|
Tanks In France
French development into tanks began during World War I as an effort to overcome the stalemate of trench warfare, and largely at the initiative of the manufacturers. The Schneider CA1 was the first tank produced by France, and 400 units were built. The French also experimented with various tank designs, such as the Frot-Laffly landship, Boirault machine and Souain experiment. Another 400 Saint-Chamond tanks were manufactured from April 1917 to July 1918 but they were underpowered and were of limited utility because the caterpillar tracks were too short for the tank's length and weight. The most significant French tank development during the war was the Renault FT light tank, which set the general layout for future tank designs and was used or redesigned by various military forces, including those of the United States. History World War I While the British began the design and use of tanks in World War I, France at the same time developed its own tracked AFVs, but the situati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Armoured Fighting Vehicle Production During World War II
This is a list of French combat vehicle production before and during the Second World War. The numbers given are generally those of vehicles actually delivered including exported vehicles. However, it includes those vehicles not yet delivered in June 1940 in the 1940 totals. For the Renault FT only the French metropolitan organic strength and matériel reserve is given. The list excludes those types having been taken out of service by May 1940. Tank production The following points should be taken into consideration: *The total export number of modern tanks was 281. The total tank assets in France and its colonies were therefore perhaps less than 5802 during the time of the German offensive. *Of the R 35 245 vehicles were exported; the production numbers of this type for June 1940 are unknown but amount probably to about 91 tanks. The number given is that of the R 35's known to be produced from photographic evidence of the series numbers. During a hearing in 1947 a total productio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
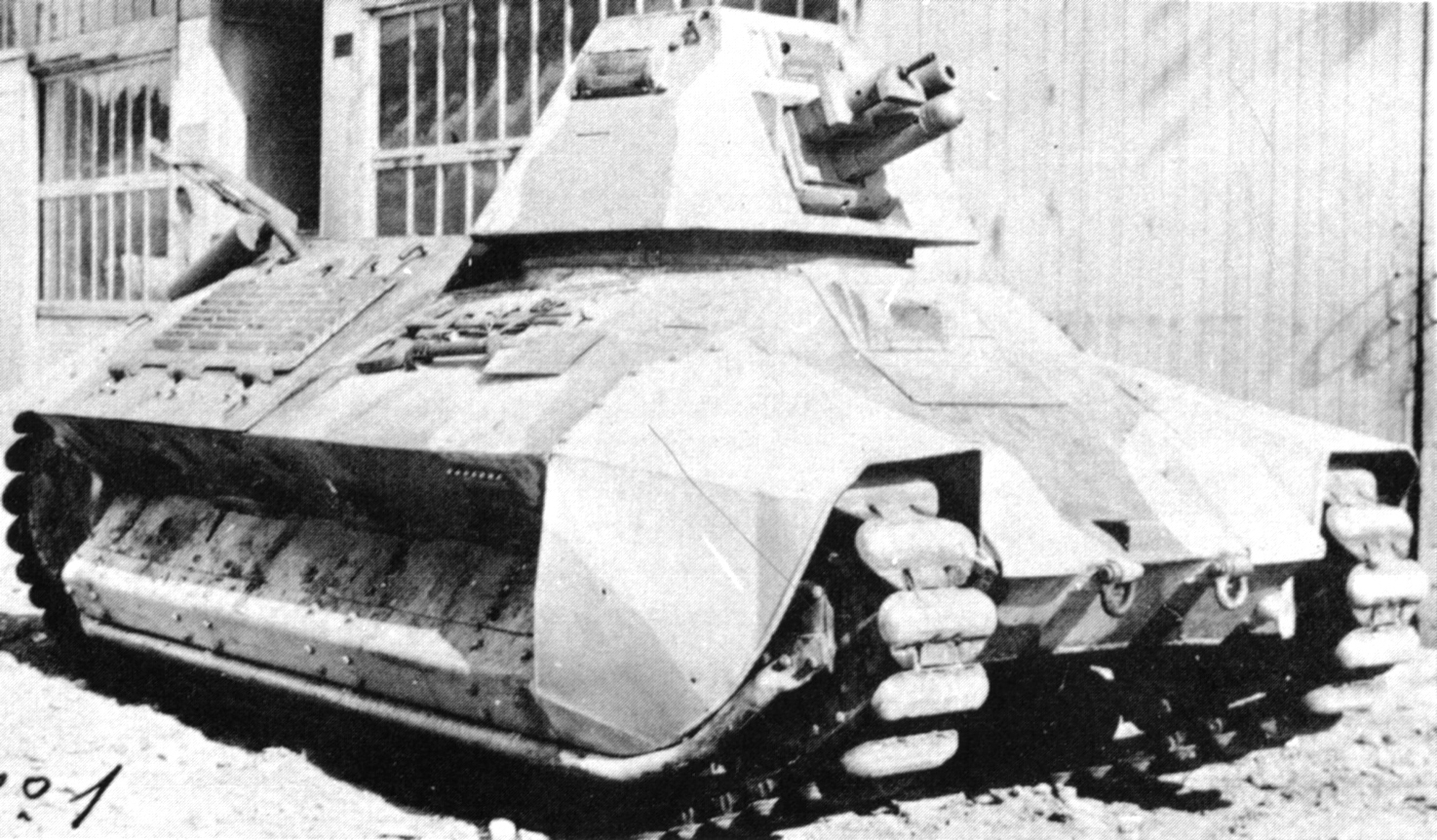
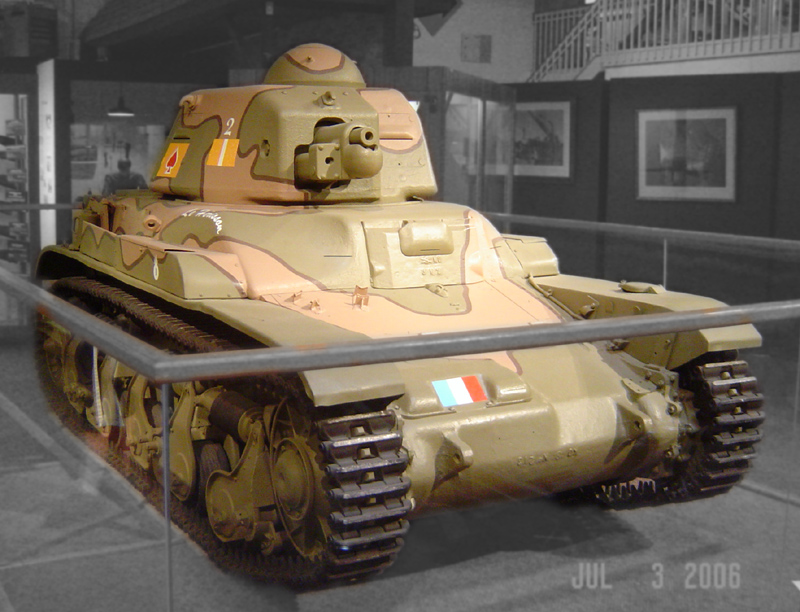
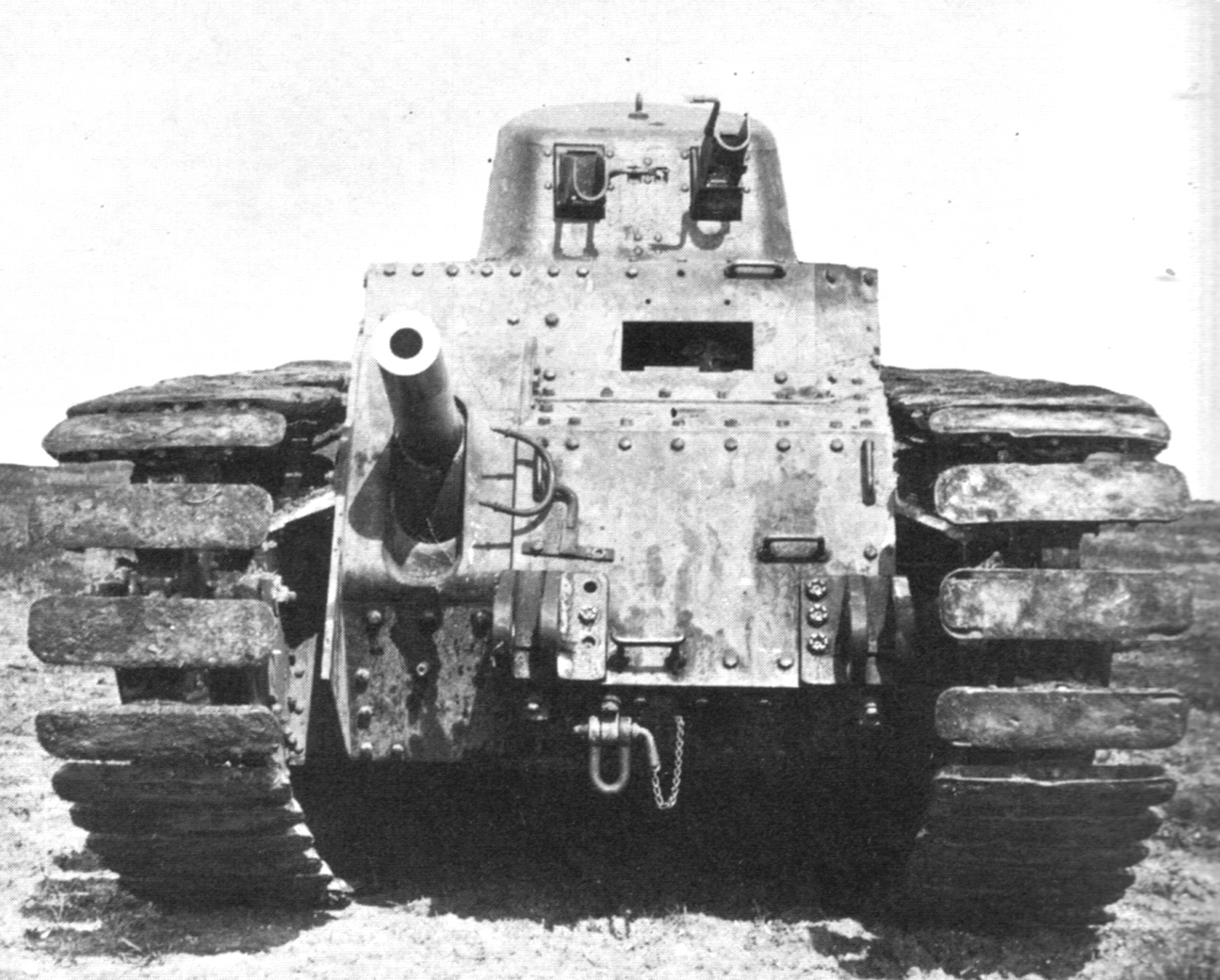
AMC 35
The AMC 35 (from ''Automitrailleuse de Combat Renault modèle 1935''), also known under a manufacturer's designation Renault ACG-1, was a French medium cavalry tank of the later Interwar era that served in the Second World War. It was developed as a result of the change of the specification that had led to the design of the AMC 34, calling for a vehicle that was not only well-armed and mobile but also well-armoured. Due to technological and financial problems production was delayed and limited. The AMC 35 was one of the few French tanks of the period featuring a two-man turret. Development Renault had developed the AMC 34 according to the specifications of the Plan 1931. On 26 June 1934 these were changed: it was now demanded that the vehicle attain a maximum speed of and be immune to anti-tank guns. On 7 March 1936 a changed prototype was delivered by Renault, who requested that the vehicle would be accepted if it met the new specifications; after all the AMC 34 had already b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
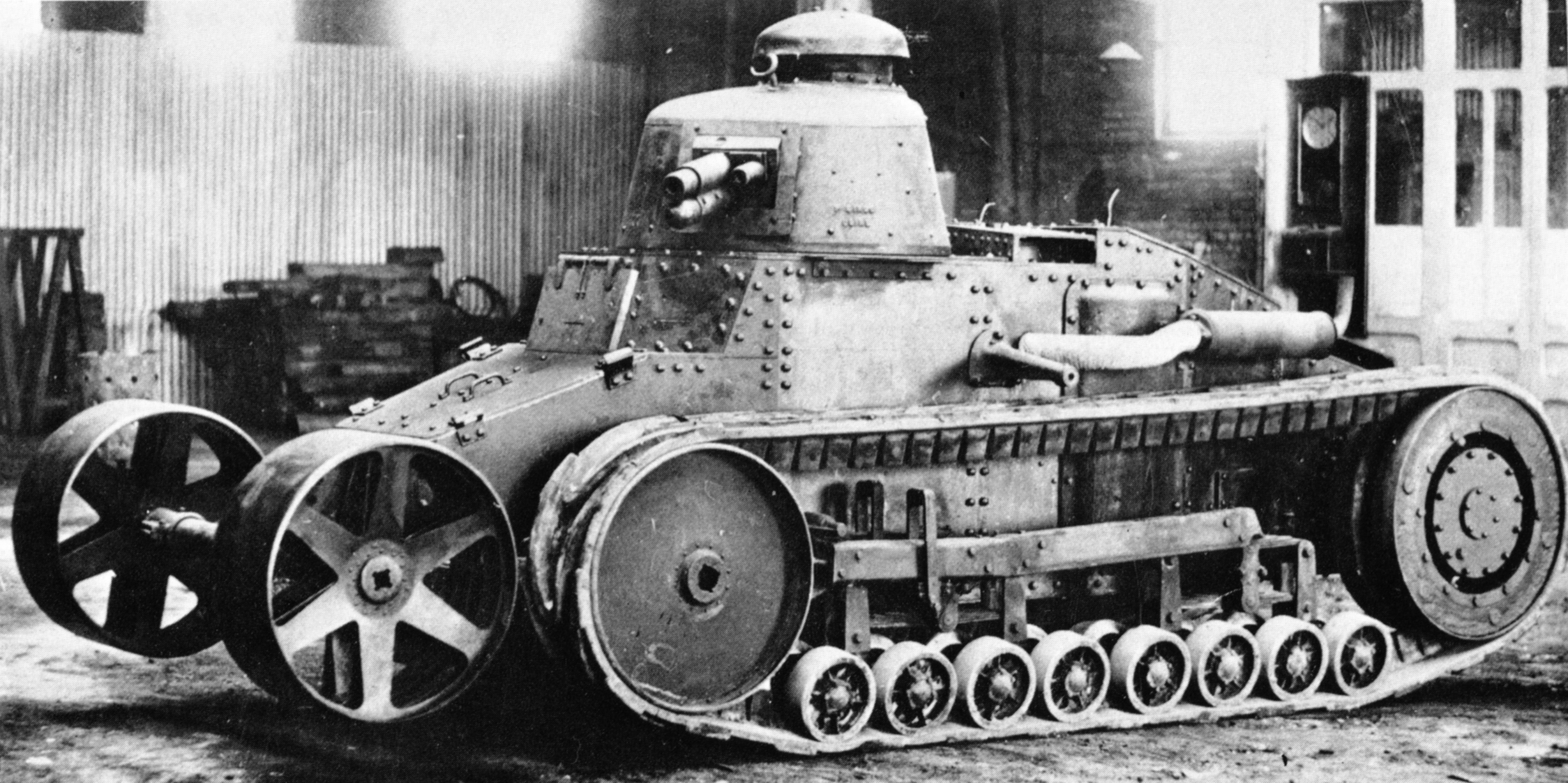
AMC 34
The AMC 34 was a French tank originally built for the French Army's cavalry units. Its production was cut short, and the few vehicles produced were out of service by the time of the Battle of France in the Second World War. Development Alarmed by the rapid build-up of the Red Army, the French Army, on 24 December 1931, conceived a preliminary plan for the mechanisation of the Cavalry. This foresaw the development of several types of ''automitrailleuses'' — the official term for cavalry tanks because ''chars'' ("tanks") were by law part of the infantry arm — among which an ''Automitrailleuse de Combat'' (AMC), a lightly armoured (weighing no more than nine tons) but swift (30 km/h cruise speed) and strongly armed (47 mm gun) combat tank, capable of fighting enemy armour. The plan was affirmed by the French Supreme Command on 23 January 1932, and approved by the ministry of defence on 9 December. Even before Plan 1931 was put on paper, Louis Renault was informed of it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hotchkiss H35
The Hotchkiss H35 or was a French Tanks in France#Inter War, cavalry tank developed prior to World War II. Despite having been designed from 1933 as a rather slow but well-armoured light infantry support tank, the type was initially rejected by the French Infantry because steering proved difficult during cross-country use, and was instead adopted in 1936 by the French Cavalry arm. From 1938 an improved version was produced with a more powerful engine, the ''Char léger modèle 1935 H modifié 39'', which from 1940 was also fitted with a longer, more powerful 37 mm gun. It was intended to make this improved variant the standard light tank, with at least four thousand produced to equip new armoured divisions of both the Cavalry and the Infantry arms, but due to the Battle of France, defeat of France in June 1940, total production of both subtypes was limited to about 1200 vehicles. For the remainder of the war Germany and its allies used captured Hotchkiss tanks in several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
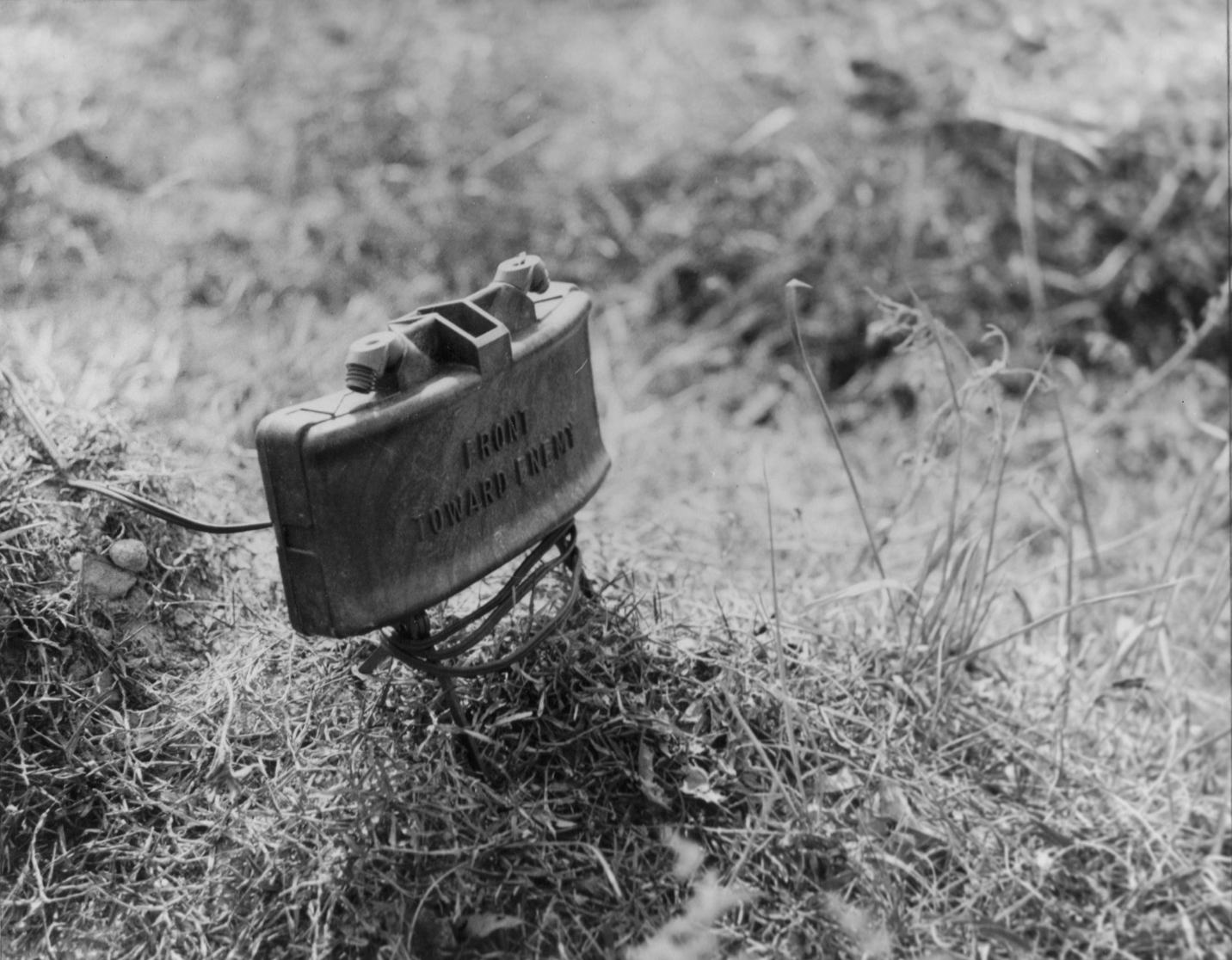
Anti-personnel
An anti-personnel weapon is a weapon primarily used to maim or kill infantry and other personnel not behind armor, as opposed to attacking structures or vehicles, or hunting game. The development of defensive fortification and combat vehicles gave rise to weapons designed specifically to attack them, and thus a need to distinguish between those systems and ones intended to attack people. For instance, an anti-personnel landmine will explode into small and sharp splinters that tear flesh but have little effect on metal surfaces, while anti-tank mines have considerably different design, using much more explosive power to effect damage to armored fighting vehicles, or use explosively formed penetrators to punch through armor plating. Many modern weapons systems can be employed in different roles. For example, a tank's main gun can fire armor-piercing ammunition in the anti-tank role, high-explosive ammunition in the anti-structure role and fragmentation shells in the anti-personn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-tank
Anti-tank warfare refers to the military strategies, tactics, and weapon systems designed to counter and destroy enemy armored vehicles, particularly tanks. It originated during World War I following the first deployment of tanks in 1916, and has since become a fundamental component of land warfare doctrine. Over time, anti-tank warfare has evolved to include a wide range of systems, from handheld infantry weapons and anti-tank guns to guided missiles and air-delivered munitions. Anti-tank warfare evolved rapidly during World War II, leading to infantry-portable weapons. Through the Cold War of 1947–1991, the United States, anti-tank weapons have also been upgraded in number and performance. Since the end of the Cold War in 1992, new threats to tanks and other armored vehicles have included remotely detonated improvised explosive devices (IEDs). During the Russian invasion of Ukraine, drones and loitering munitions have attacked and destroyed tanks. Tank threat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Char B1
The Char B1 was a French heavy tank manufactured before World War II. The Char B1 was a specialised break-through vehicle, originally conceived as a self-propelled gun with a 75 mm howitzer in the hull; later a 47 mm gun in a turret was added, to allow it to function also as a , a "battle tank" fighting enemy armour, equipping the armoured divisions of the Infantry Arm. Starting in the early twenties, its development and production were repeatedly delayed, resulting in a vehicle that was both technologically complex and expensive, and already obsolescent when real mass-production of a derived version, the Char B1 "bis", started in the late 1930s. A further up-armoured version, the Char B1 "ter", was only built in two prototypes. Among the most powerfully armed and armoured tanks of its day, the type was very effective in direct confrontations with German armour in 1940 during the Battle of France, but low speed and high fuel consumption made it ill-adapted to the war ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Char D2
The Char D2 was a French medium tank of the interwar period. In 1930, at a time the Char D1 had not even entered production, the Renault company agreed to build a better armoured version called the Char D2. By not using old-fashioned rivets, it was hoped to save weight. The tank should have the potential to serve as an alternative in the role of battle tank for the heavier Char B1, should the latter be forbidden by treaty. The failure of the armament limitation talks resulted in a severe reduction of the projected manufacture, now in the form of an interim tank. Organisational difficulties with Renault caused the actual production of a first series of fifty to be delayed to the years 1936 and 1937. A second series of fifty was ordered in 1938, despite indications that the type was mechanically unreliable, as a possible cheaper addition to the expensive Char B1. With the latter type, in case of war, only a limited number of armoured divisions for the Infantry Arm could be raised; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Char D1
The Char D1 was an Interwar period, Interwar French light tank. The French plan of 1926, calling for the creation of a Tanks in France#Inter War, Light Infantry Support Tank, led to the development of the existing Renault NC1 prototype into the Char D1. One hundred and sixty vehicles of this type were produced between 1931 and 1935. There was a pre-series of ten vehicles and later 150 standard vehicles were built. Until 1936 the vehicles were fitted with Renault FT turrets because the intended cast ST2 turrets were not yet ready. The ST2 turret was armed with a short 47mm SA34 tank gun with a coaxial 7.5mm machine gun. The hull carried a 7.5mm MG in the bow. The type did not serve as an infantry support tank as originally intended, but as France's major battle tank of the early 1930s; it was quickly phased out in 1937 because of its mechanical unreliability and relegated to colonial units in North Africa. Development After World War I, France possessed a very large fleet of Renau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FCM 36
The FCM 36 or ''Char léger Modèle 1936 FCM'', was a light infantry tank designed for the French Army prior to World War II. It had a crew of two and was equipped with a short 37mm main armament and a 7.5mm coaxial machine gun. The FCM 36 was developed from 1934 onwards as part of a programme to replace the obsolete Renault FT. As it was more expensive to produce than competing designs, only a limited production of a hundred was authorised. It featured some advanced technologies such as a diesel engine and extensive use of welded sloped armour. In 1940, the type equipped the ''503e Groupement de Bataillons de Chars'', which unsuccessfully counterattacked the decisive German breakthrough at Sedan. Development In 1933, the Hotchkiss company proposed to build a cheap mass-produced light infantry tank. In reaction to this proposal the French Army invited the whole of French industry to offer alternative designs. In the end, three of the competing prototypes would be taken into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renault R 35
The Renault R35, an abbreviation of ''Char léger Modèle 1935 R'' or R 35, was a French light infantry tank of the Second World War. Designed from 1933 onwards and produced from 1936, the type was intended as an infantry support light tank, equipping autonomous tank battalions, that would be allocated to individual infantry divisions to assist them in executing offensive operations. To this end it was relatively well-armoured but slow and lacking a good antitank capacity, fitted with a short 37 mm gun. At the outbreak of the war, the antitank role was more emphasized leading to the development and eventual production from April 1940 of a subtype with a more powerful longer gun, the Renault R40. It was planned to shift new production capacity to the manufacture of other, faster, types, but due to the defeat of France, the R35/40 remained the most numerous French tank of the war, with about 1685 vehicles having been produced by June 1940. At that moment it had also been expo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |