|
Taric Code
The TARIC code (TARif Intégré Communautaire; Integrated Tariff of the European Communities) is designed to show the various rules applying to specific products when imported into the EU. This includes the provisions of the harmonised system and the combined nomenclature but also additional provisions specified in Community legislation such as tariff suspensions, tariff quotas and tariff preferences, which exist for the majority of the Community’s trading partners. In trade with third countries, the 10-digit Taric code must be used in customs and statistical declarations. Challenges in classification for companies A proper classification can save huge amount of money for the company, which is why nowadays importers and exporters strive to find a perfect way to solve those problems: * Variety of products Companies who do import and export meet challenges of how to classify products with the growing varieties of products. Classification and restrictions, to some extent, has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated population of over 449million as of 2024. The EU is often described as a ''sui generis'' political entity combining characteristics of both a federation and a confederation. Containing 5.5% of the world population in 2023, EU member states generated a nominal gross domestic product (GDP) of around €17.935 trillion in 2024, accounting for approximately one sixth of global economic output. Its cornerstone, the European Union Customs Union, Customs Union, paved the way to establishing European Single Market, an internal single market based on standardised European Union law, legal framework and legislation that applies in all member states in those matters, and only those matters, where the states ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmonized System
The Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System, also known as the Harmonized System (HS) of tariff nomenclature is an internationally standardized system of names and numbers to classify traded products. It came into effect in 1988 and has since been developed and maintained by the World Customs Organization (WCO) (formerly the Customs Co-operation Council), an independent intergovernmental organization based in Brussels, Belgium. It is used by over 200 WCO member countries and economies as a basis for their Customs tariffs and for the collection of international trade statistics as well as many other purposes. Structure The HS is organized logically by economic activity or component material. For example, animals and animal products are found in one section of the HS, while machinery and mechanical appliances are found in another. The HS is organized into 21 Sections, which are subdivided into 96 Chapters (Chapters 1 to 97 with Chapter 77 reserved for potential future u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combined Nomenclature
Council Regulation (EEC) No 2658/87 of 23 July 1987, creates the goods nomenclature called the Combined Nomenclature, or in abbreviated form 'CN', established to meet, at one and the same time, the requirements both of the Common Customs Tariff and of the external trade statistics of the European Union. It is closely related to the Harmonized Tariff Schedule of the United States. These categories are based on the international Harmonized System, the global system of nomenclature that is used to describe most world trade in goods, maintained by the World Customs Organization (WCO). Virtually all countries base their tariff schedules on the WCO's Harmonized System. Synopsis The codes and the descriptions of goods established on the basis of the combined nomenclature shall replace those established on the basis of the nomenclatures of the Common Customs Tariff and the Nimexe. It is established on the basis of the Harmonized System. The combined nomenclature shall comprise : (a) the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
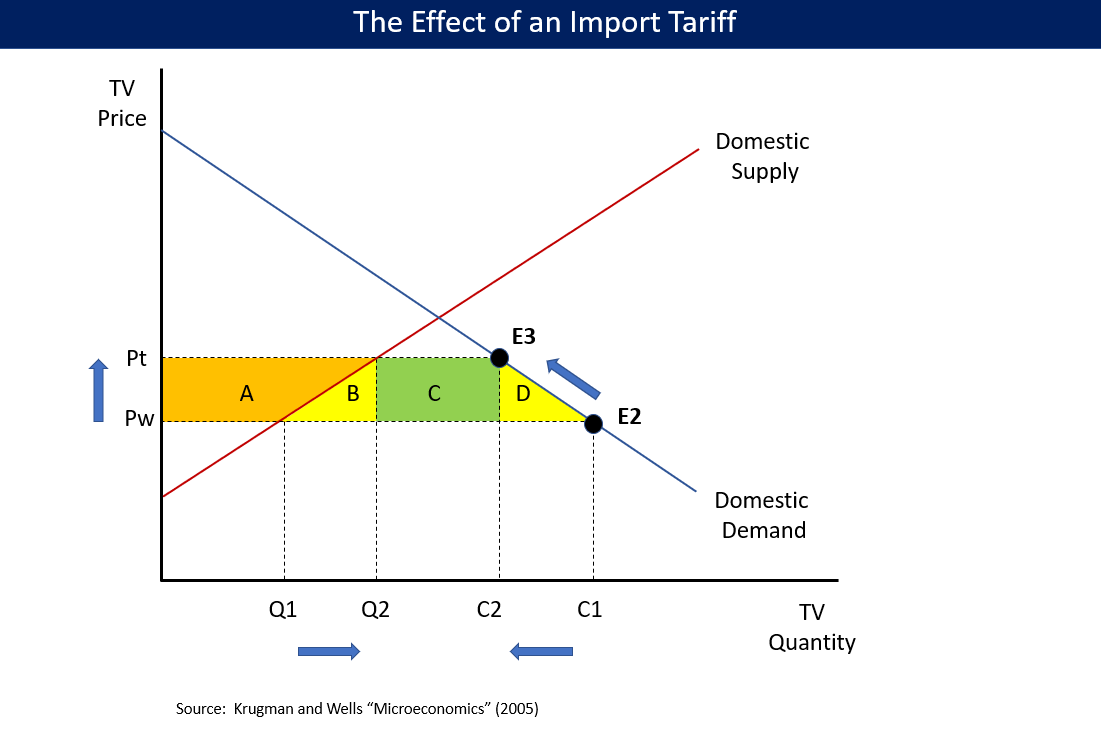
Tariff Suspensions
A tariff or import tax is a duty (tax), duty imposed by a national Government, government, customs territory, or supranational union on imports of goods and is paid by the importer. Exceptionally, an export tax may be levied on exports of goods or raw materials and is paid by the exporter. Besides being a source of revenue, import duties can also be a form of regulation of International trade, foreign trade and policy that burden foreign products to encourage or safeguard domestic industry. Protective tariffs are among the most widely used instruments of protectionism, along with import quotas and export quotas and other non-tariff barriers to trade. Tariffs can be fixed (a constant sum per unit of imported goods or a percentage of the price) or variable (the amount varies according to the price). Tariffs on imports are designed to raise the price of imported goods to discourage consumption. The intention is for citizens to buy local products instead, which, according to support ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tariff Quotas
A tariff or import tax is a duty imposed by a national government, customs territory, or supranational union on imports of goods and is paid by the importer. Exceptionally, an export tax may be levied on exports of goods or raw materials and is paid by the exporter. Besides being a source of revenue, import duties can also be a form of regulation of foreign trade and policy that burden foreign products to encourage or safeguard domestic industry. Protective tariffs are among the most widely used instruments of protectionism, along with import quotas and export quotas and other non-tariff barriers to trade. Tariffs can be fixed (a constant sum per unit of imported goods or a percentage of the price) or variable (the amount varies according to the price). Tariffs on imports are designed to raise the price of imported goods to discourage consumption. The intention is for citizens to buy local products instead, which, according to supporters, would stimulate their country's economy. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Customs
Customs is an authority or Government agency, agency in a country responsible for collecting tariffs and for controlling International trade, the flow of goods, including animals, transports, personal effects, and hazardous items, into and out of a country. Traditionally, customs has been considered as the fiscal subject that charges customs duties (i.e. tariffs) and other taxes on import and export. In recent decades, the views on the functions of customs have considerably expanded and now covers three basic issues: taxation, National security, security, and trade facilitation. Each country has its own laws and regulations for the import and export of goods into and out of a country, enforced by their respective customs authorities; the import/export of some goods may be restricted or forbidden entirely. A wide range of penalties are faced by those who break these laws. Overview Taxation The traditional function of customs has been the assessment and collection of custo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Export Administration Regulations
The Export Administration Regulations (EAR) are a set of United States export guidelines and prohibitions. They are administered by the Bureau of Industry and Security, which regulates the export restrictions of sensitive goods. The EAR apply to most U.S. origin items, foreign-produced items that incorporate controlled U.S. items, and certain "foreign-produced direct products" of U.S. items or technology, (e.g., foreign-made integrated circuits designed with U.S. electronic design automation software or manufactured with U.S.-made manufacturing equipment). In general, there are three types of controls applied by the EAR: # Technology controls: These are controls based on the item being exported, these are usually listed on the Commerce Control List. # End-user controls: These are controls based on the ultimate end user, many of these end users are listed on the Entity List. # End-use controls: These are controls based on the ultimate end use of the control. Classificatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
600px-TARIC Code Structure
6 (six) is the natural number following 5 and preceding 7. It is a composite number and the smallest perfect number. In mathematics A six-sided polygon is a hexagon, one of the three regular polygons capable of tiling the plane. A hexagon also has 6 edges as well as 6 internal and external angles. 6 is the second smallest composite number. It is also the first number that is the sum of its proper divisors, making it the smallest perfect number. It is also the only perfect number that doesn't have a digital root of 1. 6 is the first unitary perfect number, since it is the sum of its positive proper unitary divisors, without including itself. Only five such numbers are known to exist. 6 is the largest of the four all-Harshad numbers. 6 is the 2nd superior highly composite number, the 2nd colossally abundant number, the 3rd triangular number, the 4th highly composite number, a pronic number, a congruent number, a harmonic divisor number, and a semiprime. 6 is also the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Added Sugar
Added sugars or free sugars are sugar carbohydrates (caloric sweeteners) added to food and beverages at some point before their consumption. These include added carbohydrates ( monosaccharides and disaccharides), and more broadly, sugars naturally present in honey, syrup, fruit juices and fruit juice concentrates. They can take multiple chemical forms, including sucrose (table sugar), glucose (dextrose), and fructose. Medical consensus holds that added sugars contribute little nutritional value to food, leading to a colloquial description as " empty calories". Overconsumption of sugar is correlated with excessive calorie intake and increased risk of weight gain and various diseases. Individuals who consume 17–21% of their daily calories from added sugar are reported to have a 38% higher risk of dying from cardiovascular disease compared to those who consume 8% of their daily calories from added sugar. Uses United States In the United States, added sugars may include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverted Sugar Syrup
Inverted sugar syrup is a syrup mixture of the monosaccharides glucose and fructose, made by splitting disaccharide sucrose. This mixture's optical rotation is opposite to that of the original sugar, which is why it is called an ''invert'' sugar. Splitting is completed through hydrolytic saccharification. It is 1.3x sweetness, sweeter than table sugar, and foods that contain invert sugar retain moisture better and crystallize less easily than those that use table sugar instead. Bakers, who call it invert syrup, may use it more than other sweeteners. Other names include invert sugar, simple syrup, sugar syrup, sugar water, bar syrup, and sucrose inversion. Production Additives Commercially prepared enzyme-catalyzed solutions are inverted at . The optimum pH for inversion is 5.0. Invertase is added at a rate of about 0.15% of the syrup's weight, and inversion time will be about 8 hours. When completed the syrup temperature is raised to inactivate the invertase, but the syrup i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-fructose Corn Syrup
High-fructose corn syrup (HFCS), also known as glucose–fructose, isoglucose, and glucose–fructose syrup, is a sweetener made from corn starch. As in the production of conventional corn syrup, the starch is broken down into glucose by enzymes. To make HFCS, the corn syrup is further processed by D-xylose isomerase to convert some of its glucose into fructose. HFCS was first marketed in the early 1970s by the Clinton Corn Processing Company, together with the Japanese Agency of Industrial Science and Technology, where the enzyme was discovered in 1965. As a sweetener, HFCS is often compared to granulated sugar, but manufacturing advantages of HFCS over sugar include that it is cheaper. "HFCS 42" and "HFCS 55" refer to dry weight fructose compositions of 42% and 55% respectively, the rest being glucose. HFCS 42 is mainly used for processed foods and breakfast cereals, whereas HFCS 55 is used mostly for production of soft drinks. The United States Food and Drug Administr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |