|
Temple Of Zeus (organization)
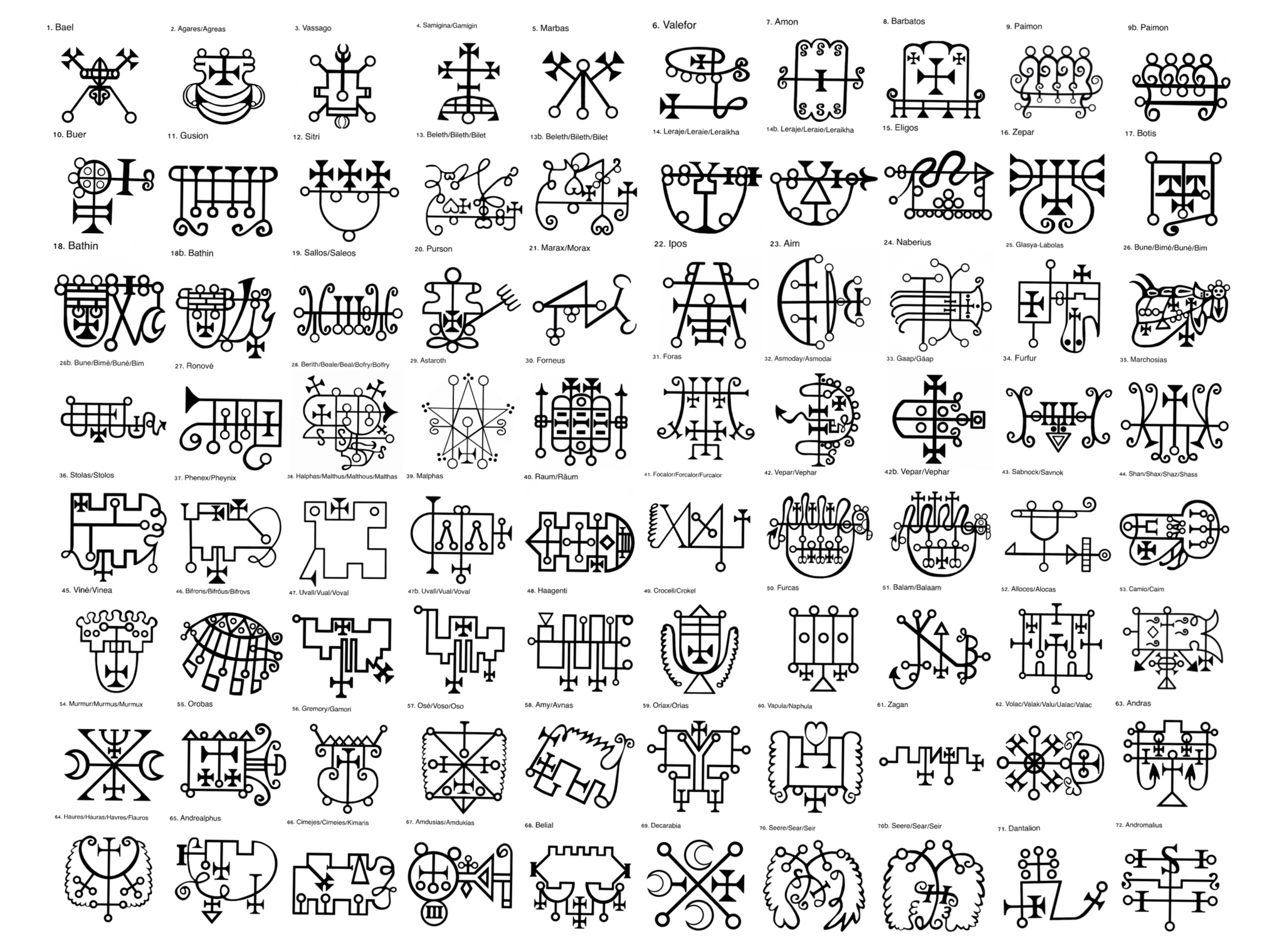
The Temple of Zeus (ToZ), originally known as the Joy of Satan Ministries, is an Occultism, occult religious organization founded in 2002 by Andrea M. Dietrich. A new religious movement and form of Western esotericism, the Temple of Zeus espouses a religion known as Zevism, whose practitioners are called Zevists, identifying itself as a form of Satanism. The Temple of Zeus advocates "Spiritual Satanism", an ideology that presents a synthesis of theistic Satanism, Occultism in Nazism, Nazi occultism, gnosticism, paganism, western esotericism, UFO conspiracy theory, UFO conspiracy theories and Extraterrestrial hypothesis, extraterrestrial beliefs. Members believe Zeus (also referred to as Satan by the organization) to be "the true father and creator God of humanity", whose desire was for his creations, humanity, to elevate themselves through knowledge and understanding. They have been the topic of significant controversy for their antisemitic beliefs and past connections to a fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temple Of Zeus (logo)
Temple of Zeus may refer to: Organization *Temple of Zeus (organization), an occult religious organization Greece * Temple of Zeus, Olympia * Temple of Olympian Zeus, Athens * Sanctuary of Zeus Polieus, Athens Italy * Temple of Olympian Zeus, Agrigento * Temple G, Selinunte Libya * Temple of Zeus, Cyrene Syria * Temple of Zeus Kyrios, Dura-Europos * Temple of Zeus Megistos, Dura-Europos * Temple of Zeus Theos, Dura-Europos * Temple of Zeus Hypsistos, Al-Dumayr {{disambiguation Temples of Zeus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Esotericism
Western esotericism, also known as the Western mystery tradition, is a wide range of loosely related ideas and movements that developed within Western society. These ideas and currents are united since they are largely distinct both from orthodox Judeo-Christian, Judeo-Christian religion and Age of Enlightenment rationalism. It has influenced, or contributed to, various forms of Western philosophy, mysticism, Western religions, religion, science, pseudoscience, Western art history, art, Western literature, literature, and Western culture#Music, music. The idea of grouping a wide range of Western traditions and philosophies together under the term ''esotericism'' developed in 17th-century Europe. Various academics have debated numerous definitions of Western esotericism. One view adopts a definition from certain esotericist schools of thought themselves, treating "esotericism" as a perennial philosophy, perennial hidden inner tradition. A second perspective sees esotericism as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melek Taus
Melek may refer to: People Given name * Melek Sina Baydur (born 1948), Turkish retired diplomat and former Ambassador of Turkey * Melek Bilge (born 1989), Turkish professional female basketball player * Melek Hu (born 1989), Chinese-born Turkish table tennis player * Melek Mosso (born 1988), Turkish singer * Melek Taus, a central figure of the Yazidi religion * Melek Tourhan (1869–1956), Queen consort of Egypt Surname * Abdurrahman Melek (1896–1978), prime minister of the Republic of Hatay Epithet * Melek Ahmed Pasha (1604–1662), Ottoman grand vizier Other uses * ''Melek'' (album), an album by Candan Erçetin * Melek, Nitra District, village in the Nitra District, Slovakia See also * Malak (other) {{disambiguation, given name, surname Arabic-language feminine given names Feminine given names Turkish feminine given names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enki
Enki ( ) is the Sumerian god of water, knowledge ('' gestú''), crafts (''gašam''), and creation (''nudimmud''), and one of the Anunnaki. He was later known as Ea () or Ae p. 324, note 27. in Akkadian (Assyrian-Babylonian) religion, and is identified by some scholars with Ia in Canaanite religion. The name was rendered Aos within Greek sources (e.g. Damascius). He was originally the patron god of the city of Eridu, but later the influence of his cult spread throughout Mesopotamia and to the Canaanites, Hittites and Hurrians. He was associated with the southern band of constellations called ''stars of Ea'', but also with the constellation AŠ-IKU, ''the Field'' ( Square of Pegasus). Beginning around the second millennium BCE, he was sometimes referred to in writing by the numeric ideogram for "40", occasionally referred to as his "sacred number". The planet Mercury, associated with Babylonian '' Nabu'' (the son of Marduk) was, in Sumerian times, identified with En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumerian Religion
Sumerian religion was the religion practiced by the people of Sumer, the first literate civilization found in recorded history and based in ancient Mesopotamia, and what is modern day Iraq. The Sumerians widely regarded their divinities as responsible for all matters pertaining to the natural and social orders of their society. Overview Before the beginning of kingship in Sumer, the city-states were effectively ruled by theocratic priests and religious officials. Later, this role was supplanted by kings, but priests continued to exert great influence on Sumerian society. In early times, Sumerian temples were simple, one-room structures, sometimes built on elevated platforms. Towards the end of Sumerian civilization, these temples developed into ziggurats—tall, pyramidal structures with sanctuaries at the tops. The Sumerians believed that the universe had come into being through a series of cosmic births such as gods. First, Nammu, the primeval waters, gave birth to Ki ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deity
A deity or god is a supernatural being considered to be sacred and worthy of worship due to having authority over some aspect of the universe and/or life. The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' defines ''deity'' as a God (male deity), god or goddess, or anything revered as divine. C. Scott Littleton defines a deity as "a being with powers greater than those of ordinary humans, but who interacts with humans, positively or negatively, in ways that carry humans to new Higher consciousness, levels of consciousness, beyond the grounded preoccupations of ordinary life". Religions can be categorized by how many deities they worship. Monotheism, Monotheistic religions accept only one deity (predominantly referred to as "God"), whereas Polytheism, polytheistic religions accept multiple deities. Henotheism, Henotheistic religions accept one God, supreme deity without denying other deities, considering them as aspects of the same divine principle. Nontheistic religions deny any supreme eter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satan Summoning His Legions, 1796-1797 By Sir Thomas Lawrence
Satan, also known as the Devil, is a devilish entity in Abrahamic religions who seduces humans into sin (or falsehood). In Judaism, Satan is seen as an agent subservient to God, typically regarded as a metaphor for the ''yetzer hara'', or 'evil inclination'. In Christianity and Islam, he is usually seen as a fallen angel or jinn who has rebelled against God, who nevertheless allows him temporary power over the fallen world and a host of demons. In the Quran, Iblis (Shaitan), the leader of the devils (''shayāṭīn''), is made of fire and was cast out of Heaven because he refused to bow before the newly created Adam. He incites humans to sin by infecting their minds with ''waswās'' ('evil suggestions'). A figure known as ''ha-satan'' ("the satan") first appears in the Hebrew Bible as a heavenly prosecutor, subordinate to Yahweh (God); he prosecutes the nation of Judah in the heavenly court and tests the loyalty of Yahweh's followers. During the intertestamental period, possi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christopher Partridge
Christopher Hugh Partridge (born 1961) is an author, editor, professor at Lancaster University, and founding Co-director of the Centre for the Study of Religion and Popular Culture. According to Gordon Lynch, Partridge is a leading scholar of topics in popular culture. Major works *''The Encyclopedia of New Religions: New Religious Movements, Sects and Alternative Spiritualities'' (Lion Hudson Plc, 2006) *''The Lure of the Dark Side: Satan & Western Demonology in Popular Culture'' (Equinox Publishing Ltd, SW11, 2008) *''The Re-Enchantment of the West: Alternative Spiritualities, Sacralization, Popular Culture and Occulture'', Vol I and Vol II, (T. & T. Clark Publishers, 2006)Jennifer Walters, "Review of ''THE RE-ENCHANTMENT OF THE WEST Volume One: Alternative Spiritualities, Sacralization, Popular Culture and Occulture''," ''TLS'' 5341 (8/12/2005): 29–29. *''Dub in Babylon: The Emergence and Influence of Dub Reggae in Jamaica and Britain from King Tubby to Post-punk'' (Equinox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LaVeyan Satanism
LaVeyan Satanism is the name given to the form of Satanism promoted by American occultist and author Anton LaVey (1930–1997). LaVey founded the Church of Satan (CoS) in 1966 in San Francisco. Although LaVey is thought to have had more influence with his Satanic aesthetics of "colourful" rites and "scandalous" clothes that created a "gigantic media circus", he also promoted his ideas in writings, such as the popular ''Satanic Bible''. LaVeyan Satanism has been classified as a new religious movement and a form of Western esotericism by scholars of religion. LaVey's ideas have been said to weave together an array of sometimes "contradictory" Laycock, ''Satanism'', 1981: section 4 The Church of Satan. LaVey’s Satanism "thinkers and tropes", combining "humanism, hedonism, aspects of pop psychology and the human potential movement", along with "a lot of showmanship", Laycock, ''Satanism'', 1981: section 4 The Church of Satan. His ideas were heavily influenced by the ideas and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Socialist Movement (United States)
The National Socialist Movement (NSM or NSM88) is a Neo-Nazi organization and political party based in the United States. Once considered to be the largest and most prominent Neo-Nazi organization in the United States, since the late 2010s its membership and prominence have plummeted. It was a part of the Nationalist Front and it is classified as a hate group by the Southern Poverty Law Center. The NSM is described by the Anti-Defamation League as "one of the more explicitly neo-Nazi groups in the United States." It seeks the transformation of the United States into a white ethnostate from which Jews, non-Whites, and members of the LGBTQ community would be expelled and barred from citizenship. History Early history The National Socialist Movement was founded in 1974 in St. Paul, Minnesota, by Robert Brannen and Clifford "Cliff" Herrington. Originally known as the "National Socialist American Workers Freedom Movement", it was one of several groups that split off from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satan
Satan, also known as the Devil, is a devilish entity in Abrahamic religions who seduces humans into sin (or falsehood). In Judaism, Satan is seen as an agent subservient to God, typically regarded as a metaphor for the '' yetzer hara'', or 'evil inclination'. In Christianity and Islam, he is usually seen as a fallen angel or jinn who has rebelled against God, who nevertheless allows him temporary power over the fallen world and a host of demons. In the Quran, Iblis (Shaitan), the leader of the devils (''shayāṭīn''), is made of fire and was cast out of Heaven because he refused to bow before the newly created Adam. He incites humans to sin by infecting their minds with ''waswās'' ('evil suggestions'). A figure known as ''ha-satan'' ("the satan") first appears in the Hebrew Bible as a heavenly prosecutor, subordinate to Yahweh (God); he prosecutes the nation of Judah in the heavenly court and tests the loyalty of Yahweh's followers. During the intertestamental period, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |