|
Testacella Scutulum
''Testacella scutulum'' is an air-breathing, carnivorous land slug, a terrestrial animal, terrestrial gastropod mollusk in the family Testacellidae, the shelled slugs. Like other species in the genus, this European slug eats earthworms, spends most of its life underground, and is rarely seen. Distribution This species is known to occur in a number of European countries and islands including: * List of non-marine molluscs of Great Britain, Great Britain''Testacella scutulum'' AnimalBase, accessed 22 December 2008. * List of non-marine molluscs of Ireland, Ireland * Spain * Croatia * Italy and Sicily * List of non-marine molluscs of the Canary Islands, Canary Islands * Switzerland * and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Brettingham Sowerby I
George Brettingham Sowerby I (12 August 1788 – 26 July 1854) was a British naturalist, illustrator and conchologist. Life He was the second son of James Sowerby. George was educated at home under private tutors, and afterwards assisted his father in the production of illustrated works on natural history. On the latter's death in 1822, he and his brother James De Carle Sowerby continued their father's work on fossil shells, publishing the latter parts of the ''Mineral Conchology of Great Britain''. He published about 50 papers on molluscs and started several comprehensive, illustrated books on the subject, the most important the ''Thesaurus Conchyliorum'', a work that was continued by his son, George Brettingham Sowerby II and his grandson George Brettingham Sowerby III. One of his first works was the cataloguing of the collection of the Earl of Tankerville. He also dealt in shells and natural history objects, his place of business being first in King Street, Covent Gard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnivorous
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant whose food and energy requirements derive from animal tissues (mainly muscle, fat and other soft tissues) whether through hunting or scavenging. Nomenclature Mammal order The technical term for mammals in the order Carnivora is ''carnivoran'', and they are so-named because most member species in the group have a carnivorous diet, but the similarity of the name of the order and the name of the diet causes confusion. Many but not all carnivorans are meat eaters; a few, such as the large and small cats (felidae) are ''obligate'' carnivores (see below). Other classes of carnivore are highly variable. The Ursids, for example: While the Arctic polar bear eats meat almost exclusively (more than 90% of its diet is meat), almost all other bear species are omnivorous, and one species, the giant panda, is nearly exclusively herbiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Slug
Slug, or land slug, is a common name for any apparently shell-less terrestrial gastropod mollusc. The word ''slug'' is also often used as part of the common name of any gastropod mollusc that has no shell, a very reduced shell, or only a small internal shell, particularly sea slugs and semislugs (this is in contrast to the common name ''snail'', which applies to gastropods that have a coiled shell large enough that they can fully retract their soft parts into it). Various taxonomic families of land slugs form part of several quite different evolutionary lineages, which also include snails. Thus, the various families of slugs are not closely related, despite a superficial similarity in the overall body form. The shell-less condition has arisen many times independently as an example of convergent evolution, and thus the category "slug" is polyphyletic. Taxonomy Of the six orders of Pulmonata, two – the Onchidiacea and Soleolifera – solely comprise slugs. A third family, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terrestrial Animal
Terrestrial animals are animals that live predominantly or entirely on land (e.g. cats, dogs, ants, spiders), as compared with aquatic animals, which live predominantly or entirely in the water (e.g. fish, lobsters, octopuses), and amphibians, which rely on a combination of aquatic and terrestrial habitats (e.g. frogs and newts). Some groups of insects are terrestrial, such as ants, butterflies, earwigs, cockroaches, grasshoppers and many others, while other groups are partially aquatic, such as mosquitoes and dragonflies, which pass their larval stages in water. Terrestrial animals tend to be more developed and intelligent than aquatic animals. Terrestrial classes The term "terrestrial" is typically applied to species that live primarily on the ground, in contrast to arboreal species, which live primarily in trees. There are other less common terms that apply to specific groups of terrestrial animals: * Saxicolous creatures are rock dwelling. "Saxicolous" is d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastropod
The gastropods (), commonly known as snails and slugs, belong to a large taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda (). This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, from freshwater, and from land. There are many thousands of species of sea snails and slugs, as well as freshwater snails, freshwater limpets, and land snails and slugs. The class Gastropoda contains a vast total of named species, second only to the insects in overall number. The fossil history of this class goes back to the Late Cambrian. , 721 families of gastropods are known, of which 245 are extinct and appear only in the fossil record, while 476 are currently extant with or without a fossil record. Gastropoda (previously known as univalves and sometimes spelled "Gasteropoda") are a major part of the phylum Mollusca, and are the most highly diversified class in the phylum, with 65,000 to 80,000 living snail and slug species. The anatomy, behavior, feeding, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mollusk
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000 additional species. The proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied. Molluscs are the largest marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. Numerous molluscs also live in freshwater and terrestrial habitats. They are highly diverse, not just in size and anatomical structure, but also in behaviour and habitat. The phylum is typically divided into 7 or 8 taxonomic classes, of which two are entirely extinct. Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, are among the most neurologically advanced of all invertebrates—and either the giant squid or the colossal squid is the largest known invertebrate species. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Non-marine Molluscs Of Great Britain
This list comprises 231 species of non-marine molluscs that have been recorded in the scientific literature as part of the fauna of the island of Great Britain; this total excludes species found only in hothouses and aquaria. The list includes terrestrial and aquatic gastropods, and aquatic bivalves. Molluscs that are fully marine (adapted to live in the sea) are not included here, except for two marine pulmonate snails. In other words, this list includes land snails and slugs, and freshwater and brackish water snails. It also includes freshwater mussels and clams, including some that can tolerate brackish water. Great Britain is a European island in the northeastern Atlantic, comprising the contiguous countries of England, Scotland and Wales. (Great Britain is not the same entity as the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland; for more information on the complex nomenclature of this area, please see terminology of the British Isles.) The mollusc fauna of the island ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Non-marine Molluscs Of Ireland
This list of the non-marine molluscs of Ireland comprises 165 species of non-marine molluscs which have been recorded as part of the fauna of Ireland. These are terrestrial and aquatic gastropods, and bivalves; the list does not include species of molluscs which are considered to be fully marine. In other words: this list includes land snails and slugs, and freshwater and brackish water snails. It also includes freshwater mussels and freshwater clams, including some that can tolerate brackish water. Molluscs that are fully adapted to live in the sea are not included here. Ireland is an island in the northeastern Atlantic. It consists of the Republic of Ireland, also known simply as Ireland (or in the Irish language ''Éire''), and Northern Ireland, which is part of the United Kingdom. The mollusc fauna of the island of Ireland has not been as thoroughly researched as that of the island of Great Britain, and therefore it is possible that some uncommon and local species (whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biodiversity Journal
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') level. Biodiversity is not distributed evenly on Earth; it is usually greater in the tropics as a result of the warm climate and high primary productivity in the region near the equator. Tropical forest ecosystems cover less than 10% of earth's surface and contain about 90% of the world's species. Marine biodiversity is usually higher along coasts in the Western Pacific, where sea surface temperature is highest, and in the mid-latitudinal band in all oceans. There are latitudinal gradients in species diversity. Biodiversity generally tends to cluster in hotspots, and has been increasing through time, but will be likely to slow in the future as a primary result of deforestation. It encompasses the evolutionary, ecological, and cultural process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Non-marine Molluscs Of The Canary Islands
The non-marine molluscs of the Canary Islands are a part of the molluscan fauna of the Canary Islands. A number of species of non-marine molluscs are found in the wild in Canary Islands. Freshwater gastropods Hydrobiidae * ''Pseudamnicola canariensis'' Glöer & Reuselaars, 2020 - endemic to Gran Canaria Thiaridae * '' Melanoides tuberculatus'' (O. F. Müller, 1774)Núñez Brito, L.; Núñez Fraga, J. (2010). "Mollusca". In: Arechavaleta, M.; Rodríguez, S.; Zurita, N.; García, A. (Eds.). ''Lista de especies silvestres de Canarias. Hongos, plantas y animales terrestres. 2009''. Gobierno de Canarias Lymnaeidae * '' Galba truncatula'' (O. F. Müller, 1774) - probably non-indigenous * '' Pseudosuccinea columella'' (Say, 1817) Physidae * '' Physella acuta'' (Draparnaud, 1805) - probably non-indigenous Planorbidae * ''Ancylus striatus'' Quoy & Gaimard, 1833 - endemic to the Canary Islands * ''Gyraulus clymene'' (Shuttleworth, 1852) - endemic to La Palma and Tenerife ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
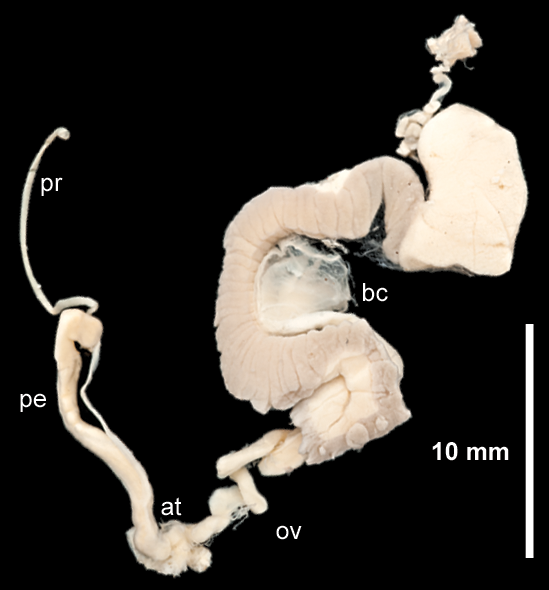
Testacella Scutulum Reproductive System
''Testacella'' is genus of small to medium-large, predatory, air-breathing, land slugs. MolluscaBase eds. (2022). MolluscaBase. Testacella Lamarck, 1801. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=818595 on 2022-09-13 They are terrestrial gastropod mollusks in the family Testacellidae, the shelled slugs. They are not often seen because they live underground. ''Testacella'' is the only genus in the family, in other words it is a monotypic family. ''Testacella'' is the type genus of the family Testacellidae. Distribution Species within this genus of slugs live in north Africa, southern and western Europe, and Britain."Family summary for Testacellidae" AnimalBase, last modified 8 August 2010, accessed 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)



