|
The Holocaust In Romania
The Holocaust saw the genocide of Jews in the Kingdom of Romania and in Romanian-controlled territories of the Soviet Union between 1940 and 1944. While historically part of The Holocaust, these actions were mostly independent from the similar acts committed by Nazi Germany, Romania being the only ally of the Third Reich that carried out a genocidal campaign without the intervention of Heinrich Himmler's SS. Various numbers have been advanced by researchers for the lives lost in the genocide, with most estimates in the range of 250,000 to 380,000, to which can be added another 12,000 Romani victims. Another approximately 132,000 Jews from the Hungarian-controlled Northern Transylvania were killed during this period by the Nazis with the collaboration of the Hungarian authorities. Romania ranks first among Holocaust perpetrator countries other than Germany. Background In the first decades of the 20th century, antisemitic views increased in number and intensity in publications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
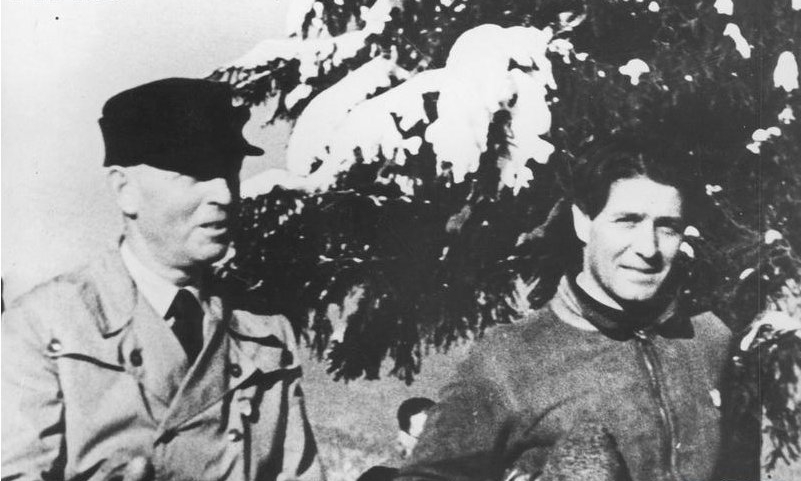
Ion Antonescu
Ion Antonescu (; ; – 1 June 1946) was a Romanian military officer and Mareșal (Romania), marshal who presided over two successive Romania during World War II, wartime dictatorships as Prime Minister of Romania, Prime Minister and ''Conducător'' during most of World War II. Having been responsible for facilitating the Holocaust in Romania, he was overthrown in 1944, before being tried for war crimes and executed two years later in 1946. A Romanian Army career officer who made his name during the 1907 Romanian peasants' revolt, 1907 peasants' revolt and the Romania in World War I, World War I Romanian campaign, the antisemitic Antonescu sympathized with Far-right politics, far-right and Fascism, fascist politics. He was a military attaché to France and later Chief of the Romanian General Staff, Chief of the General Staff, briefly serving as Ministry of National Defense (Romania), Defence Minister in the National Christian cabinet of Octavian Goga as well as the subsequent F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deportations Of Romani People To Transnistria
During the Ion Antonescu regime, in the context of the Romani genocide, more than 25,000 Romani people from the Kingdom of Romania were deported to concentration camps in the Transnistria Governorate. The regime deemed Romani people "a burden and a danger to public order". In the camps the imprisoned people were used as slave labour, and witnesses described the conditions as abysmal, with many dying from exposure and starvation. Preparations One year after the starting of The Holocaust in Romania, Ion Antonescu ordered surveys to assess the Romani population in Romania. The results estimated 208,700 people of Romani ethnicity, out of whom the ones without fixed residence and those deemed "dangerous" - for example those who had previous criminal convictions or even those who were jobless - fell under the criteria for deportation. More than 30,000 people met the criteria. According to researcher Shannon Woodcock the vague labelling of "nomadic" and "non-nomadic dangerous Țigani" by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mircea Eliade
Mircea Eliade (; – April 22, 1986) was a Romanian History of religion, historian of religion, fiction writer, philosopher, and professor at the University of Chicago. One of the most influential scholars of religion of the 20th century and interpreter of religious experience, he established paradigms in religious studies that persist to this day. His theory that Hierophany, ''hierophanies'' form the basis of religion, splitting the human experience of reality into Sacred-profane dichotomy, sacred and profane space and time, has proved influential.Wendy Doniger, "Foreword to the 2004 Edition", Eliade, ''Shamanism'', p. xiii One of his most instrumental contributions to religious studies was his theory of Eternal return (Eliade), ''eternal return'', which holds that myths and rituals do not simply commemorate hierophanies, but (at least in the minds of the religious) actually participate in them. Eliade's literary works belong to the Fantastique, fantastic and Autobiographical n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nae Ionescu
Nae Ionescu (, born Nicolae C. Ionescu; – 15 March 1940) was a Romanian philosopher, logician, mathematician, professor, and journalist. Life Born in Brăila, Ionescu studied Letters at the University of Bucharest until 1912. Upon graduation, he was appointed teacher at the Matei Basarab National College, Matei Basarab High School in Bucharest. When World War I began, he traveled to German Empire, Germany for additional studies at the University of Göttingen. Romania's entry into the war on the Allies of World War I, Entente side prevented him from returning, but he was awarded a doctorate in philosophy in 1919 from the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, University of Munich. His thesis was entitled ''Die Logistik als Versuch einer neuen Begründung der Mathematik'' ("Formal logic as an attempt at a new foundation of mathematics"). Back in Romania, after another brief stint teaching, Ionescu was appointed assistant to Constantin Rădulescu-Motru at the University of B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interwar Period
In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period, also known as the interbellum (), lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days) – from the end of World War I (WWI) to the beginning of World War II (WWII). It was relatively short, yet featured many social, political, military, and economic changes throughout the world. Petroleum-based energy production and associated mechanisation led to the prosperous Roaring Twenties, a time of social mobility, social and economic mobility for the middle class. Automobiles, electric lighting, radio, and more became common among populations in the developed world, first world. The era's indulgences were followed by the Great Depression, an unprecedented worldwide economic downturn that severely damaged many of the world's largest economies. Politically, the era coincided with the rise of communism, starting in Russia with the October Revolution and Russian Civil War, at the end of WWI, and ended with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fascism
Fascism ( ) is a far-right, authoritarian, and ultranationalist political ideology and movement. It is characterized by a dictatorial leader, centralized autocracy, militarism, forcible suppression of opposition, belief in a natural social hierarchy, subordination of individual interests for the perceived interest of the nation or Race (human categorization), race, and strong regimentation of society and the economy. Opposed to communism, democracy, liberalism, Pluralism (political philosophy), pluralism, and socialism, fascism is at the far right of the traditional left–right spectrum.; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; Fascism rose to prominence in early-20th-century Europe. The first fascist movements Italian fascism, emerged in Italy during World War I, before Fascism in Europe, spreading to other European countries, most notably Nazi Germany, Germany. Fascism also had adherents outside of Europe. Fascists saw World War I as a revolution that brought massive changes to the nature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-communism
Anti-communism is Political movement, political and Ideology, ideological opposition to communism, communist beliefs, groups, and individuals. Organized anti-communism developed after the 1917 October Revolution in Russia, and it reached global dimensions during the Cold War, when the United States and the Soviet Union engaged in an intense rivalry. Anti-communism has been an element of many movements and different political positions across the political spectrum, including anarchism, centrism, conservatism, fascism, liberalism, nationalism, social democracy, socialism, leftism, and libertarianism, as well as broad movements #Evasion of censorship, resisting communist governance. Anti-communism has also been expressed by #Religions, several religious groups, and in art and #Literature, literature. The first organization which was specifically dedicated to opposing communism was the Russian White movement, which fought in the Russian Civil War starting in 1918 against the recent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legion Of Archangel Michael
The Iron Guard () was a Romanian militant revolutionary religious fascist movement and political party founded in 1927 by Corneliu Zelea Codreanu as the Legion of the Archangel Michael () or the Legionary Movement (). It was strongly anti-democratic, anti-communist, and anti-semitic. It differed from other European far-right movements of the period due to its spiritual basis, as the Iron Guard was deeply imbued with Romanian Orthodox Christian mysticism. In March 1930, Codreanu formed the Iron Guard as a paramilitary branch of the Legion, which in 1935 changed its official name to the "Totul pentru Țară" party—literally, "Everything for the Country". It existed into the early part of the Second World War, during which time it came to power. Members were called Legionnaires or, outside of the movement, "Greenshirts" because of the predominantly green uniforms they wore. When Marshal Ion Antonescu came to power in September 1940, he brought the Iron Guard into the governme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corneliu Zelea Codreanu
Corneliu Zelea Codreanu (; 13 September 1899 – 30 November 1938), born Corneliu Zelinski and commonly known as Corneliu Codreanu, was a far-right Romanian politician, the founder and charismatic leader of the Iron Guard or ''The Legion of the Archangel Michael'' (also known as the ''Legionary Movement''), an ultranationalist and violently antisemitic organization active throughout most of the interwar period. Generally seen as the main variety of local fascism, and noted for its mystical and Romanian Orthodox-inspired revolutionary message, the Iron Guard gained prominence on the Romanian political stage, coming into conflict with the political establishment and the democratic forces, and often resorting to terrorism. The Legionnaires traditionally referred to Codreanu as ''Căpitanul'' ("The Captain"), and he held absolute authority over the organization until his death. Codreanu, who began his career in the wake of World War I as an anticommunist and antisemitic agit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicolae Paulescu
Nicolae Constantin Paulescu (; 30 October 1869 (O.S.) – 17 July 1931) was a Romanians, Romanian physiologist, professor of medicine, and politician, most famous for his work on diabetes, including patenting ''pancreine'' (a pancreatic extract containing insulin). The "pancreine" was an extract of bovine pancreas in salted water, after which some impurites were removed with hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide. Paulescu was also, with A. C. Cuza, co-founder of the National Christian Union and later, of the National-Christian Defense League, an early ultranationalist and anti-Semitic Romanian party. He was also a leading member of the militant religious fascist Iron Guard. Early life and education Born in Bucharest, he was the first of four children of Costache and Maria Paulescu. He displayed remarkable abilities as early as his first school years. He learned French language, French, Latin and Ancient Greek at an early age, so that a few years later he became fluent in all the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicolae Iorga
Nicolae Iorga (17 January 1871 – 27 November 1940) was a historian, politician, literary critic, memoirist, Albanologist, poet and playwright. Co-founder (in 1910) of the Democratic Nationalist Party (PND), he served as a member of Parliament, President of the Deputies' Assembly and Senate, cabinet minister and briefly (1931–32) as Prime Minister. A child prodigy, polymath and polyglot, Iorga produced an unusually large body of scholarly works, establishing his international reputation as a medievalist, Byzantinist, Latinist, Slavist, art historian and philosopher of history. Holding teaching positions at the University of Bucharest, the University of Paris and several other academic institutions, Iorga was founder of the International Congress of Byzantine Studies and the Institute of South-East European Studies (ISSEE). His activity also included the transformation of Vălenii de Munte town into a cultural and academic center. In parallel with his academic contributi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |