|
The Easter Sunday Raid On Colombo
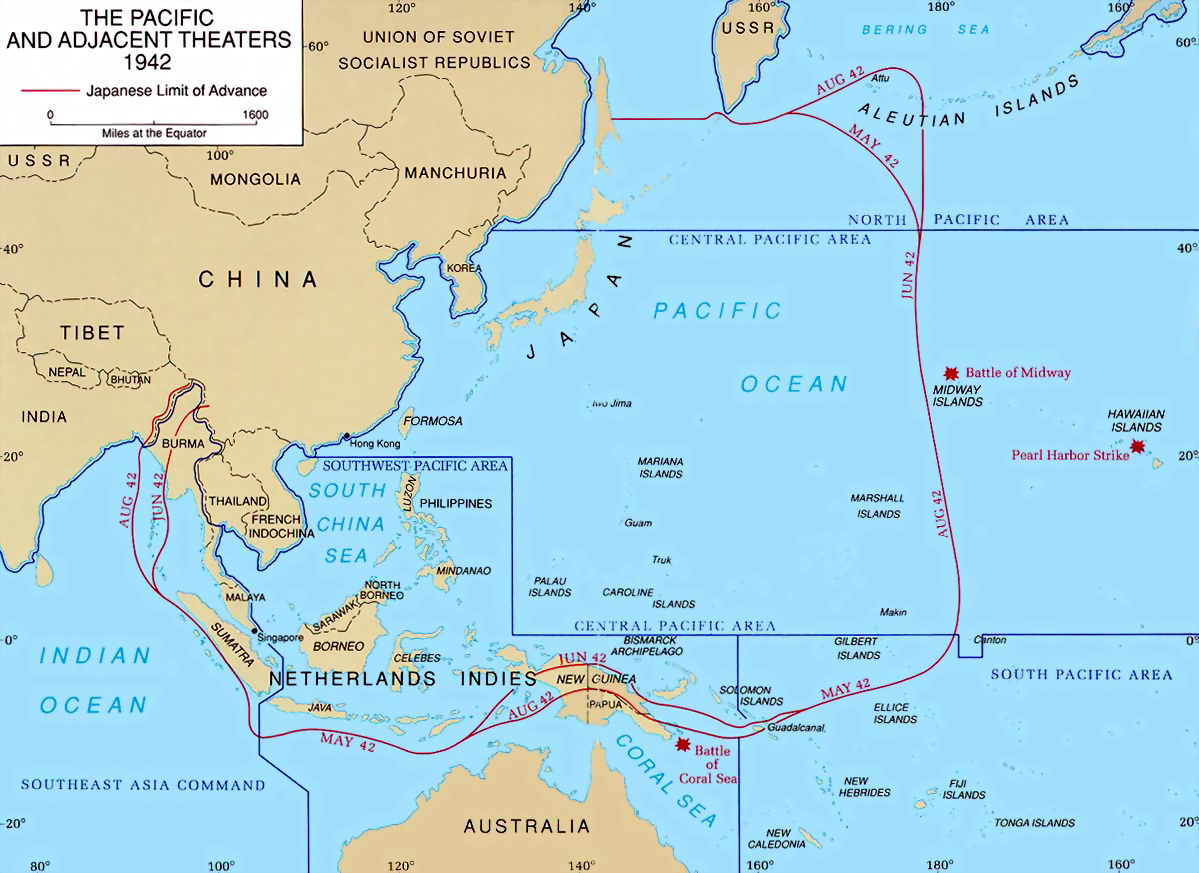
The Easter Sunday Raid was an air attack on Colombo, Ceylon during the Indian Ocean raid by carrier-based aircraft of the Imperial Japanese Navy on 5 April 1942. The Japanese objective was to destroy the Ceylon-based British Eastern Fleet in harbour. The British preemptively dispersed shipping from the harbours before the attacks due to advance warning from intelligence in March 1942, and air reconnaissance during the raid. The attacking Japanese aircraft were met by fighters of the Royal Air Force's (RAF) 222 Group, commanded by Air Vice-Marshal John D'Albiac, and the Royal Navy's Fleet Air Arm (FAA), and anti-aircraft artillery. Port facilities were damaged, and ships both in harbour and – having dispersed – on the ocean were sunk or damaged. The bulk of the British Eastern Fleet was not found and survived. The raid demonstrated Ceylon's vulnerability; British forces were not prepared to face further Japanese carrier raids. The Eastern Fleet relocated its main base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific War
The Pacific War, sometimes called the Asia–Pacific War or the Pacific Theatre, was the Theater (warfare), theatre of World War II fought between the Empire of Japan and the Allies of World War II, Allies in East Asia, East and Southeast Asia, the Pacific Ocean, Pacific and Indian Oceans, and Oceania. It was geographically the largest theatre of the war, including the Pacific Ocean theater of World War II, Pacific Ocean theatre, the South West Pacific theater of World War II, South West Pacific theatre, the Second Sino-Japanese War, and the brief Soviet–Japanese War, and included some of the Largest naval battle in history, largest naval battles in history. War between Japan and the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China had begun in 1937, with hostilities dating back to Japanese invasion of Manchuria, Japan's invasion of Manchuria in 1931, but the Pacific War is more widely accepted to have started in 1941, when the United States and United Kingdom entered the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Eastern Fleet
The East Indies Station was a formation and command of the British Royal Navy. Created in 1744 by the Admiralty, it was under the command of the Commander-in-Chief, East Indies. Even in official documents, the term ''East Indies Station'' was often used. In 1941, the ships of the China Squadron and East Indies Squadron were merged to form the Eastern Fleet under the control of the Commander-in-Chief, Eastern Fleet. The China Station then ceased as a separate command. The East Indies Station was disbanded in 1958. It encompassed Royal Navy Dockyards and bases in East Africa, Middle East, India and Ceylon, and other ships not attached to other fleets. For many years under rear admirals, from the 1930s the Commander-in-Chief was often an Admiral or a Vice-Admiral. History The East Indies Station was established as a Royal Navy command in 1744. From 1831 to 1865, the East Indies and the China Station were a single command known as the East Indies and China Station. The Eas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karachi
Karachi is the capital city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Sindh, Pakistan. It is the List of cities in Pakistan by population, largest city in Pakistan and 12th List of largest cities, largest in the world, with a population of over 20 million. It is situated at the Geography of Pakistan, southern tip of the country along the Arabian Sea coast and formerly served as the Federal Capital Territory (Karachi), country's capital from 1947 to 1959. Ranked as a Global city, beta-global city, it is Pakistan's premier industrial and financial centre, with an estimated GDP of over $200 billion (Purchasing power parity, PPP) . Karachi is a metropolitan city and is considered Pakistan's most cosmopolitan city, and among the country's most linguistically, ethnically, and religiously diverse regions, as well as one of the country's most progressive and socially liberal cities. The region has been inhabited for millennia, but the city was formally founded as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
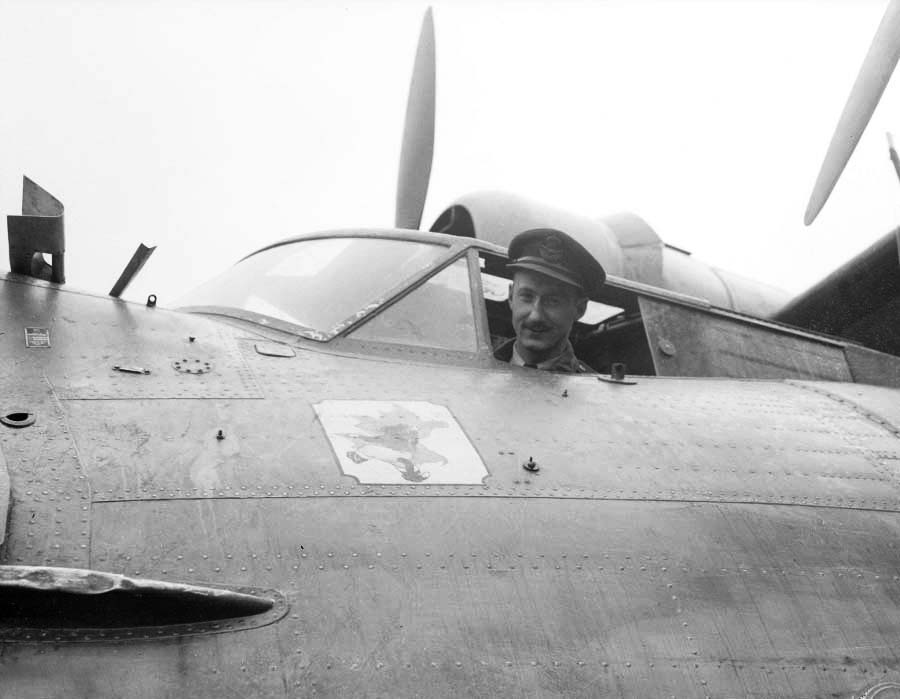
Hawker Hurricane
The Hawker Hurricane is a British single-seat fighter aircraft of the 1930s–40s which was designed and predominantly built by Hawker Aircraft Ltd. for service with the Royal Air Force (RAF). It was overshadowed in the public consciousness by the Supermarine Spitfire during the Battle of Britain in 1940, but the Hurricane inflicted 60% of the losses sustained by the ''Luftwaffe'' in the campaign, and fought in all the major theatres of the Second World War. The Hurricane originated from discussions between RAF officials and aircraft designer Sir Sydney Camm about a proposed monoplane derivative of the Hawker Fury biplane in the early 1930s. Despite an institutional preference for biplanes and lack of interest by the Air Ministry, Hawker refined its monoplane proposal, incorporating several innovations which became critical to wartime fighter aircraft, including retractable landing gear and the more powerful Rolls-Royce Merlin engine. The Air Ministry ordered Hawker's ''Interce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bombing Of Darwin
The Bombing of Darwin, also known as the Battle of Darwin, on 19 February 1942 was the largest single attack ever mounted by a foreign power on Australia. On that day, 242 Empire of Japan, Japanese aircraft, in two separate raids, attacked the town, ships in Darwin Harbour and the town's two airfields in an attempt to prevent the Allies of World War II, Allies from using them as bases to contest the Battle of Timor, invasion of Timor and Battle of Java (1942), Java during World War II. Darwin, Northern Territory, Darwin was lightly defended relative to the size of the attack, and the Japanese inflicted heavy losses upon Allied forces at little cost to themselves. The urban areas of Darwin also suffered some damage from the raids and there were a number of civilian casualties. More than half of Darwin's civilian population left the area permanently, before or immediately after the attack. The two Japanese air raids were the first, and largest, of more than 100 Air raids on Aust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attack On Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Empire of Japan on the United States Pacific Fleet at Naval Station Pearl Harbor, its naval base at Pearl Harbor on Oahu, Territory of Hawaii, Hawaii, on December 7, 1941. At the time, the U.S. was a Neutral powers during World War II, neutral country in World War II. The air raid on Pearl Harbor, which was launched from Aircraft carrier, aircraft carriers, resulted in the U.S. entering the war on the side of the Allies of World War II, Allies on the day following the attack. The Imperial General Headquarters, Japanese military leadership referred to the attack as the Hawaii Operation and Operation AI, and as Operation Z during its planning. The attack on Pearl Harbor was preceded by months of negotiations between the U.S. and Japan over the future of the Pacific Ocean, Pacific. Japanese demands included that the U.S. ABCD line, end its sanctions against Japan, cease aidi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or approximately 20% of the water area of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia (continent), Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by the Southern Ocean or Antarctica, depending on the definition in use. The Indian Ocean has large marginal or regional seas, including the Andaman Sea, the Arabian Sea, the Bay of Bengal, and the Laccadive Sea. Geologically, the Indian Ocean is the youngest of the oceans, and it has distinct features such as narrow continental shelf, continental shelves. Its average depth is 3,741 m. It is the warmest ocean, with a significant impact on global climate due to its interaction with the atmosphere. Its waters are affected by the Indian Ocean Walker circulation, resulting in unique oceanic currents and upwelling patterns. The Indian Ocean is ecologically diverse, with important ecosystems such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Line Of Communication
A line of communication (or communications) is the route that connects an operating military unit with its supply base. Supplies and reinforcements are transported along the line of communication. Therefore, a secure and open line of communication is vital for any military force to continue to operate effectively. Prior to the advent of the use of the telegraph and radio in warfare, lines of communication were also the routes used by dispatch riders on horseback and runners to convey and deliver orders and battle updates to and from unit commanders and headquarters. Thus, a unit whose lines of communication were compromised was vulnerable to becoming isolated and destroyed, as the means for requesting reinforcements and resupply is lost. The standard military abbreviation is LOC. There is also SLOC for Sea Line of Communication, GLOC for Ground Line of Communication, or ALOC for Air Line of Communication. The interdiction of supplies and reinforcements to units closer to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Raj
The British Raj ( ; from Hindustani language, Hindustani , 'reign', 'rule' or 'government') was the colonial rule of the British The Crown, Crown on the Indian subcontinent, * * lasting from 1858 to 1947. * * It is also called Crown rule in India, * * * * or direct rule in India. * Quote: "Mill, who was himself employed by the British East India company from the age of seventeen until the British government assumed direct rule over India in 1858." * * The region under British control was commonly called India in contemporaneous usage and included areas directly administered by the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom, which were collectively called ''Presidencies and provinces of British India, British India'', and areas ruled by indigenous rulers, but under British British paramountcy, paramountcy, called the princely states. The region was sometimes called the Indian Empire, though not officially. As ''India'', it was a founding member of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Singapore
The fall of Singapore, also known as the Battle of Singapore, took place in the South–East Asian theatre of the Pacific War. The Empire of Japan captured the British stronghold of Singapore, with fighting lasting from 8 to 15 February 1942. Singapore was the foremost British military base and economic port in South–East Asia and had been of great importance to British interwar defence strategy. The capture of Singapore resulted in the largest British surrender in history. Before the battle, Japanese General Tomoyuki Yamashita had advanced with approximately 30,000 men down the Malayan Peninsula in the Malayan campaign. The British erroneously considered the jungle terrain impassable, leading to a swift Japanese advance as Allied defences were quickly outflanked. The British Lieutenant-General, Arthur Percival, commanded 85,000 Allied troops at Singapore, although many units were under-strength and most units lacked experience. The British outnumbered the Japanese but mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torpedo Bomber
A torpedo bomber is a military aircraft designed primarily to attack ships with aerial torpedoes. Torpedo bombers came into existence just before the World War I, First World War almost as soon as aircraft were built that were capable of carrying the weight of a torpedo, and remained an important aircraft type until they were rendered obsolete by anti-ship missiles. They were an important element in many famous World War II, Second World War battles, notably the United Kingdom, British Battle of Taranto, attack at Taranto, the sinking of the German battleship German battleship Bismarck, ''Bismarck'', the sinking of the British battleship ''HMS Prince of Wales (53), HMS Prince Of Wales'' and the British battlecruiser ''HMS Repulse (1916), HMS Repulse'' and the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor. Types Torpedo bombers first appeared immediately prior to the First World War. Generally, they carried torpedo, torpedoes specifically designed for air launch, which were smaller and lighte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairey Seal
The Fairey Seal was a British carrier-borne spotter-reconnaissance aircraft, operated in the 1930s. The Seal was derived – like the Gordon – from the IIIF. To enable the Fairey Seal to be launched by catapult from warships, it could be fitted with floats. Service life and operations The Seal was designed and built by Fairey Aviation. It first flew in 1930 and entered squadron service with the Fleet Air Arm (FAA) in 1933. Ninety-one aircraft were produced. The FAA started to replace it with the Swordfish Mk1 from 1936. By 1938 all FAA torpedo squadrons had been entirely re-equipped with the Swordfish. The Seal was removed from front-line service by 1938, but remained in secondary and support roles. By the outbreak of the Second World War, only four remained in service. The type was retired fully by 1943. The type was last used in India as an instructional airframe from the Royal Navy Photographic Unit. The RAF also operated the Seal as a target tug. Twelve aircraft were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |