|
Tetraneuris Scaposa
''Tetraneuris scaposa'' (common names stemmy four-nerve daisy and stemmy hymenoxys) is a North American species of flowering plant in the sunflower family. It is native to the southwestern and south-central United States (Nebraska, Kansas, Oklahoma, Texas, New Mexico, Arizona, Utah, and Colorado) and northern Mexico ( Chihuahua, Coahuila, Nuevo León, Tamaulipas, San Luis Potosí, and Zacatecas). ''Tetraneuris scaposa'' is a perennial herb up to 40 cm (16 inches) tall. It forms a branching underground caudex sometimes producing as many as 100 above-ground stems. Leaves are concentrated low on the stem, close to the ground. Flower heads can either be present individually one per stem, or multiply in tight clumps. Each head has 12–26 ray flowers surrounding 25–180 disc flowers. Uses The Zuni people use an infusion Infusion is the process of extracting chemical compounds or flavors from plant material in a solvent such as water, oil or alcohol, by allowing the mater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Lee Greene
Edward Lee Greene (August 20, 1843–November 10, 1915) was an American botanist known for his numerous publications including the two-part ''Landmarks of Botanical History'' and the describing of over 4,400 species of plants in the American West. Early life Edward Lee Greene was born on August 20, 1843, in Hopkinton, Rhode Island. In 1859 Greene moved to Wisconsin and began studying at Albion Academy, a very reputable institution with a religious emphasis. There Greene met Thure Kumlien, a Swedish naturalist with an interest in botany. Greene accompanied Kumlein on field trips, further developing Greene's interest in botany. In August 1862, Greene joined his father and brothers in joining the 13th Wisconsin Volunteer Infantry Regiment of the Union Army. Though he never rose above the rank of private in his three years of service, Greene was able to advance his botanical studies, collecting specimens as he marched through Tennessee, Kentucky and Alabama. Following his re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Luis Potosí
San Luis Potosí, officially the Free and Sovereign State of San Luis Potosí, is one of the 32 states which compose the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 59 municipalities and is named after its capital city, San Luis Potosí. It is located in eastern and central Mexico and is bordered by seven other Mexican states: Nuevo León to the north; Tamaulipas to the north-east; Veracruz to the east; Hidalgo, Querétaro and Guanajuato to the south; and Zacatecas to the north-west. In addition to the capital city, other major cities in the state include Ciudad Valles, Matehuala, Rioverde, and Tamazunchale. History In pre-Columbian times, the territory now occupied by the state of San Luis Potosí contained parts of the cultural areas of Mesoamerica and Aridoamerica. Its northern and western-central areas were inhabited by the Otomi and Chichimeca tribes. These indigenous groups were nomadic hunter-gatherers. Although many indigenous people died during Spanish colon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plants Used In Traditional Native American Medicine
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with cyanobacteria to produce sugars from carbon dioxide and water, using the green pigment chlorophyll. Exceptions are parasitic plants that have lost the genes for chlorophyll and photosynthesis, and obtain their energy from other plants or fungi. Most plants are multicellular, except for some green algae. Historically, as in Aristotle's biology, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi. Definitions have narrowed since then; current definitions exclude fungi and some of the algae. By the definition used in this article, plants form the clade Viridiplantae (green plants), which consists of the green algae and the embryophytes or land plants ( hornworts, liverworts, mosses, lycophytes, ferns, conifers and other gym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of The Great Plains (North America)
Flora (: floras or florae) is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring ( indigenous) native plants. The corresponding term for animals is ''fauna'', and for fungi, it is '' funga''. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora as in the terms ''gut flora'' or ''skin flora'' for purposes of specificity. Etymology The word "flora" comes from the Latin name of Flora, the goddess of plants, flowers, and fertility in Roman mythology. The technical term "flora" is then derived from a metonymy of this goddess at the end of the sixteenth century. It was first used in poetry to denote the natural vegetation of an area, but soon also assumed the meaning of a work cataloguing such vegetation. Moreover, "Flora" was used to refer to the flowers of an artificial garden in the seventeenth century. The distinction between vegetation (the general appearance of a community) and flora (the taxonomic composition of a community) wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of The United States
The native flora of the United States includes about 17,000 species of vascular plants, plus tens of thousands of additional species of other plants and plant-like organisms such as algae, lichens and other fungi, and mosses. About 3,800 additional non-native species of vascular plants are recorded as established outside of cultivation in the U.S., as well as a much smaller number of non-native non-vascular plants and plant relatives. The United States possesses one of the most diverse temperate floras in the world, comparable only to that of China. Several biogeographic factors contribute to the richness and diversity of the U.S. flora. While most of the United States has a temperate climate, Alaska has vast arctic areas, the southern part of Florida is tropical, as well as Hawaii (including high mountains), and the U.S. territories in the Caribbean and the Pacific, and alpine summits are present on many western mountains, as well as a few in the Northeast. The U.S. coastl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundaries with the Pacific Ocean to the west, the Caribbean Sea to the southeast, and the Gulf of Mexico to the east. Mexico covers 1,972,550 km2 (761,610 sq mi), and is the thirteenth-largest country in the world by land area. With a population exceeding 130 million, Mexico is the tenth-most populous country in the world and is home to the largest number of native Spanish speakers. Mexico City is the capital and largest city, which ranks among the most populous metropolitan areas in the world. Human presence in Mexico dates back to at least 8,000 BC. Mesoamerica, considered a cradle of civilization, was home to numerous advanced societies, including the Olmecs, Maya, Zapotecs, Teotihuacan civilization, and Purépecha. Spanish c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetraneuris
''Tetraneuris'', commonly known as four-nerve daisy or bitterweed, is a genus of North American plants in the Helenieae, sneezeweed tribe within the Asteraceae, daisy family. The genus includes one annual species, ''Tetraneuris linearifolia'', with all the other species being perennials. The name is of Greek origin, deriving from ''tetra'', meaning "four", and ''neuron'', meaning "nerve", which refers to the venation of the rays: three-lobed with the outer lobes themselves having an apparent vein down the middle. ; SpeciesFlann, C (ed) 2009+ Global Compositae Checklist [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
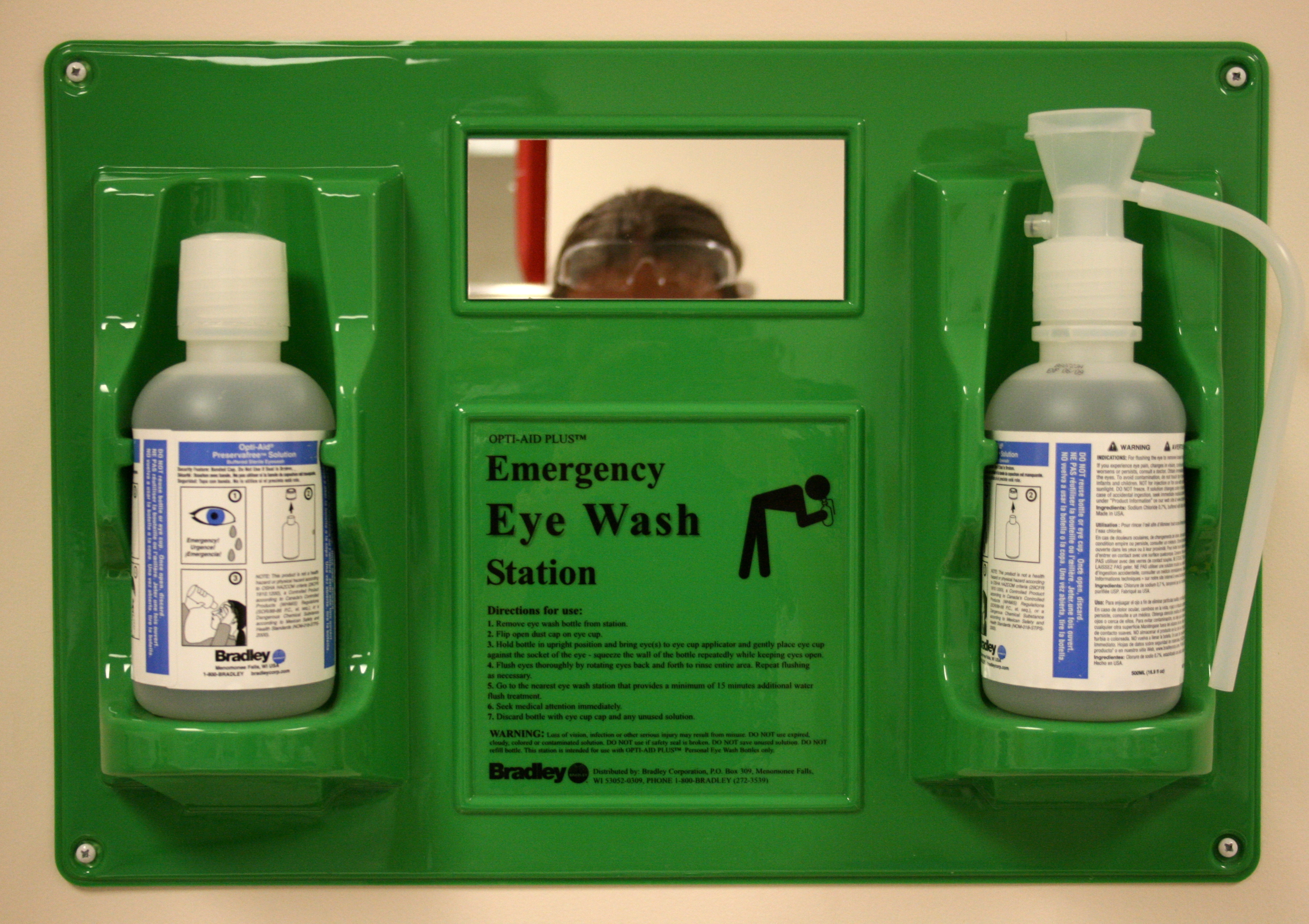
Eyewash
Eyewash is a fluid, commonly saline, used to physically wash the eyes in the case that they may be contaminated by foreign materials or substances. Eyewashes may be beneficial to those with sensitive eyes and can provide relief to the painful side effects of sensitivity. However, prolonged usage of such products will cause mild side effects, such as the reddening of the eye and/or pupil and cause itchiness. Occupational safety In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA; ) is a regulatory agency of the United States Department of Labor that originally had federal visitorial powers to inspect and examine workplaces. The United States Congress established ... (OSHA) was created as a result of the Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970. The law was created to help further protect employee safety while providing "safe & healthful working conditions." OSHA's primary eyewash standard, 29 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infusion
Infusion is the process of extracting chemical compounds or flavors from plant material in a solvent such as water, oil or alcohol, by allowing the material to remain suspended in the solvent over time (a process often called steeping). An infusion is also the name for the resultant liquid. The process of infusion is distinct from both decoction—a method of extraction involving boiling the plant material—and percolation, in which water is passed through the material (as in a coffeemaker). History The first recorded use of essential oils was in the 10th or 11th century by the Persian polymath Avicenna, possibly in ''The Canon of Medicine''. Tea is far older than this, dating back to the 10th century BC as the earliest recorded reference. Preparation techniques Infusion is a chemical process that uses botanicals (typically dried herbs, flowers or berries) that are volatile and release their active ingredients readily in water, oil, or alcohol. In this process, a liquid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zuni People
The Zuni (; formerly spelled ''Zuñi'') are Native American Pueblo peoples native to the Zuni River valley. The Zuni people today are federally recognized as the Zuni Tribe of the Zuni Reservation, New Mexico, and most live in the Pueblo of Zuni on the Zuni River, a tributary of the Little Colorado River, in western New Mexico, United States. The Pueblo of Zuni is south of Gallup, New Mexico. The Zuni tribe lived in multi level adobe houses. In addition to the reservation, the tribe owns trust lands in Catron County, New Mexico, and Apache County, Arizona. The Zuni call their homeland ''Halona Idiwan’a ''or Middle Place. The word ''Zuni'' is believed to derive from the Western Keres language ( Acoma) word ''sɨ̂‧ni'', or a cognate thereof. History Archaeology suggests that the Zuni have been farmers in the general area for 3,000 to 4,000 years. It is now thought that the Ancestral Zuni people inhabited the Zuni River valley from the last millennium B.C., when the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caudex
A caudex (: caudices) of a plant is a stem, but the term is also used to mean a rootstock and particularly a basal stem structure from which new growth arises.pages 456 and 695 In the strict sense of the term, meaning a stem, "caudex" is most often used with plants that have a different stem morphology from the typical angiosperm dicotyledon stem: examples of this include palms, ferns, and cycads. The largest of all caudices is that of the ombu (''Phytolacca dioecea'') of the Pampas of South America which can be fifty feet (fifteen meters) thick. The related term caudiciform, literally meaning stem-like, is sometimes used to mean pachycaul, thick-stemmed. Caudices should not be confused with lignotubers which can also be very large. Etymology The term is from the Latin Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zacatecas
Zacatecas, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Zacatecas, is one of the Political divisions of Mexico, 31 states of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Zacatecas, 58 municipalities and its capital city is Zacatecas City, Zacatecas. It is located in north-central Mexico and is bordered by the states of Durango to the northwest, Coahuila to the north, Nayarit to the west, San Luis Potosí and Nuevo León to the east, and Jalisco, Guanajuato and Aguascalientes to the south. The state is best known for its rich deposits of silver and other minerals, its Spanish Colonial architecture, colonial architecture and its importance during the Mexican Revolution. Its main economic activities are mining, agriculture and tourism. Geography Zacatecas is located in the center-north of Mexico, and covers an area of 75,284 km2, the tenth-largest state in the country. It borders the states of Nayarit, Jalisco, Aguascalientes, San Luis Potosí, Coahuila and Durango and is divided in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |