|
Thalassiodracon Hawkinsi
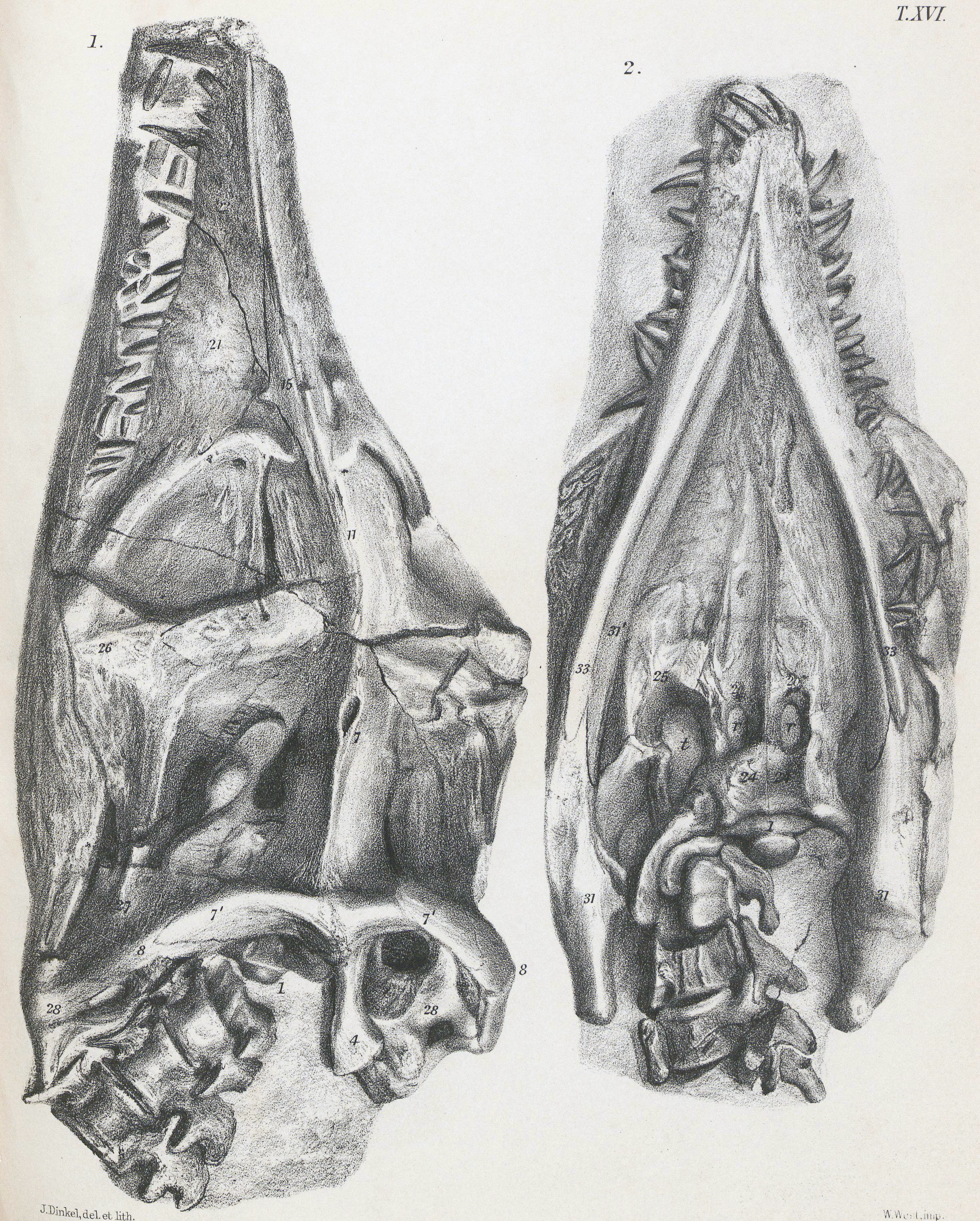
''Thalassiodracon'' (tha-LAS-ee-o-DRAY-kon) is an extinct genus of plesiosauroid from the Pliosauridae that was alive during the Late Triassic-Early Jurassic (Rhaetian-Hettangian) and is known exclusively from the Lower Lias of England. The type and only species, is ''Thalassiodracon'' (''Plesiosaurus'') ''hawkinsii'' (Owen, 1838). Owen, R. (1838). A description of Viscount Cole's specimen of '' Plesiosaurus macrocephalus'' ( Conybeare). ''Proceedings of the Geological Society of London 2'', 663-666. Discovery and naming left, Sculpture in Crystal Palace Park ''Thalassiodracon hawkinsii'' is known from a number of complete skeletons (lectotype: NHMUK PV OR 2018) acquired by the fossil collector Thomas Hawkins in Somerset, England during the early 1830s, before 1834. Hawkins, an eccentric Pre-Adamite who had his fossils heavily restored and illustrated by distinguished artists in expensive editions to propagate his ideas, named these ''Plesiosaurus triotarsostinus'' in 1834 an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhaetian
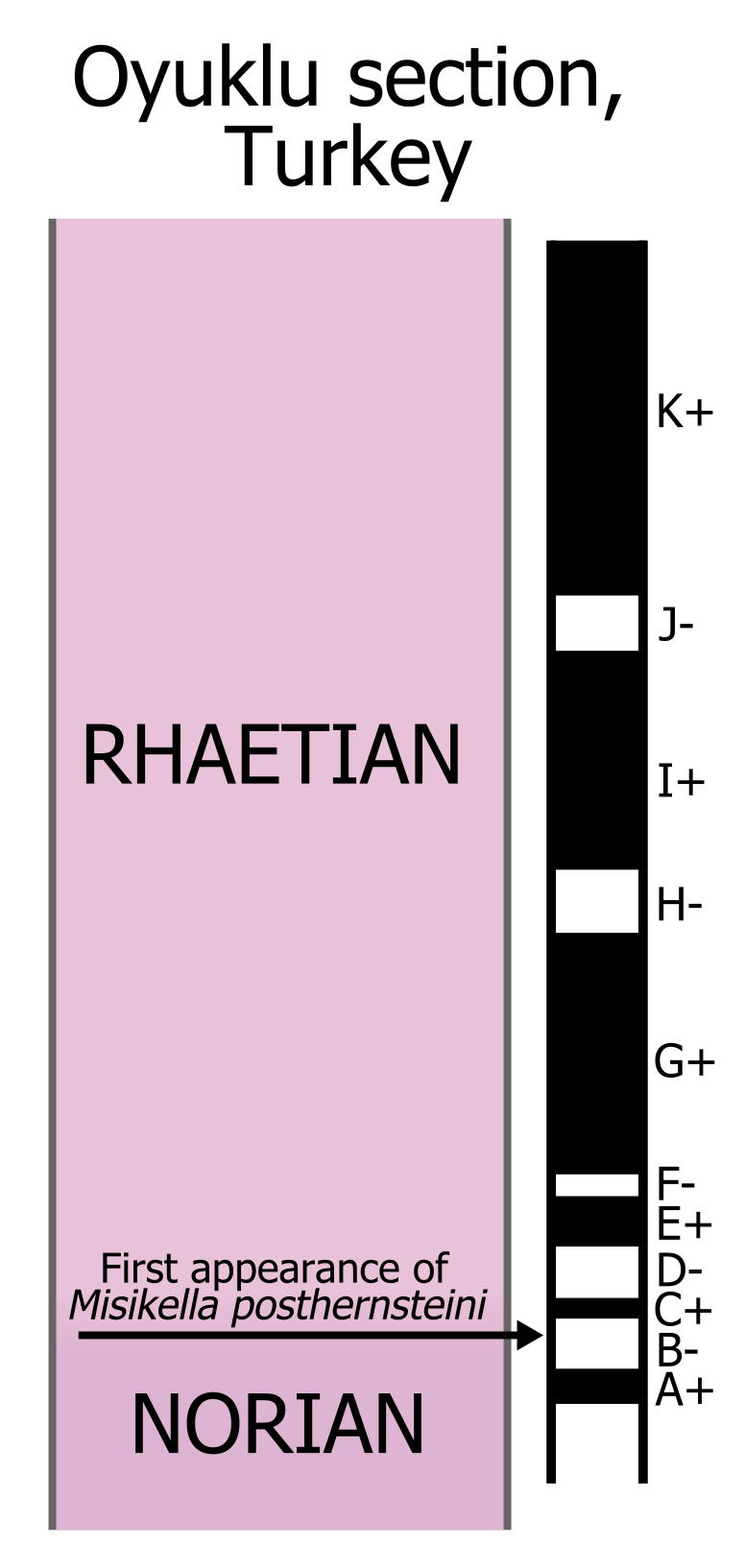
The Rhaetian is the latest age (geology), age of the Triassic period (geology), Period (in geochronology) or the uppermost stage (stratigraphy), stage of the Triassic system (stratigraphy), System (in chronostratigraphy). It was preceded by the Norian and succeeded by the Hettangian (the lowermost stage or earliest age of the Jurassic). The base of the Rhaetian lacks a formal Global Boundary Stratotype Section and Point, GSSP, though candidate sections include Steinbergkogel section, Steinbergkogel in Austria (since 2007) and Pignola-Abriola section, Pignola-Abriola in Italy (since 2016). The end of the Rhaetian (and the base of the overlying Hettangian Stage) is more well-defined. According to the current International Commission on Stratigraphy, ICS (International Commission on Stratigraphy) system, the Rhaetian ended ± 0.2 Ma (million years ago). In 2010, the base of the Rhaetian (i.e. the Norian-Rhaetian boundary) was voted to be defined based on the first appearance of ''Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Conybeare (geologist)
William Daniel Conybeare Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS (7 June 178712 August 1857), dean of Llandaff, was an England, English geologist, palaeontologist and clergyman. He is probably best known for his ground-breaking work on fossils and excavation in the 1820s, including important papers for the Geological Society of London on ichthyosaur anatomy and the first published scientific description of a plesiosaur. Life and career Childhood and education He was a grandson of John Conybeare, bishop of Bristol (1692–1755), a notable preacher and divine, and son of Dr William Conybeare, rector of St Botolph-without-Bishopsgate. Born in London, he was educated there at Westminster School, then went in 1805 to Christ Church, Oxford, where in 1808 he took his degree of BA, with a first in classics and second in mathematics, and proceeded to Master's degree, MA three years later. Early career Having entered holy orders he became in 1814 curate of Wardington, near Banbury, and he acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the second and middle period of the Mesozoic, Mesozoic Era as well as the eighth period of the Phanerozoic, Phanerozoic Eon and is named after the Jura Mountains, where limestone strata from the period were first identified. The start of the Jurassic was marked by the major Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, associated with the eruption of the Central Atlantic magmatic province, Central Atlantic Magmatic Province (CAMP). The beginning of the Toarcian Age started around 183 million years ago and is marked by the Toarcian Oceanic Anoxic Event, a global episode of Anoxic event, oceanic anoxia, ocean acidification, and elevated global temperatures associated with extinctions, likely caused by the eruption of the Kar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic
The Triassic ( ; sometimes symbolized 🝈) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.5 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.4 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era and the seventh period of the Phanerozoic Eon. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalassiodracon BW
''Thalassiodracon'' (tha-LAS-ee-o-DRAY-kon) is an extinct genus of plesiosauroid from the Pliosauridae that was alive during the Late Triassic-Early Jurassic (Rhaetian-Hettangian) and is known exclusively from the Lower Lias of England. The type and only species, is ''Thalassiodracon'' (''Plesiosaurus'') ''hawkinsii'' (Owen, 1838). Owen, R. (1838). A description of Viscount Cole's specimen of '' Plesiosaurus macrocephalus'' ( Conybeare). ''Proceedings of the Geological Society of London 2'', 663-666. Discovery and naming left, Sculpture in Crystal Palace Park ''Thalassiodracon hawkinsii'' is known from a number of complete skeletons (lectotype: NHMUK PV OR 2018) acquired by the fossil collector Thomas Hawkins in Somerset, England during the early 1830s, before 1834. Hawkins, an eccentric Pre-Adamite who had his fossils heavily restored and illustrated by distinguished artists in expensive editions to propagate his ideas, named these ''Plesiosaurus triotarsostinus'' in 1834 an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plesiosaur
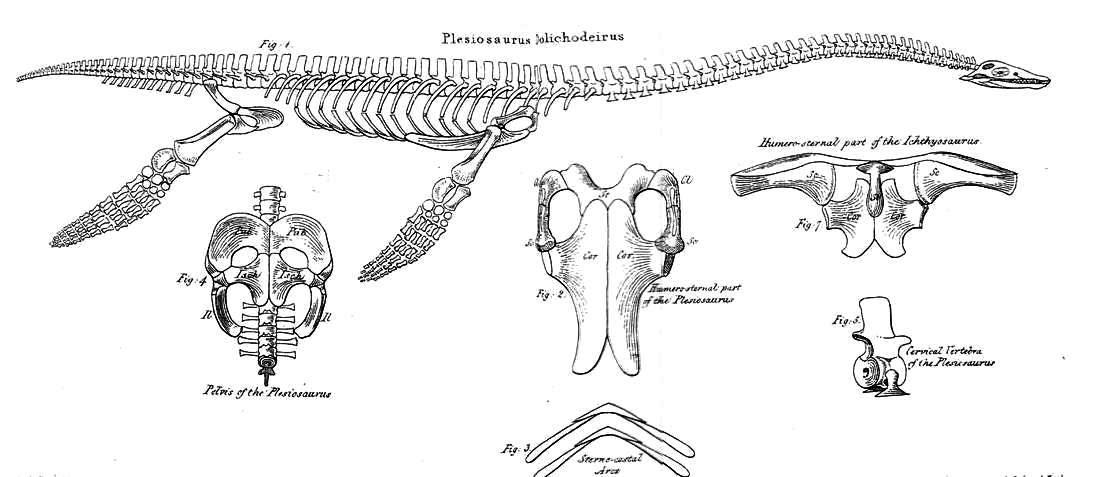
The Plesiosauria or plesiosaurs are an Order (biology), order or clade of extinct Mesozoic marine reptiles, belonging to the Sauropterygia. Plesiosaurs first appeared in the latest Triassic Period (geology), Period, possibly in the Rhaetian stage, about 203 million years ago. They became especially common during the Jurassic Period, thriving until their disappearance due to the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event at the end of the Cretaceous Period, about 66 million years ago. They had a worldwide oceanic distribution, and some species at least partly inhabited freshwater environments. Plesiosaurs were among the first fossil reptiles discovered. In the beginning of the nineteenth century, scientists realised how distinctive their build was and they were named as a separate order in 1835. The first plesiosaurian genus, the eponymous ''Plesiosaurus'', was named in 1821. Since then, more than a hundred valid species have been described. In the early twenty-first cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grant Museum Of Zoology And Comparative Anatomy
The Grant Museum of Zoology and Comparative Anatomy is a natural history museum that is part of University College London in London, England. It was established by Robert Edmond Grant in 1828 as a teaching collection of zoological specimens and material for dissection. It is one of the oldest natural history collections in the UK, and is the last remaining university natural history museum in London. Notable specimens and objects held by the museum include a rare quagga skeleton, thylacine specimens, dodo bones and Glass sea creatures, Blaschka glass models. History Robert Edmond Grant was the first Chair of Zoology in England, the founder of the Grant Museum collection and its first curator. He set the precedent that the Chair of Zoology at UCL (then the University of London) was also the curator of the comparative zoology collection. On his death Grant left his own collection to the museum, and was briefly succeeded by William Henry Allchin before care of the collection passe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ray Lankester
Sir Edwin Ray Lankester (15 May 1847 – 13 August 1929) was a British zoologist.New International Encyclopaedia. An invertebrate zoologist and evolutionary biologist, he held chairs at University College London and Oxford University. He was the third Director of the Natural History Museum, London, and was awarded the Copley Medal of the Royal Society. Life Ray Lankester was born on 15 May 1847 on Burlington Street in London, the son of Edwin Lankester, a coroner and doctor-naturalist who helped eradicate cholera in London, and his wife, the botanist and author Phebe Lankester. Ray Lankester was probably named after the naturalist John Ray: his father had just edited the memorials of John Ray for the Ray Society. In 1855 Ray went to boarding school at Leatherhead, and in 1858 to St Paul's School. His university education was at Downing College, Cambridge, and Christ Church, Oxford; he transferred from Downing, after five terms, at his parents' behest because Christ Church ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Augustus Ward
Henry Augustus Ward (March 9, 1834 – July 4, 1906) was an American naturalist and geologist. Biography Henry Augustus Ward was born in Rochester, New York on March 9, 1834. After attending Williams College and the Lawrence Scientific School, Harvard, where he was an assistant of Louis Agassiz, he traveled in Egypt, Arabia, and Palestine, and studied at the Jardin des Plantes, the Sorbonne, and the School of Mines in Paris, and at the universities of Munich and Freiberg. Subsequently, he traveled in West Africa and the West Indies, making natural history collections. In 1860, he returned to Rochester where he was professor at the University of Rochester until 1865. In Rochester, he founded Ward's Natural Science Establishment, a pioneering enterprise that collected and prepared taxidermy, fossils, and other animal remains from all parts of the world for sale to colleges, universities, museums, and private collectors. He published: * ''Notices of the Megatherium Cuvieri'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holotype
A holotype (Latin: ''holotypus'') is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several examples, but explicitly designated as the holotype. Under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), a holotype is one of several kinds of name-bearing types. In the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) and ICZN, the definitions of types are similar in intent but not identical in terminology or underlying concept. For example, the holotype for the butterfly '' Plebejus idas longinus'' is a preserved specimen of that subspecies, held by the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard University. In botany and mycology, an isotype is a duplicate of the holotype, generally pieces from the same individual plant or samples from the same genetic individual. A holotype is not necessarily "ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural History Museum, London
The Natural History Museum in London is a museum that exhibits a vast range of specimens from various segments of natural history. It is one of three major museums on Exhibition Road in South Kensington, the others being the Science Museum (London), Science Museum and the Victoria and Albert Museum. The Natural History Museum's main frontage, however, is on Cromwell Road. The museum is home to life and earth science specimens comprising some 80 million items within five main collections: botany, entomology, mineralogy, palaeontology and zoology. The museum is a centre of research specialising in Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy, identification and conservation. Given the age of the institution, many of the collections have great historical as well as scientific value, such as specimens collected by Charles Darwin. The museum is particularly famous for its exhibition of dinosaur skeletons and ornate architecture—sometimes dubbed a ''cathedral of nature''—both exemplified by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-Adamite
The pre-Adamite hypothesis or pre-Adamism is the theological belief that humans (or intelligent yet non-human creatures) existed before the biblical character Adam. Pre-Adamism is therefore distinct from the conventional Abrahamic belief that Adam was the first human. "Pre-Adamite" is used as a term, both for those humans (or human-like animals) believed to exist before Adam, and for believers or proponents of this hypothesis. Early development The first known debate about human antiquity took place in 170 AD between a Christian, Theophilus of Antioch, and an Egyptian pagan, Apollonius the Egyptian (probably Apollonius Dyscolus), who argued that the world was 153,075 years old. An early challenge to biblical Adamism came from the Roman Emperor Julian the Apostate, who, upon his rejection of Christianity and his return to paganism, accepted the idea that many pairs of original people had been created, a belief termed co-Adamism or multiple Adamism. Augustine of Hippo's ''T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |