wales by Edward I took place between 1277 and 1283. It is sometimes referred to as the Edwardian Conquest of Wales,Examples of historians using the term include Professor J. E. Lloyd, regarded as the founder of the modern academic study of Welsh history, in his ''History of Wales from the Earliest Times to the Edwardian Conquest'', first published in 1911, and Professor R. R. Davies, the leading modern scholar of the period, in his works including ''The Age of Conquest: Wales, 1063–1415'', published 2000. to distinguish it from the earlier (but partial) Norman conquest of Wales. In two campaigns, in 1277 and 1282–83, respectively, Edward I of England first greatly reduced the territory of Llywelyn ap Gruffudd ("Llywelyn the Last"), and then completely overran it, as well as the other remaining Welsh principalities. By the 13th century, Wales was divided between native Welsh principalities and the territories of the Anglo-Norman Marcher lords. The leading pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fictional Houses
Fiction is any creative work, chiefly any narrative work, portraying individuals, events, or places that are imaginary, or in ways that are imaginary. Fictional portrayals are thus inconsistent with history, fact, or plausibility. In a traditional narrow sense, "fiction" refers to written narratives in prose often referring specifically to novels, novellas, and short stories. More broadly, however, fiction encompasses imaginary narratives expressed in any medium, including not just writings but also live theatrical performances, films, television programs, radio dramas, comics, role-playing games, and video games. Definition Typically, the fictionality of a work is publicly marketed and so the audience expects the work to deviate in some ways from the real world rather than presenting, for instance, only factually accurate portrayals or characters who are actual people. Because fiction is generally understood to not fully adhere to the real world, the themes and contex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
14th-century Poems
As a means of recording the passage of time, the 14th century was a century lasting from 1 January 1301 ( MCCCI), to 31 December 1400 (MCD). It is estimated that the century witnessed the death of more than 45 million lives from political and natural disasters in both Europe and the Mongol Empire. West Africa experienced economic growth and prosperity. In Europe, the Black Death claimed 25 million lives wiping out one third of the European population while the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of France fought in the protracted Hundred Years' War after the death of Charles IV, King of France led to a claim to the French throne by Edward III, King of England. This period is considered the height of chivalry and marks the beginning of strong separate identities for both England and France as well as the foundation of the Italian Renaissance and Ottoman Empire. In Asia, Tamerlane (Timur), established the Timurid Empire, history's third largest empire to have been ever establis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
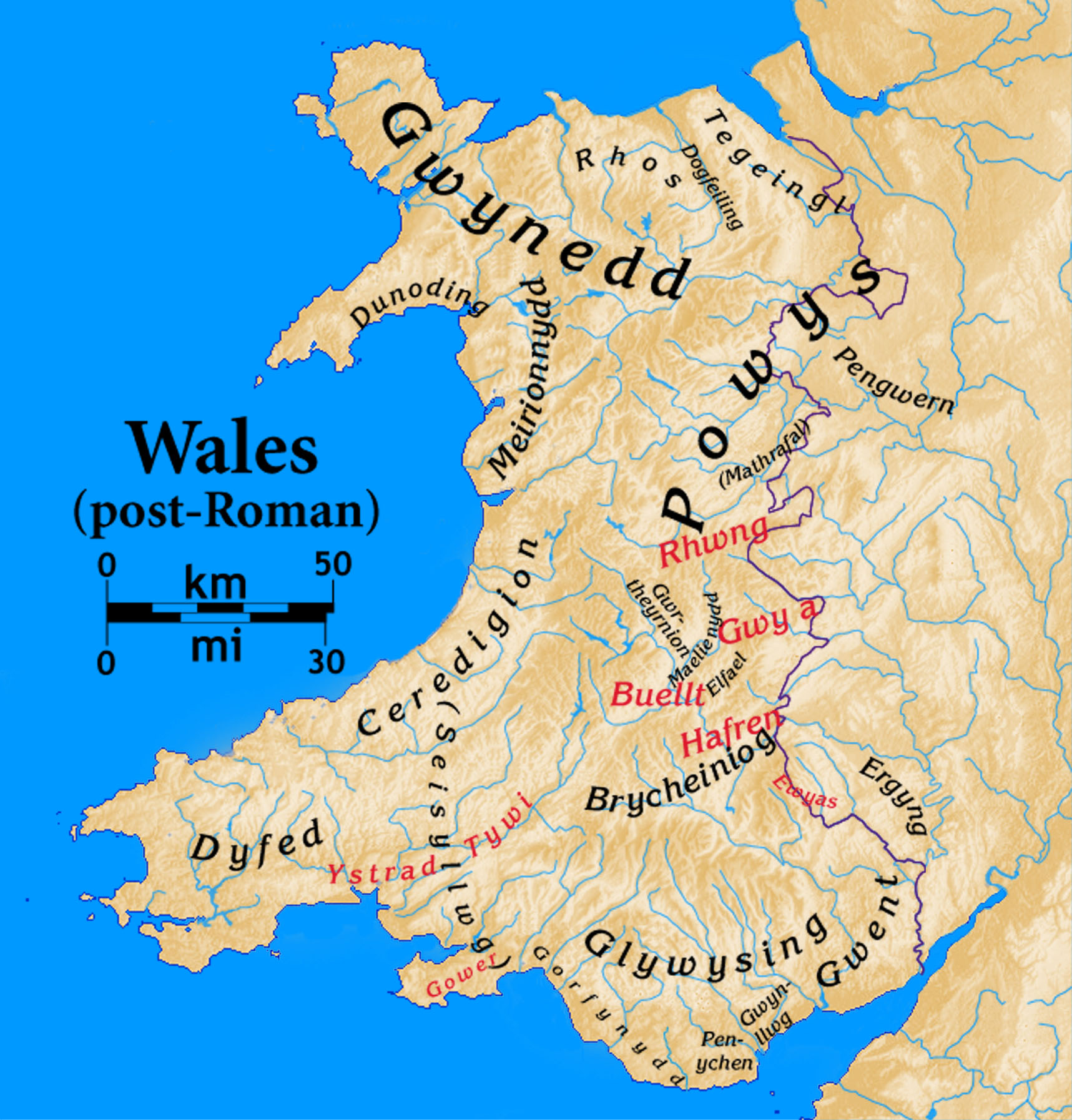
Pengwern
Pengwern was a Brythonic settlement of sub-Roman Britain situated in what is now the English county of Shropshire, adjoining the modern Welsh border. It is generally regarded as being the early seat of the kings of Powys before its establishment at Mathrafal, further west, but the theory that it may have been an early kingdom (or a sub-kingdom of Powys itself) has also been postulated. Its precise location is uncertain. History and legend Nothing is known about the foundation of Pengwern, although according to Welsh tradition it was part of the Welsh kingdom of Powys in the early Middle Ages. Early Powys, much larger in extent than the later medieval kingdom, seems to have ''roughly'' coincided with the territory of the Celtic Cornovii tribe whose ''civitas'' capital or administrative centre was '' Viroconium Cornoviorum'' (now Wroxeter). The exploits of Cynddylan, as imagined around the ninth century, are told in the Old Welsh '' Canu Heledd'' (a cycle of poems named a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cynddylan
Cynddylan (Modern Welsh pronunciation: /kən'ðəlan/), or Cynddylan ap Cyndrwyn was a seventh-century Prince of Powys associated with Pengwern. Cynddylan is attested only in literary sources: unlike many kings from Brittonic post-Roman Britain, he does not appear in the early Welsh genealogies or other historical sources. The son of King Cyndrwyn, Cynddylan is described in the probably seventh-century poem ''Marwnad Cynddylan'' (''Elegy for Cynddylan'') and seems to have been a chieftain in Powys. Historical context Some understanding of the historical context in which Cynddylan must have lived is afforded by Bede's ''Historia ecclesiastica gentis Anglorum'', the ''Historia Brittonum'', and early Welsh genealogies. With the collapse of the Roman Empire and the invasion of the Saxons, the remains of the civitas of the Cornovii held on to their lands in the lowland border regions of Wales (Herefordshire and Shropshire). By the beginning of the seventh century King Cystennin was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canu Heledd
''Canu Heledd'' (modern Welsh /'kani 'hɛlɛð/, the songs of Heledd) are a collection of early Welsh ''englyn''-poems. They are rare among medieval Welsh poems for being set in the mouth of a female character. One prominent figure in the poems is Heledd's dead brother Cynddylan. Summary Dorothy Ann Bray summarised the cycle thus: The entire cycle of the Heledd poems ... is a statement of mourning from which a background story has been deduced: Cynddylan, prince of Powys, and his brothers along with his heroic band are slain in battle, defending their country against the English in the mid-seventh century. Heledd, his sister, is one of the few survivors, who witnessed the battle and the destruction of Cynddylan's hall at Pengwern. She has lost not only all her brothers, but also her sisters and her home, and the poems suggest that she blames herself for the destruction of Cynddylan's court because of some ill-spoken words. As with the other so-called 'saga ''englynion''’ ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canu Llywarch Hen
''Canu Llywarch Hen'' (modern Welsh /'kani 'ɬəwarχ heːn/, the songs of Llywarch Hen) are a collection of early Welsh ''englyn''-poems. They comprise the most famous of the early Welsh cycles of ''englynion'' about heroes of post-Roman North Britain. Contents and themes As edited by Jenny Rowland, the contents of ''Canu Llywarch Hen'' are as follows: The poems contemplate martial, masculine culture, fate, and old age from a critical standpoint. As with the other so-called 'saga ''englynion''’ (pre-eminently '' Canu Urien'' and ''Canu Heledd''), there is considerable uncertainty and debate as to how the poems of ''Canu Llywarch'' might originally have been performed. It is usually assumed that they must have been accompanied by some kind of prose narrative, to which they provided emotional depth; but this is not certain. In all the independent witnesses bar NLW 4973a, the Llywarch Hen poems are preceded by the ''englyn''-poem '' Claf Abercuawg'', which in the White Book is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Englyn
(; plural ) is a traditional Welsh and Cornish short poem form. It uses quantitative metres, involving the counting of syllables, and rigid patterns of rhyme and half rhyme. Each line contains a repeating pattern of consonants and accent known as . Early history The is found in the work of the earliest attested Welsh poets (the ), where the main types are the three-line and . It is the only set stanzaic metre found in the early Welsh poetic corpus, and explanations for its origins have tended to focus on stanzaic Latin poetry and hymns; however, it is as likely to be a development within the Brittonic poetic tradition. Whereas the metrical rules of later are clear (and are based on counting syllables), the precise metre of the early is debated and could have involved stress-counting. The earliest are found as marginalia written in a tenth-century hand in the Juvencus Manuscript. Many early form poems which seem to represent moments of characters' emotional reflection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Church
In ecclesiology, the Christian Church is what different Christian denominations conceive of as being the true body of Christians or the original institution established by Jesus. "Christian Church" has also been used in academia as a synonym for Christianity, despite the fact that it is composed of multiple churches or denominations, many of which hold a doctrinal claim of being the " one true church", to the exclusion of the others. For many Protestant Christians, the Christian Church has two components: the church visible, institutions in which "the Word of God purely preached and listened to, and the sacraments administered according to Christ's institution", as well as the church invisible—all "who are truly saved" (with these beings members of the visible church). In this understanding of the invisible church, "Christian Church" (or catholic Church) does not refer to a particular Christian denomination, but includes all individuals who have been saved. The branch the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contemptus Mundi
''Contemptus mundi'', the "contempt of the world (theology), world" and worldly concerns, is a theme in the intellectual life of both Classical Antiquity and of Christianity, both in its mystical vein and its ambivalence towards secular life, that figures largely in the Western world's history of ideas. In inculcating a turn of mind that would lead to a state of serenity untrammeled by distracting material appetites and feverish emotional connections, which the Greek philosophers called ''ataraxia'', it drew upon the assumptions of Stoicism and a neoplatonism that was distrustful of deceptive and spurious appearances. In the familiar rhetorical polarity in Hellenic philosophy between the active and the contemplative life, which Christians, who expressly rejected "the World, Flesh (theology), the Flesh and the Devil", might exemplify as the way of Martha and the way of Mary of Bethany, Mary, ''contemptus mundi'' assumed that only the contemplative life was of lasting value and the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |