|
Testosterone Glucuronide
Testosterone glucuronide is an endogenous, naturally occurring steroid and minor urinary metabolite of testosterone Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting se .... See also * Androstanediol glucuronide * Androsterone glucuronide * Etiocholanolone glucuronide * Testosterone sulfate References Testosterone Glucuronide esters Human metabolites {{biochemistry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endogenous
Endogeny, in biology, refers to the property of originating or developing from within an organism, tissue, or cell. For example, ''endogenous substances'', and ''endogenous processes'' are those that originate within a living system (e.g. an organism or a cell). For instance, estradiol is an endogenous estrogen hormone A hormone (from the Ancient Greek, Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of cell signaling, signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physio ... produced within the body, whereas ethinylestradiol is an exogenous synthetic estrogen, commonly used in birth control pills. In contrast, '' exogenous substances'' and ''exogenous'' ''processes'' are those that originate from outside of an organism. References External links *{{Wiktionary-inline, endogeny Biology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Product
A natural product is a natural compound or substance produced by a living organism—that is, found in nature. In the broadest sense, natural products include any substance produced by life. Natural products can also be prepared by chemical synthesis (both semisynthesis and total synthesis and have played a central role in the development of the field of organic chemistry by providing challenging synthetic targets). The term ''natural product'' has also been extended for commercial purposes to refer to cosmetics, dietary supplements, and foods produced from natural sources without added artificial ingredients. Within the field of organic chemistry, the definition of natural products is usually restricted to organic compounds isolated from natural sources that are produced by the pathways of primary or secondary metabolism. Within the field of medicinal chemistry, the definition is often further restricted to secondary metabolites. Secondary metabolites (or specialized meta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
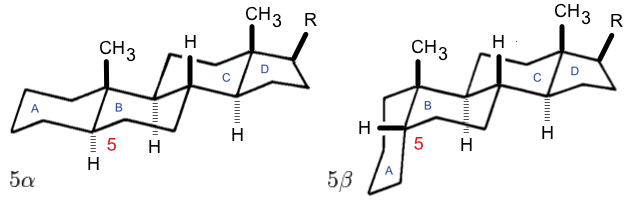
Steroid
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused compound, fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and as signal transduction, signaling molecules. Examples include the lipid cholesterol, sex hormones estradiol and testosterone, anabolic steroids, and the anti-inflammatory corticosteroid drug dexamethasone. Hundreds of steroids are found in Fungus, fungi, plants, and animals. All steroids are manufactured in cells from a sterols, sterol: Cholesterol, cholesterol (animals), lanosterol (opisthokonts), or cycloartenol (plants). All three of these molecules are produced via Cyclic compound, cyclization of the triterpene squalene. Structure The steroid nucleus (parent structure, core structure) is called gonane (cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene). It is typically composed of seventeen carbon atoms, bonded in fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and many other animals. In placental mammals, urine flows from the Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder and exits the urethra through the penile meatus (males) or urethral meatus of the vulva (females) during urination. In other vertebrates, urine is excreted through the cloaca. Urine contains water-soluble by-products of Cell (biology), cellular metabolism that are rich in nitrogen and must be clearance (medicine), cleared from the Circulatory system, bloodstream, such as urea, uric acid and creatinine. A urinalysis can detect nitrogenous wastes of the mammalian body. Urine plays an important role in the earth's nitrogen cycle. In balanced ecosystems, urine fertilizes the soil and thus helps plants to grow. Therefore, Reuse of excreta, urine can be used as a fertilizer. Some animals use it to territory (animal)#Scent marking, mark their territories. Historically, aged or fermented urine (kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolite
In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism. The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, catalytic activity of their own (usually as a cofactor to an enzyme), defense, and interactions with other organisms (e.g. pigments, odorants, and pheromones). A primary metabolite is directly involved in normal "growth", development, and reproduction. Ethylene exemplifies a primary metabolite produced large-scale by industrial microbiology. A secondary metabolite is not directly involved in those processes, but usually has an important ecological function. Examples include antibiotics and pigments such as resins and terpenes etc. Some antibiotics use primary metabolites as precursors, such as actinomycin, which is created from the primary metabolite tryptophan. Some sugars are metabolites, such as fructose or glucose, which ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting secondary sexual characteristics such as increased muscle and bone mass, and the growth of androgenic hair, body hair. It is associated with increased aggression, sex drive, Dominance hierarchy, dominance, courtship display, and a wide range of behavioral characteristics. In addition, testosterone in both sexes is involved in health and well-being, where it has a significant effect on overall mood, cognition, social and sexual behavior, metabolism and energy output, the cardiovascular system, and in the prevention of osteoporosis. Insufficient levels of testosterone in men may lead to abnormalities including frailty, accumulation of adipose fat tissue within the body, anxiety and depression, sexual performance issues, and bone loss. Excessiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Androstanediol Glucuronide
3α-Androstanediol glucuronide (3α-ADG) is a metabolite formed from human androgens; compounds involved in the development and maintenance of sexual characteristics. It is formed by the glucuronidation of dihydrotestosterone, and has been proposed as means of measuring androgenic activity. In women the adrenal steroids, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, androstenedione and dehydroepiandrosterone Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), also known as androstenolone, is an endogenous steroid hormone precursor. It is one of the most abundant circulating steroids in humans. DHEA is produced in the adrenal glands, the gonads, and the brain. It funct ... are the major precursors of plasma 3α-ADG, accounting for almost the totality of circulating 3α-ADG. Levels of 3α-ADG decrease significantly with age. 3α-ADG is used as a marker of target tissue cellular action. 3α-ADG correlates with level of 5α-reductase activity (testosterone and 3α-androstanediol to dihydrotestosterone) in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Androsterone Glucuronide
Androsterone glucuronide (ADT-G) is a major circulating and urinary metabolite of testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT). It accounts for 93% of total androgen glucuronides in women. ADT-G is formed from androsterone by UDP-glucuronosyltransferases, with the major enzymes being UGT2B15 and UGT2B17. It is a marker of acne in women while androstanediol glucuronide is a marker of hirsutism (excess hair growth) in women. Relevance in women's health Quantification of ADT-G and 3α-diol-G levels in Serum (blood) is an effective means of assessing androgen content in blood and androgenic activity in women. Androsterone glucuronide content can be estimated using Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. If an unusual level of ADT-G is observed in the blood (either an elevated or decreased amount), proper treatment plans can be developed in order to treat related symptoms. Elevated levels of androsterone glucuronide in the blood have been observed in adult females who present w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etiocholanolone Glucuronide
Etiocholanolone glucuronide (ETIO-G) is an endogenous, naturally occurring metabolite of testosterone. It is formed in the liver from etiocholanolone by UDP-glucuronyltransferases. ETIO-G has much higher water solubility than etiocholanolone and is eventually excreted in the urine via the kidneys. Along with androsterone glucuronide, it is one of the major inactive metabolites of testosterone. See also * 3α,5β-Androstanediol * 5β-Dihydrotestosterone * Androstanediol glucuronide 3α-Androstanediol glucuronide (3α-ADG) is a metabolite formed from human androgens; compounds involved in the development and maintenance of sexual characteristics. It is formed by the glucuronidation of dihydrotestosterone, and has been propos ... References External links Metabocard for Etiocholanolone Glucuronide (HMDB04484) - Human Metabolome Database Etiocholanes Glucuronide esters Human metabolites Steroid esters {{biochemistry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testosterone Sulfate
Testosterone sulfate is an endogenous, naturally occurring steroid and minor urinary metabolite of testosterone Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting se .... See also * Androstanediol glucuronide * Androsterone glucuronide * Etiocholanolone glucuronide * Testosterone glucuronide References Abandoned drugs Androstanes Human metabolites Sulfate esters Testosterone esters {{biochemistry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting secondary sexual characteristics such as increased muscle and bone mass, and the growth of androgenic hair, body hair. It is associated with increased aggression, sex drive, Dominance hierarchy, dominance, courtship display, and a wide range of behavioral characteristics. In addition, testosterone in both sexes is involved in health and well-being, where it has a significant effect on overall mood, cognition, social and sexual behavior, metabolism and energy output, the cardiovascular system, and in the prevention of osteoporosis. Insufficient levels of testosterone in men may lead to abnormalities including frailty, accumulation of adipose fat tissue within the body, anxiety and depression, sexual performance issues, and bone loss. Excessiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucuronide Esters
A glucuronide, also known as glucuronoside, is any substance produced by linking glucuronic acid to another substance via a glycosidic bond. The glucuronides belong to the glycosides. Glucuronidation, the conversion of chemical compounds to glucuronides, is a method that animals use to assist in the excretion of toxic substances, drugs or other substances that cannot be used as an energy source. Glucuronic acid is attached via a glycosidic bond to the substance, and the resulting glucuronide, which has a much higher water solubility than the original substance, is eventually excreted by the kidneys. Enzymes that cleave the glycosidic bond of a glucuronide are called glucuronidases. Classes of glucuronides Acyl glucuronide Carboxylic acids are a common functional group in many medications, such as NSAIDS, anticonvulsants, and diuretics. One common pathway for the clearance of carboxylic-acid-containing drugs is via glucuronidation. By conjugating one such drug to a glucuron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |