|
Te Wera Hauraki
Te Wera Hauraki (?–1839) a '' rangatira'' (chieftain) of the Ngāti Hineira and Te Uri Taniwha hapū of the Ngāpuhi iwi from the Northland region of New Zealand. From about 1818 to 1821, Te Wera went on expeditions and fought battles in the Bay of Plenty and the East Coast. In 1823, he was one of the leaders of the Ngāpuhi attack which defeated Te Arawa at Mokoia island on Lake Rotorua. Following the attack, Te Wera and his wife, Te Ao-kapurangi, negotiated a peace that prevented Ngāpuhi from taking further action against Te Arawa. After the conclusion of peace, he continued east and settled at Māhia Peninsula in Hawke's Bay, where he allied with Te Whareumu of Ngāti Rakaipaaka and Ngāti Hikairo and Te Pareihe of Ngāti Te Whatuiāpiti, helping them to fight off incursions from other tribes, especially Ngāti Te Ūpokoiri and Ngāti Raukawa. He remained at Māhia until his death in 1839. Early life Hauraki was the son of Kaiteke or Kaitara, a leader of Ngāti Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rangatira
In Māori culture, () are tribal chiefs, the hereditary Māori leaders of a hapū. Ideally, rangatira were people of great practical wisdom who held authority () on behalf of the tribe and maintained boundaries between a tribe's land and that of other tribes. Changes to land ownership laws in the 19th century, particularly the individualisation of land title, undermined the power of rangatira, as did the widespread loss of land under the colonial government. The concept of rangatira and rangatiratanga, however, remain strong, and a return to rangatiratanga and the uplifting of Māori by the system has been widely advocated for since the Māori renaissance. Moana Jackson, Ranginui Walker, Tipene O'Regan are among the most famous of these advocates. The concept of a rangatira is central to —a Māori system of governance, self-determination and sovereignty—based on the essential leadership of all peoples through direct democracy. Etymology The word means "chief (male ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mokoia Island
__NOTOC__ Mokoia Island is located in Lake Rotorua in New Zealand. It has an area of 1.35 square kilometres. The uninhabited island is a rhyolite lava dome, rising to 180 metres above the lake surface. It was formed after the Rotorua caldera collapsed and rhyolitic magma was pushed through the cracks. One of the cracks was below where Mokoia island is today. The foreshores of the island have geothermal springs with hot spring water forming the Hinemoa pool, known to locals as Waikimihia. It also has very rich volcanic soil, which was why the local Māori grew kūmara on it. The stone statue of Matuatonga on the island protected the island's kūmara crop, and tohunga would bring seed kūmara to touch the statue. It was also a very good strategic location, which was why it was often fought over. Mokoia Island is privately owned by local Māori iwi, who run it in conjunction with the New Zealand Department of Conservation. It is a bird sanctuary and access is limited to tour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pongakawa
Pongakawa is a rural community in the Bay of Plenty of New Zealand's North Island. runs through it. The local Tokerau Marae and Pikiao meeting house are a traditional meeting ground of the Ngāti Pikiao tribe. The name of the settlement comes from Māori terms meaning "Bitter ferns". Reed, A.W. (1975). ''Place names of New Zealand''. Wellington: A.H. & A.W. Reed. p. 333. Demographics Pongakawa statistical area, which also includes Paengaroa, covers and had an estimated population of as of with a population density of people per km2. Pongakawa had a population of 3,081 at the 2018 New Zealand census, an increase of 408 people (15.3%) since the 2013 census, and an increase of 381 people (14.1%) since the 2006 census. There were 1,080 households, comprising 1,602 males and 1,476 females, giving a sex ratio of 1.09 males per female. The median age was 36.7 years (compared with 37.4 years nationally), with 741 people (24.1%) aged under 15 years, 522 (16.9%) aged 15 to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tauranga
Tauranga () is a coastal city in the Bay of Plenty region and the fifth most populous city of New Zealand, with an urban population of , or roughly 3% of the national population. It was settled by Māori late in the 13th century, colonised by Europeans in the early 19th century, and was constituted as a city in 1963. The city lies in the north-western corner of the Bay of Plenty, on the south-eastern edge of Tauranga Harbour. The city extends over an area of , and encompasses the communities of Bethlehem, on the south-western outskirts of the city; Greerton, on the southern outskirts of the city; Matua, west of the central city overlooking Tauranga Harbour; Maungatapu; Mount Maunganui, located north of the central city across the harbour facing the Bay of Plenty; Otūmoetai; Papamoa, Tauranga's largest suburb, located on the Bay of Plenty; Tauranga City; Tauranga South; and Welcome Bay. Tauranga is one of New Zealand's main centres for business, international trade, cult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waipaoa
''Waipaoa'' is a genus of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Cancellariidae Cancellariidae, common name the nutmeg snails or nutmeg shells, are a family of small to medium-large sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the clade Neogastropoda. Some of the shells of the species in this family resemble a nutmeg seed. Di ..., the nutmeg snails. Species Species within the genus ''Waipaoa'' include: * '' Waipaoa marwicki'' Dell, 1956 References Cancellariidae Monotypic gastropod genera {{Cancellariidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Te Teko
Te Teko is a small inland town along the banks of the Rangitaiki River in the Bay of Plenty region of New Zealand's North Island. The township includes a racecourse, golf course, police station, and a primary school. The primary school was established in 1881. Te Hoko is in the ''rohe'' (tribal area) of the Ngāti Awa iwi. History and culture History In the mid-1860s, Te Teko was the site of a significant siege on a Māori pā as part of the East Cape War. After peace came to the region, a hotel was established on the banks of the Rangitaiki River in 1879 and Te Teko rose in importance as a boat service was established to ferry hotel customers and travellers across the river. A bridge made the boat service redundant in 1915. Marae Te Teko has several marae, which are meeting grounds for Ngāti Awa hapū: * Kokohinau or Tuhimata Marae and O Ruataupare meeting house are affiliated with Te Pahipoto. * Te Māpou Marae and Rongotangiawa meeting house are affiliated with Ngāt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerikeri
Kerikeri () is the largest town in Northland, New Zealand. It is a tourist destination north of Auckland and north of the northern region's largest city, Whangarei. It is sometimes called the Cradle of the Nation, as it was the site of the first permanent mission station in the country, and it has some of the most historic buildings in the country. A rapidly expanding centre of subtropical and allied horticulture, Kerikeri is in the Far North District of the North Island and lies at the western extremity of the Kerikeri Inlet, a northwestern arm of the Bay of Islands, where fresh water of the Kerikeri River enters the Pacific Ocean. The village was established by New Zealand's pioneering missionaries, who called it Gloucester Town, but the name did not endure. The Māori word ''Kerikeri'' was interpreted by said missionaries as Keddi Keddi or Kiddeekiddee, before the romanisation methods they used were revised to what is used today. In 1814, Samuel Marsden acqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
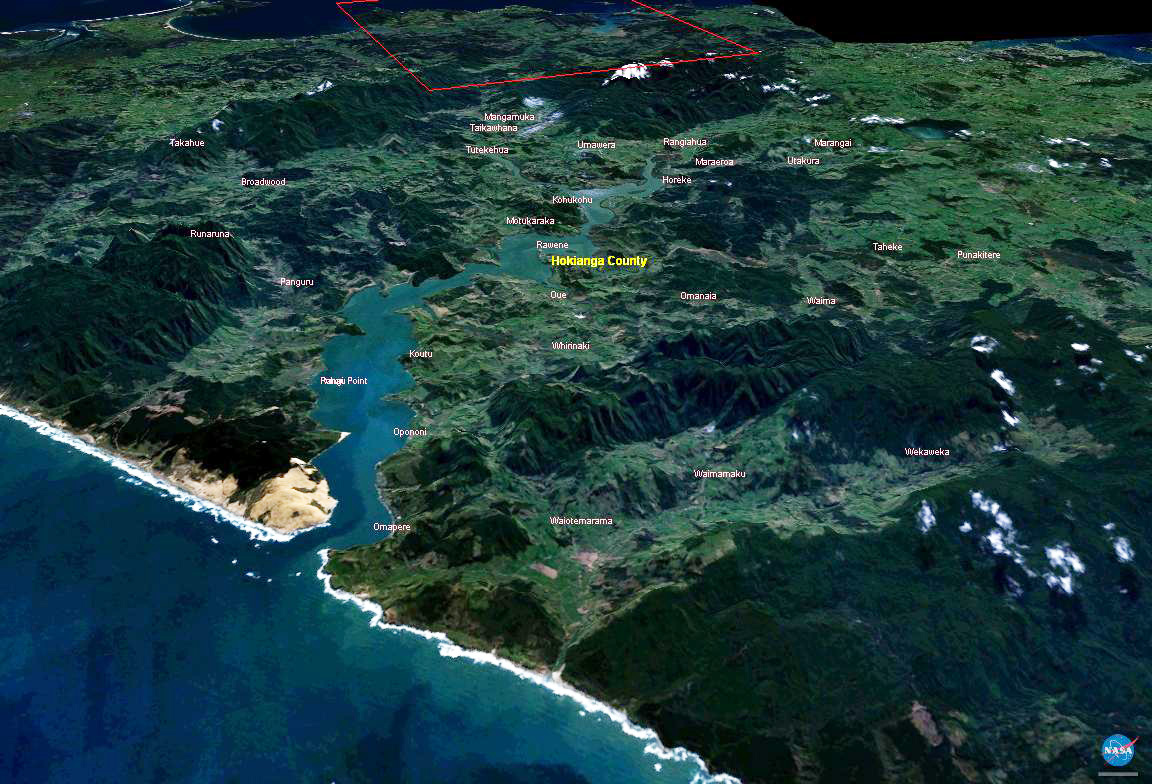
Hokianga
The Hokianga is an area surrounding the Hokianga Harbour, also known as the Hokianga River, a long estuarine drowned valley on the west coast in the north of the North Island of New Zealand. The original name, still used by local Māori, is ''Te Kohanga o Te Tai Tokerau'' ("the nest of the northern people") or ''Te Puna o Te Ao Marama'' ("the wellspring of moonlight"). The full name of the harbour is Te Hokianga-nui-a-Kupe — "the place of Kupe's great return". Geography The Hokianga is in the Far North District, which is in the Northland Region. The area is northwest of Whangarei—and west of Kaikohe—by road. The estuary extends inland for from the Tasman Sea. It is navigable for small craft for much of its length, although there is a bar across the mouth. In its upper reaches the Rangiora Narrows separate the mouths of the Waihou and Mangamuka Rivers from the lower parts of the harbour. 12,000 years ago, the Hokianga was a river valley flanked by steep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whangaroa
Whangaroa is a settlement on Whangaroa Harbour in the Far North District of New Zealand. It is 8 km north-west of Kaeo and 35 km north-west of Kerikeri. The harbour is almost landlocked and is popular both as a fishing spot in its own right and as a base for deep-sea fishing. History The harbour was the scene of one of the most notorious incidents in early New Zealand history, the Boyd massacre. In December 1809 almost all the crew and 70 passengers were killed as ''utu'' (revenge) for the mistreatment of Te Ara, the son of a Ngāti Uru chief, who had been in the crew of the ship. Several days later the ship was burnt out after gunpowder was accidentally ignited. Relics of the ''Boyd'' are now in a local museum. On 16 July 1824 on a voyage to Sydney from Tahiti, the crew and passengers of the colonial schooner ''Endeavour'' (Capt John Dibbs) stopped in Whangaroa Harbour. An altercation with the local Māori Ngāti Pou hapū (subtribe) of the Ngā Puhi iwi resulte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |